What size furnace do I need? This question is crucial for any homeowner considering a new furnace or evaluating an existing one. Choosing the right size furnace isn’t just about comfort; it impacts energy efficiency, cost, and the longevity of your system. This comprehensive guide will walk you through understanding your home’s needs, evaluating your options, and ultimately selecting the perfect furnace for your space and budget.
We’ll delve into factors like home size, climate, and energy efficiency, helping you make an informed decision. From comparing different furnace types to understanding the role of insulation, this guide covers everything you need to know to find the ideal furnace size for your home.
Understanding Home Size and Needs: What Size Furnace Do I Need
Choosing the right furnace size is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home. This involves understanding the relationship between your home’s size, construction, and energy needs. A properly sized furnace ensures adequate heating without unnecessary energy consumption, ultimately saving you money and reducing your environmental impact.Understanding your home’s characteristics is the first step in selecting the right furnace.
Factors like square footage, insulation, and energy-efficient features all play a role in determining the optimal furnace size. This section will delve into these aspects, providing a comprehensive overview to help you make informed decisions.
Home Size and Heating Requirements
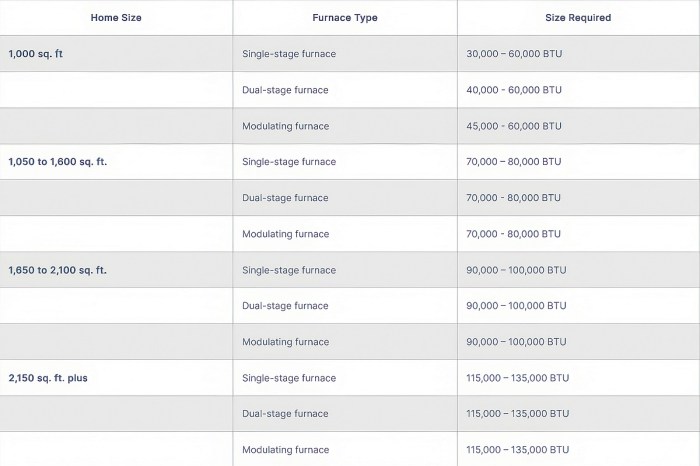
Home size directly correlates with the amount of heat required. A larger home naturally needs a more powerful furnace to effectively heat the entire space. Accurate estimations of your heating needs are essential for avoiding under- or over-sizing your furnace.
| Home Size Category | Approximate Square Footage Range |
|---|---|
| Small | 1,000-1,500 square feet |
| Medium | 1,500-2,500 square feet |
| Large | 2,500+ square feet |
Homes with intricate architectural designs, multiple stories, or significant exterior exposure will require more heating power than homes of comparable square footage with simpler layouts and better insulation. This is because these factors influence heat loss.
Energy Efficiency of Home Construction Materials
Different building materials have varying degrees of thermal resistance. This directly impacts the furnace’s required capacity.
- Insulation: Higher levels of insulation in walls, attics, and basements significantly reduce heat loss. This means a smaller furnace can adequately heat the home. Homes with poor insulation require a larger furnace to compensate for the increased heat loss.
- Windows and Doors: Energy-efficient windows and doors with good seals minimize heat transfer through these critical areas. Consider the type of glass used, the frames, and the overall tightness of the seal when assessing your home’s energy efficiency.
- Exterior Walls: The material used in the exterior walls impacts heat transfer. Homes with thicker walls or those made of materials with higher thermal mass (e.g., brick) require a different furnace sizing compared to those with thinner walls or materials with lower thermal mass (e.g., wood frame).
Homes with improved insulation and energy-efficient windows will generally require a smaller furnace to achieve the same level of comfort as a less insulated home.
Energy-Saving Features and Furnace Selection
Various features can significantly influence the required furnace capacity. These features include the quality of insulation, the efficiency of windows and doors, and the use of energy-saving appliances.
- Insulation: Properly insulated walls, attics, and basements minimize heat loss. This results in lower energy consumption for heating.
