Water shut off valve types are crucial for plumbing systems, ensuring safe and efficient water flow. Understanding the various types, their applications, and proper installation is key to preventing costly repairs and maintaining a healthy home. This guide dives deep into the different types of water shut-off valves, covering everything from ball valves to check valves. We’ll also explore their construction, sizing, installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting, empowering you with the knowledge to confidently handle your water system.
From simple residential installations to complex industrial applications, the right water shut-off valve is essential. Choosing the correct valve ensures optimal performance, longevity, and safety. This comprehensive guide breaks down the essential aspects of water shut-off valve selection, providing clear and concise information to help you make informed decisions.
Introduction to Water Shut-off Valves
Water shut-off valves are crucial components in plumbing systems, ensuring the safety and efficiency of water distribution. They are designed to control the flow of water in pipes, enabling maintenance, repairs, and emergency shutdowns. Understanding the various types and their applications is essential for proper plumbing design and operation.Water shut-off valves are indispensable in a variety of water-dependent systems.
Their primary function is to isolate sections of piping, enabling plumbers to work on specific areas without disrupting the entire system. This localized control is critical for maintenance tasks, repair work, and emergency water shutoffs. The proper selection of valves is paramount, as the wrong choice can lead to leaks, inefficient use of water, or even damage to the system.
Choosing the right water shut-off valve type depends on your plumbing setup, but a key consideration is its accessibility. For example, if you’re looking for a convenient way to manage kitchen scraps, checking out the best countertop compost bins could lead to a surprisingly neat solution. Ultimately, the best water shut-off valve will depend on the specific needs of your plumbing system.
Types of Water Shut-off Valves
A variety of water shut-off valves are available, each designed for specific applications. Understanding the key features and limitations of each type is crucial for selecting the appropriate valve for a given situation. Factors such as the pressure rating, flow rate, and size of the pipe must be considered to ensure proper function.
| Valve Type | Application | Key Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Valve | General plumbing applications, especially for water supply lines | Simple design, quick opening and closing, good flow characteristics. | Relatively inexpensive, easy to operate, good flow rate. | Can be prone to leakage if not properly maintained, not ideal for high-pressure applications. |
| Gate Valve | Water main lines, large pipelines, and high-pressure applications. | Precise flow control, large flow capacity, and durable design. | High flow rate, suitable for high-pressure environments, reliable and long-lasting. | Difficult to operate at very low flow rates, and slower to open/close compared to ball valves. |
| Globe Valve | Applications requiring precise flow control, such as in chemical plants and industrial settings. | Offers excellent control over flow rate, and high pressure resistance. | Precise control, ideal for throttling applications, reliable in high-pressure systems. | Higher cost than ball or gate valves, lower flow rate than gate valves. |
| Check Valve | Preventing backflow in systems, such as in water heaters and pumps. | Allows flow in one direction only, preventing reverse flow. | Reliable in preventing backflow, simple design. | Lower flow capacity than other valves, may not be ideal for high-flow situations. |
Types of Water Shut-off Valves: Water Shut Off Valve Types

Understanding the different types of water shut-off valves is crucial for selecting the right valve for a specific application. Proper valve selection ensures efficient water control, minimizes potential damage, and maximizes the lifespan of the plumbing system. This section delves into the characteristics, working mechanisms, and applications of various valve types.
Ball Valves
Ball valves are widely used for on/off control of water flow. Their simple design makes them cost-effective and easy to operate. The valve’s round body features a hollow ball with a hole that allows water to pass through when the ball is correctly positioned. Rotating the ball either blocks or opens the water flow path.
Gate Valves
Gate valves are characterized by a gate-like mechanism that opens and closes the water flow passage. When fully open, the gate allows water to flow unimpeded. When closed, the gate completely blocks the flow. They are known for their high flow capacity when fully open and are often used in large-scale water systems.