- Air Sealing: Identifying and sealing air leaks in your home significantly reduces drafts and heat loss. This is a key factor in reducing the size of furnace required for the same level of heating.
- Windows and Doors: Energy-efficient windows and doors with proper seals reduce heat transfer. These features can reduce the furnace size needed to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
A well-insulated home with energy-efficient windows and doors can often use a smaller, more energy-efficient furnace compared to a similar-sized home with inadequate insulation or older windows.
Examples of Home Styles and Furnace Size Needs
Determining the ideal furnace size depends on the specific home style. Different architectural designs influence heat loss, requiring varying furnace capacities.
| Home Style | Typical Furnace Size Needs |
|---|---|
| Ranch | 10-15 tons (depending on square footage and insulation) |
| Two-story colonial | 15-20 tons (depending on square footage and insulation) |
| Large, contemporary home with multiple stories | 20+ tons (depending on square footage, insulation, and energy efficiency features) |
These are just examples; individual needs vary. Factors like the number of occupants, climate conditions, and the specific construction materials of the home should be considered when making a final decision.
Figuring out the right furnace size can be tricky, but it’s crucial for efficiency and comfort. Think about how much heat your home needs, and consider clever ways to reuse parchment paper, like lining your oven for easier cleanup. For example, checking out clever ways to reuse parchment paper could spark some innovative ideas for your home.
Ultimately, choosing the correct furnace size depends on square footage, insulation, and local climate.
Identifying Heating Needs
Choosing the right furnace size is crucial for both energy efficiency and comfort. A furnace that’s too small will struggle to heat your home adequately, leading to discomfort and potentially higher energy bills. Conversely, an oversized unit wastes energy and can lead to uneven temperatures. Understanding the factors influencing heating needs helps ensure you select the optimal furnace for your specific home and climate.Accurately determining your home’s heating requirements necessitates careful consideration of various factors.
These include not only the size of your home but also its specific characteristics, the climate in which you live, and your personal preferences for comfort levels. This detailed analysis allows for a precise furnace sizing calculation, maximizing efficiency and minimizing energy waste.
Factors Influencing Heating Output
Several factors influence the required heating output of a furnace. Climate plays a significant role. Homes located in colder climates, or regions with frequent and severe temperature drops, require furnaces with higher output capacities to maintain comfortable temperatures throughout the year. Home orientation also impacts heating needs. A home facing north or east will experience more heat loss than a home facing south or west, thus necessitating a furnace with greater heating power.
The number of occupants in a home and their individual comfort preferences also affect the required heating output. Larger homes and those with more occupants require furnaces with higher heating capabilities.
Importance of Highest Expected Outdoor Temperatures
The highest expected outdoor temperatures in an area are critical to consider when sizing a furnace. A furnace must be capable of maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature, even during the hottest months of the year. The difference between the outdoor temperature and the desired indoor temperature dictates the furnace’s required output. This ensures the furnace can effectively handle the load and maintain a steady indoor temperature during the coldest periods.
For example, a home in a region experiencing extreme cold snaps will require a furnace with a greater heating capacity compared to a home in a region with milder winters.
Comparison of Heating Systems
Different heating systems have varying implications for furnace sizing. Forced-air systems, commonly used in homes, circulate heated air throughout the house via ducts. Radiant heating systems, on the other hand, heat surfaces directly, such as floors or walls. Radiant heat systems typically require smaller furnaces since they heat the surfaces, which in turn heat the air, minimizing heat loss to the environment.
Figuring out the right furnace size can be tricky, but it’s crucial for heating efficiency. Thinking about your kitchen’s aesthetic can also help! Modern gray and white kitchen ideas gray and white kitchen ideas often feature sleek appliances, and the right furnace size is key to keeping those stylish spaces cozy. Ultimately, the furnace size depends on the square footage of your home, and factors like insulation and windows.
The specific type of heating system used in a home will influence the necessary furnace size.
Impact of Window and Door Placement on Heat Loss
Window and door placement significantly affects heat loss. Windows and doors located on exposed sides of a home, or in areas that receive direct sunlight or drafts, will contribute to increased heat loss. The placement of windows and doors influences the amount of heat that escapes the home, thus impacting the furnace’s required heating capacity. Homes with numerous windows or large, poorly insulated doors on exterior walls require larger furnaces to maintain desired temperatures.
Energy Consumption Comparison
The energy consumption of different furnace types varies. Gas furnaces are typically more energy-efficient than electric furnaces. However, the cost of fuel and electricity can vary significantly by region and supplier, which will also affect the total energy consumption over time.
| Furnace Type | Fuel Type | Energy Consumption (estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Furnace | Natural Gas/Propane | Generally lower, depending on efficiency rating |
| Electric Furnace | Electricity | Generally higher, depending on efficiency rating |
Note: Energy consumption values are approximate and can vary based on factors such as furnace efficiency, climate, and home insulation. Energy efficiency ratings for furnaces can provide more specific information.
Evaluating Existing Systems
Knowing your current furnace’s capabilities is crucial for selecting the right replacement or optimizing its performance. A thorough assessment of the existing system helps determine if the unit is adequately sized for your home’s needs, preventing costly over- or under-sizing in a new installation. This evaluation also allows for the identification of potential maintenance issues that may impact its efficiency and longevity.
Identifying Furnace BTU Rating
The BTU (British Thermal Unit) rating is a fundamental measure of a furnace’s heating capacity. A furnace’s BTU output dictates its ability to heat your home. Higher BTU ratings correspond to greater heating power. Understanding the BTU rating is essential for comparing it to your home’s calculated heating needs. This comparison reveals whether the current furnace is appropriately sized for your specific heating demands.
A furnace that produces significantly fewer BTUs than needed will struggle to maintain a comfortable temperature, especially during extreme weather. Conversely, a furnace with a much higher BTU rating than required will operate inefficiently, wasting energy and potentially causing wear and tear on the system.
Interpreting Manufacturer Specifications
Manufacturer specifications provide critical details about the furnace’s capabilities. These specifications often include the furnace’s BTU output at different operating conditions, along with the typical operating range and efficiency ratings. Carefully reviewing these specifications helps in understanding the furnace’s performance characteristics and its suitability for your home. For example, specifications might detail the furnace’s capacity to heat a specific square footage under varying ambient temperatures.
A thorough review of these details is crucial for a precise assessment of the furnace’s heating capacity.
Figuring out the right furnace size can be tricky, but it’s crucial for efficient heating. To ensure your home stays cozy, you need to consider factors like square footage and insulation. Knowing how to whiten yellowed clothes can also be a helpful analogy; just like you need the right detergent and techniques to brighten your whites, you need the correct furnace size to heat your home properly.
So, remember to consider these factors when determining what size furnace you need for your home. how to whiten yellowed clothes Choosing the correct furnace size will save you money on energy bills and keep your home comfortable year-round.
Calculating Heating Load
Determining the heating load of your home is essential for assessing the furnace’s adequacy. This calculation considers several factors, including the home’s square footage, insulation quality, the climate’s typical temperature fluctuations, and the presence of windows and doors. A well-insulated home, for instance, requires less heating than a poorly insulated one, affecting the heating load calculation. Accurately estimating the heating load is crucial for selecting the correct size furnace and ensuring efficient heating.
This process ensures that the furnace effectively meets the home’s heating needs without unnecessary energy consumption.
Calculating BTU Output
Accurately determining the furnace’s BTU output is crucial for comparison with the calculated heating load. To determine the BTU output, gather the following information:
- Furnace model number:
- Manufacturer’s specifications (including BTU rating at various operating conditions):
- Furnace’s age and condition:
These details allow for a thorough evaluation of the furnace’s heating capabilities. By combining this information with other data, a more precise assessment can be performed.