Globe Valves
Globe valves are designed for precise control of water flow. The valve’s body features a globe-shaped design with a plug or disc that regulates the flow. Their construction enables a gradual and controlled opening and closing, facilitating precise adjustments to water flow rates. Globe valves are excellent for applications requiring fine flow control, such as in industrial processes.
Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves use a circular disc that rotates to open or close the water flow. Their compact design and low cost make them popular choices for various applications. They are typically suitable for applications with moderate flow rates and less stringent control requirements. Their simple design and fast operation make them ideal for applications where frequent on/off operation is needed.
Check Valves
Check valves are designed to allow water flow in only one direction. They prevent backflow of water, safeguarding systems from unwanted water return. Their unidirectional design ensures water flows in the desired path, protecting downstream components from damage. Commonly used in water distribution systems and pumps to prevent water from flowing back into the source.
Comparison of Water Shut-off Valves
| Valve Type | Construction | Operation | Application | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Valve | Simple, round body with a hollow ball | Rotating the ball opens or closes the flow path | On/off control, general water applications | Cost-effective, easy operation, quick response | Limited flow control, less precise control |
| Gate Valve | Gate-like mechanism that slides | Sliding the gate opens or closes the flow path | Large flow applications, pipelines | High flow capacity, long service life | Difficult to adjust flow precisely, less efficient for low flow |
| Globe Valve | Globe-shaped body with a plug | Rotating the plug controls flow rate | Precise flow control, industrial processes | Precise flow regulation, gradual control | Lower flow capacity, more complex design |
| Butterfly Valve | Circular disc that rotates | Rotating the disc opens or closes the flow path | Moderate flow applications, pipelines | Compact design, cost-effective | Less precise control, potentially lower durability |
| Check Valve | One-way flow design with a hinged or spring-loaded component | Allows flow in one direction, prevents backflow | Preventing backflow, water pumps | Simple design, prevents backflow | Limited flow control, not suitable for regulating flow |
Materials and Construction
The construction of water shut-off valves is a critical aspect, directly impacting their performance, durability, and overall lifespan. Choosing the right materials and employing appropriate manufacturing techniques are essential for ensuring reliable operation and longevity, especially in harsh environments. The selection process considers not only the inherent properties of the materials but also their resistance to corrosion and potential interactions with the water supply.Selecting the appropriate material is crucial for the long-term reliability and functionality of a water shut-off valve.
Factors such as pressure resistance, temperature tolerance, and corrosion resistance play a vital role in determining the valve’s lifespan and safety. Different materials offer varying levels of these properties, and the selection must be made with careful consideration of the specific application.
Choosing the right water shut-off valve types depends on your needs, but consider the various types available. Knowing the proper size insulation for your 2×4 and 2×6 walls is equally important for preventing costly issues. This guide will help you determine the ideal insulation thickness. Ultimately, selecting the correct water shut-off valve is crucial for plumbing maintenance and safety.
Common Materials Used
Various materials are used in the construction of water shut-off valves, each with its own set of characteristics. Cast iron, brass, bronze, and various types of steel are frequently employed, each offering unique advantages. The choice of material often depends on factors like the intended use, pressure requirements, and the anticipated lifespan of the valve.
Material Selection and Performance
The selection of materials directly impacts the valve’s performance and durability. For instance, cast iron valves are often chosen for their robustness and ability to withstand high pressures, but they may be more susceptible to corrosion than brass or bronze. Conversely, brass and bronze valves are often preferred for their corrosion resistance, but they might have lower pressure ratings compared to cast iron.
The selection process necessitates a careful evaluation of the application’s specific needs.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is paramount for water shut-off valves. Water, especially if it contains impurities, can lead to corrosion of the valve components, potentially compromising the valve’s functionality and safety. Different materials exhibit varying degrees of resistance to corrosion, necessitating a strategic choice depending on the water quality in the specific application. For instance, valves used in coastal areas or areas with high mineral content in the water supply might require materials with superior corrosion resistance.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing processes used in creating water shut-off valves influence the valve’s quality and performance. Different manufacturing techniques, such as casting, machining, and forging, result in valves with varying properties. The precision and quality control during these processes directly affect the valve’s ability to withstand pressure and its overall lifespan. The chosen manufacturing method must be compatible with the material selected and the intended application.