Heating Load Calculation Table
The table below demonstrates a simplified method for estimating the heating load based on square footage, climate zone, and insulation type. The values are approximate and should be adjusted based on specific home characteristics. Adjustments based on specific conditions like window placement and insulation thickness should be considered.
| Home Size (sq ft) | Climate Zone | Insulation Level | Estimated Heating Load (BTU) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1500 | Cold (Zone 1-3) | Average | 45,000-60,000 |
| 1500 | Moderate (Zone 4-6) | Average | 35,000-50,000 |
| 1500 | Mild (Zone 7-9) | Average | 25,000-40,000 |
| 2000 | Cold (Zone 1-3) | Average | 60,000-80,000 |
Note: Consult with a qualified HVAC technician for a more precise assessment. This table is a general guide only.
Exploring Furnace Sizing Options
Choosing the right furnace size is crucial for optimal heating performance and energy efficiency in your home. A poorly sized furnace can lead to discomfort, higher energy bills, and potential damage to the system over time. Understanding the different sizing options available is key to making an informed decision.Proper furnace sizing ensures the system can adequately heat your home without overworking or underworking.
This directly impacts both comfort and energy costs. Factors such as the size and insulation of your home, the climate you live in, and the specific needs of your family all influence the appropriate furnace size.
Furnace Sizing Options
Different furnace sizes cater to varying home needs. Standard furnaces are commonly sized for average-sized homes, while oversized and undersized furnaces are designed for specific circumstances.
Standard Furnace Sizing
Standard furnace sizing is a common approach, providing a balance between efficiency and cost. These furnaces are generally suitable for homes within the average size and insulation ranges. The BTU rating for a standard furnace aligns with the typical heating demands of the home. This size ensures adequate heating without undue strain on the system.
Oversized Furnace Sizing
Oversized furnaces have higher BTU ratings than necessary for the home’s heating needs. While they can provide quick heating, they are often less energy-efficient than standard or appropriately sized furnaces.
Oversized furnaces may use more energy than necessary, increasing utility costs, and potentially reducing lifespan.
The added cost of the oversized unit may not be justified by the slight, if any, added convenience.
Undersized Furnace Sizing
Undersized furnaces have lower BTU ratings than required for the home’s heating needs. They often struggle to maintain adequate temperatures, especially during extreme weather conditions. This can lead to discomfort, uneven heating, and potential damage to the system.
Undersized furnaces may cycle on and off frequently, increasing wear and tear and reducing overall efficiency.
The constant cycling can also lead to increased energy consumption.
Examples of Furnace Models and Home Sizes
To illustrate the relationship between furnace size and home characteristics, consider the following examples:
- A 2,000 square foot home with average insulation might require a 60,000 BTU furnace.
- A 3,000 square foot home in a colder climate with excellent insulation might require a 90,000 BTU furnace.
These are just examples; precise sizing depends on factors like insulation, location, and specific heating needs.
Energy Savings and Cost Implications
The table below highlights potential energy savings and cost implications for different furnace sizes. It illustrates how a properly sized furnace can contribute to lower utility costs over time.
| Furnace Size | BTU Rating | Estimated Energy Savings (per year) | Estimated Cost Implications (initial cost) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | 60,000 BTU | $100-$200 | $3,000-$4,000 |
| Oversized (80,000 BTU) | 80,000 BTU | $50-$100 | $3,500-$5,000 |
| Undersized (40,000 BTU) | 40,000 BTU | $200-$300 | $2,500-$3,500 |
Note: These figures are estimates and may vary based on individual circumstances.
Professional Consultation
Choosing the right furnace size is crucial for efficient heating and long-term cost savings. A professional consultation with a qualified HVAC technician provides invaluable insights beyond basic calculations. Their expertise ensures accurate sizing, optimal performance, and reduced energy consumption.A qualified HVAC technician possesses in-depth knowledge of furnace types, heating loads, and local climate conditions. This knowledge is essential for accurately determining the optimal furnace size for a specific home.
Furthermore, their experience with various systems and troubleshooting ensures a smooth installation and efficient operation.
Benefits of Professional Consultation
A professional consultation offers numerous advantages. A qualified technician can accurately assess the specific heating needs of your home, considering factors like insulation, window efficiency, and the number of occupants. This ensures a more precise furnace sizing, preventing under- or oversized units. An oversized furnace may result in unnecessary energy costs, while an undersized one may struggle to maintain a comfortable temperature, leading to potential discomfort and increased utility bills.
Qualifications and Experience Levels of HVAC Technicians
HVAC technicians should hold relevant certifications and licenses. These credentials demonstrate a baseline of knowledge and competence in heating and cooling systems. A technician’s experience level also matters, as extensive experience translates to a deeper understanding of various system types, installation techniques, and troubleshooting procedures. They can handle more complex installations and diagnose potential issues with greater accuracy.
Scheduling a Consultation with a Heating and Cooling Expert
Scheduling a consultation with a heating and cooling expert is straightforward. Contact local HVAC companies or technicians directly. Provide them with details about your home, such as the square footage, the type of insulation, and any known heating issues. Most reputable companies will offer a free consultation or an estimate based on the provided information. A convenient appointment time can be arranged.
Information to Provide to a Technician During a Consultation
Providing accurate and comprehensive information is crucial for a productive consultation. Homeowners should share details about their home’s square footage, insulation type and R-value, window efficiency, the number of occupants, and any existing heating problems. Providing previous utility bills can help in assessing energy consumption patterns and identifying potential areas for improvement. Specific details about the home’s construction, like the presence of exterior walls or attics, can also assist the technician in making informed decisions.
Essential Questions to Ask an HVAC Professional About Furnace Sizing
| Question | Explanation |
|---|---|
| What factors influence furnace sizing for my home? | Understanding the variables, such as square footage, insulation, and climate, helps assess the necessary heating capacity. |
| What is the recommended furnace size for my home? | The technician provides a specific recommendation based on their assessment. |
| What are the potential issues with an undersized or oversized furnace? | Knowing the drawbacks helps in making an informed decision and avoiding problems. |
| What are the estimated operating costs of different furnace sizes? | Comparing the costs provides insight into long-term financial implications. |
| What warranties and maintenance plans are available? | Understanding the warranty and maintenance procedures is essential for future care and cost management. |
| How does the chosen furnace size compare with industry standards and best practices? | Understanding the benchmarks provides confidence in the selection process. |
| What are the expected energy efficiency ratings of the recommended furnace? | Understanding the energy efficiency helps in making an environmentally conscious decision. |
| What are the different furnace types and which is suitable for my needs? | Understanding the options allows for the selection of a suitable furnace type. |
Furnace Selection Considerations

Choosing the right furnace is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home. This involves careful consideration of various factors beyond just size, including the specific technology and fuel source. Understanding these aspects ensures you make an informed decision that aligns with your budget, energy needs, and environmental concerns.Selecting a furnace is a multifaceted process. Factors like efficiency ratings, fuel type, warranty terms, and maintenance requirements all play a significant role in long-term cost and performance.
A well-considered selection will contribute to energy savings, minimize environmental impact, and ensure the furnace serves your heating needs reliably for years to come.
Efficiency Ratings
Furnace efficiency is a key determinant of operating costs. Higher efficiency ratings translate to lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills. Manufacturers typically rate furnaces based on their Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) percentage. A higher AFUE signifies a more efficient furnace. For instance, a furnace with an AFUE of 95% will use 5% less fuel than one with an AFUE of 80% to achieve the same heating output.
This difference can amount to substantial savings over the furnace’s lifespan.
Fuel Type Considerations
Different fuel types for furnaces offer varying advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these distinctions is essential to making an informed choice.
- Gas Furnaces: Gas furnaces are a popular choice due to their affordability and readily available fuel supply. They typically offer good efficiency, especially those with newer technologies. However, fluctuations in gas prices can impact operating costs. Installation and maintenance requirements should also be considered.
- Electric Furnaces: Electric furnaces are generally quieter and simpler to install than gas furnaces. They are often a good option for areas with reliable and affordable electricity. However, electricity costs can be higher than gas in some regions, affecting long-term operating expenses. Their efficiency is also dependent on the specific technology used. Some electric models offer high efficiency levels, while others may not be as economical.