Material Properties Table
| Material | Properties | Application | Cost | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Strong, durable, resistant to high pressure | Water mains, large-diameter piping systems | Medium | High |
| Brass | Corrosion resistant, good for potable water systems | Residential plumbing, smaller piping systems | High | Medium-high |
| Bronze | Excellent corrosion resistance, high strength | Marine applications, high-pressure systems | High | High |
| Stainless Steel | Exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength | High-pressure applications, corrosive environments | High | Very High |
Valve Sizing and Selection
Choosing the right water shut-off valve is crucial for maintaining water pressure, preventing leaks, and ensuring efficient water usage. Proper sizing and selection depend on several factors, including the anticipated flow rate, pressure, and temperature of the water system. Incorrect sizing can lead to inadequate performance, premature valve failure, and even safety hazards. Understanding these factors and their interplay is key to making informed decisions.Selecting the appropriate valve size and type involves a careful evaluation of the specific application’s requirements.
The valve’s ability to handle the expected flow rate, pressure, and temperature range directly impacts its longevity and effectiveness. This section will delve into these considerations, providing guidelines for selecting valves based on various parameters.
Factors Affecting Valve Selection
Understanding the system’s operating conditions is paramount for selecting the correct valve. Factors such as flow rate, pressure, and temperature significantly influence valve performance and lifespan.
Flow Rate Considerations
The flow rate, measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM), dictates the valve’s capacity to handle the water volume. Higher flow rates require larger valve openings to prevent pressure drops and maintain efficient water delivery. A valve undersized for the flow rate can lead to reduced pressure and potential leaks.
Pressure Considerations
Pressure, measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) or kilopascals (kPa), is another critical factor. Valves are rated for specific pressure ranges. Exceeding this rating can damage the valve components and compromise safety. The pressure rating must exceed the maximum expected pressure in the system.
Temperature Considerations
Temperature also plays a significant role. Different materials are suitable for different temperature ranges. Selecting a valve made of a material that can withstand the expected temperature range is crucial to prevent degradation and leakage. High temperatures can accelerate material deterioration, potentially shortening the valve’s lifespan.
Valve Sizing Calculation
Determining the appropriate valve size involves considering the specific application’s flow rate, pressure, and temperature. The required valve size is often determined through engineering calculations, considering factors like pipe diameter and system characteristics. No single formula covers all cases; however, general guidelines are available.
A thorough understanding of the system’s design and hydraulic characteristics is essential for precise valve sizing.
Guidelines for Selecting Valve Sizes, Water shut off valve types
| Flow Rate (GPM) | Pressure (PSI) | Temperature (°C) | Valve Size (inches) | Recommended Valve Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 80 | 40 | 1 | Ball Valve |
| 25 | 100 | 60 | 1.5 | Gate Valve |
| 50 | 120 | 80 | 2 | Globe Valve |
| 75 | 150 | 100 | 2.5 | Gate Valve |
Examples of Different Valve Requirements
Different applications require different valve types and sizes. For example, a residential water supply might use a smaller ball valve, while a large industrial facility might need a larger gate valve. The precise selection depends on the specific demands of the system. Irrigation systems will need a larger valve with higher flow rate capabilities. A boiler system may need a specialized valve that can withstand higher temperatures and pressures.
Choosing the right water shut-off valve is crucial for any DIY project, especially when you’re dealing with plumbing. Different types are designed for various needs, from simple drip-stop valves to more complex ball valves. For example, if you’re planning a beautiful lavender garden, you’ll need to consider watering needs, and understanding different water shut-off valve types will be vital.
Fortunately, a great resource for learning about growing French lavender is available in this french lavender growing guide , which offers detailed advice on how to ensure your lavender thrives. Ultimately, selecting the correct valve for your specific project will save you time, money, and potential headaches down the road.