- Oil Furnaces: Oil furnaces are often chosen for their lower upfront cost compared to gas furnaces in some areas. However, oil prices can be volatile, and their efficiency may be lower than modern gas or electric models. They also require oil storage and handling, which might present safety concerns.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of different fuel types varies significantly. Gas furnaces generally produce fewer emissions compared to oil furnaces. Electric furnaces have the lowest emissions, particularly if the electricity is generated from renewable sources. Understanding these distinctions can guide you towards a more environmentally responsible choice.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison Table
| Fuel Type | Typical AFUE Range (%) | Environmental Impact | Operating Cost Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas | 90-98 | Lower emissions than oil | Dependent on gas prices |
| Electric | 95-98 | Lowest emissions if using renewable energy | Dependent on electricity prices |
| Oil | 78-88 | Higher emissions than gas | Dependent on oil prices |
Warranty and Maintenance, What size furnace do i need
A comprehensive warranty provides peace of mind and protects your investment. A longer warranty period often signifies greater manufacturer confidence in the product’s quality and durability. Regular maintenance is vital for ensuring the furnace operates efficiently and reliably. Routine maintenance schedules should be followed to prevent potential breakdowns and maintain optimal performance. A well-maintained furnace will often operate with higher efficiency and lower energy costs.
Visual Aids and Examples
Choosing the right furnace size is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home. Visual aids and examples can significantly aid in understanding the complexities of this process. These tools provide a clear picture of the system’s layout, calculation methods, and the various types of furnaces available, enabling homeowners to make informed decisions.Visual representations simplify the often-technical aspects of furnace sizing, making the process more accessible and understandable.
This section offers practical examples to clarify the procedures involved, from system layouts to BTU calculations.
Typical Home Heating System Layout
A visual representation of a typical home’s heating system layout clarifies the components and the furnace’s role within the system. The diagram would illustrate the furnace’s position in relation to the ductwork, showing how air is circulated throughout the house. Key components like the blower, air filter, and heat exchanger should be clearly labeled, allowing the homeowner to visualize the flow of air and heat.
Heating Load Calculation Diagram
A detailed diagram illustrating the process of calculating heating load for a specific home will be a valuable tool. The diagram should depict the steps involved in determining the required BTU output. It will likely include elements like: measuring the home’s square footage, considering the insulation level, identifying the climate zone, and accounting for window and door areas.
This visual representation will break down the calculation process, making it more manageable and understandable.
Flowchart for Determining Furnace Size
A flowchart outlining the steps to determine the appropriate furnace size will visually guide homeowners through the process. The flowchart would begin with an assessment of the home’s size and insulation. It would then branch out to consider factors like climate zone, window/door placement, and the existing heating system. Each step should be clearly labeled, leading the homeowner through the decision-making process.
This visual guide will ensure a systematic approach to furnace selection.
Types of Furnaces and Components
A detailed image illustrating the different types of furnaces and their components would compare different models and technologies. This visual representation will include diagrams of various furnace types (e.g., gas furnaces, electric furnaces, heat pumps), highlighting their respective components, such as the heat exchanger, blower motor, and controls. The image will help homeowners understand the differences between various furnace types, considering efficiency and cost.
Homeowner’s Home Layout with BTU Calculation Example
Imagine a homeowner’s home with a layout diagram including measurements. The diagram would represent the home’s floor plan, clearly indicating the dimensions of each room. Measurements of windows and doors, as well as the home’s insulation level, should be noted. The calculated heating load, based on these factors, would be illustrated alongside the furnace size recommendation, using a recognized BTU calculation formula.
This visual example would be an invaluable aid in applying the calculation method to a real-world scenario.
Summary
In conclusion, determining the right furnace size is a multifaceted process. By considering your home’s unique characteristics, evaluating your heating needs, and consulting with a qualified professional, you can ensure a comfortable, energy-efficient, and cost-effective heating solution. This guide provides a strong foundation for making an informed decision, but remember, professional advice is invaluable. Happy heating!