Installation and Maintenance
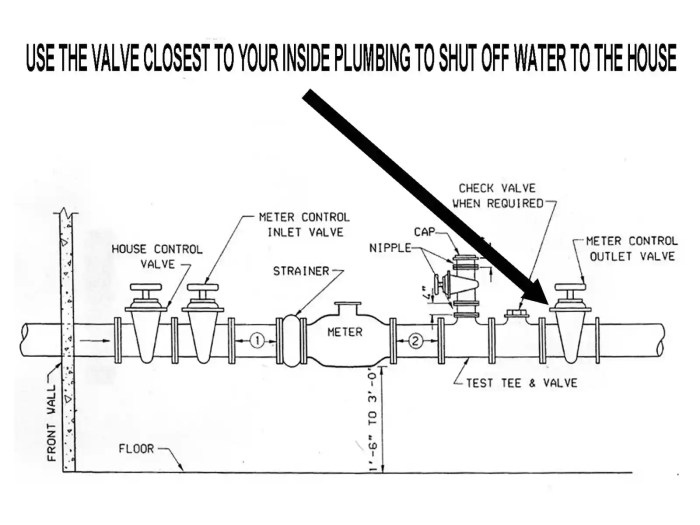
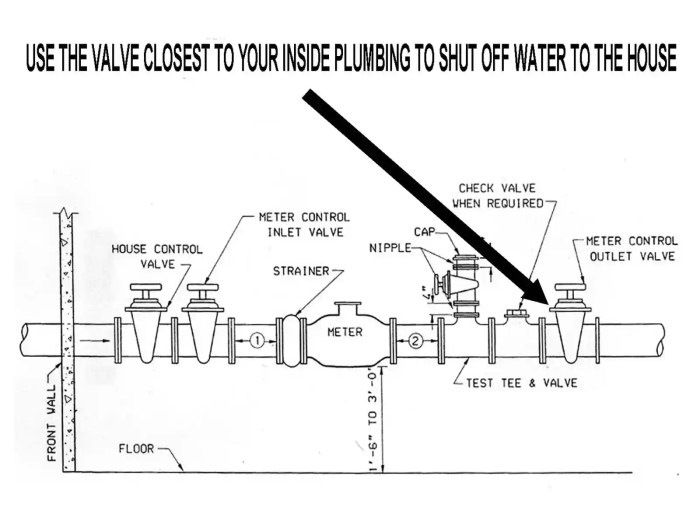
Proper installation and maintenance of water shut-off valves are crucial for ensuring safe and efficient water service. Neglecting these aspects can lead to costly repairs, water damage, and even safety hazards. This section delves into the detailed steps involved in installing various valve types, highlighting the importance of correct installation, and outlining best practices for maintaining these critical components.
Installation Procedures
Correct installation of water shut-off valves is paramount for optimal performance and safety. Improper installation can lead to leaks, reduced lifespan, and potential water damage. The specific installation steps vary based on the valve type and location, but general principles remain consistent.
| Step | Procedure | Tools | Safety Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Ensure the area is clear and accessible. Verify the water supply is turned off at the main shut-off valve. Gather necessary tools and materials. | Adjustable wrench, pipe wrench, pipe cutters, Teflon tape, gloves | Turn off the main water supply before starting any installation. Wear appropriate safety gear. |
| 2. Valve Placement | Position the valve in the designated location, ensuring proper alignment and support. | Level, measuring tape, plumbing clamps | Check the valve’s alignment to avoid strain on the pipes. |
| 3. Pipe Connection | Connect the valve to the water supply pipes using appropriate fittings and connections. Use Teflon tape for leak prevention. | Pipe fittings, Teflon tape, pliers | Ensure all connections are secure and properly sealed to prevent leaks. |
| 4. Testing | Slowly open the valve and check for leaks. Check for proper water flow. | Water pressure gauge | Never work on a system under pressure unless you have taken the necessary safety measures. |
| 5. Final Adjustments | Tighten all connections and ensure the valve functions smoothly. | Adjustable wrench, pipe wrench | Ensure the valve operates freely and without binding. |
Common Installation Errors and Consequences
Several common installation errors can compromise the effectiveness and safety of water shut-off valves. For instance, using incorrect pipe fittings can result in leaks. Using insufficient Teflon tape can lead to leaks as well. Incorrect valve alignment can stress the pipes and reduce the valve’s lifespan.
- Using the wrong size pipe fittings leads to improper connection and leaks.
- Insufficient Teflon tape application results in leaks and potential corrosion.
- Failure to properly align the valve can cause stress on the pipes and premature failure.
- Insufficient tightening of connections leads to leaks, allowing water to flow out of the system.
Maintenance Best Practices
Regular maintenance of water shut-off valves is vital for preventing failures and ensuring their longevity. Routine inspections can detect potential problems before they escalate into major issues. Periodically checking for leaks, ensuring the valve operates smoothly, and lubricating moving parts are essential steps.
- Regular visual inspections should be conducted to detect leaks or damage.
- Operate the valve regularly to ensure smooth operation and identify any binding or unusual sounds.
- Lubricate moving parts as needed to maintain smooth operation and prevent wear.
- Maintain a log of maintenance activities to track the history of the valve.
Troubleshooting and Repair
Water shut-off valves, crucial for controlling water flow, can sometimes malfunction. Understanding common problems, their causes, and effective troubleshooting methods is vital for preventing water damage and ensuring efficient repairs. This section details how to identify and resolve issues with water shut-off valves, emphasizing safe procedures during repairs.
Common Water Shut-off Valve Problems
Knowing the potential issues that can arise with water shut-off valves empowers you to address problems proactively. This understanding allows for quick and effective repairs, preventing costly water damage. A proactive approach minimizes disruptions and ensures efficient water service.
| Problem | Symptoms | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valve Won’t Turn | The valve handle doesn’t turn or feels stiff, or it turns but doesn’t shut off the water. | Frozen pipes, mineral deposits, damaged internal components, or corroded parts. | First, check for frozen pipes. If frozen, use a hair dryer on low heat to thaw the pipe slowly. If mineral deposits are suspected, try using a specialized plumbing cleaner. If the problem persists, consult a qualified plumber for internal component inspection and repair. |
| Water Leaks Around the Valve | Water drips or streams from the valve’s connections or base. | Loose connections, worn-out seals, or a damaged valve body. | Tighten all connections. If leaks persist, replace the seals or the entire valve if necessary. |
| Valve Leaks Internally | Water continues to flow even when the valve handle is fully turned off. | Damaged or worn-out internal valve components, such as the valve stem or packing. | The most effective solution is to replace the valve. If the leak is minimal, a qualified plumber can sometimes repair the internal components, but replacement often proves more efficient and reliable in the long run. |
| Valve Handle is Loose or Broken | The valve handle is loose, wobbly, or broken, making it difficult or impossible to turn. | Loose connections or a damaged handle. | Tighten the handle connections if possible. If the handle is broken, replace it with a new one. |
Safe Water Shutoff Procedures
Prioritizing safety during water shut-off procedures is paramount to preventing accidents. Following these steps minimizes risks and ensures a smooth repair process.
- Locate the main water shut-off valve for your home or building. Knowing the location is essential in an emergency and when conducting repairs.
- Turn the valve clockwise to shut off the water supply. This action isolates the affected area, minimizing water flow.
- Turn off the water supply to the specific fixture or appliance. If the shut-off valve is near the fixture, turn it clockwise to stop water flow.
- Check for leaks or drips after shutting off the water supply. A thorough inspection ensures no water continues to flow from unintended sources.
Repairing or Replacing a Faulty Valve
Addressing a faulty water shut-off valve requires careful consideration and the right approach. Proper handling and procedures minimize potential hazards and ensure successful repair or replacement.
- Gather necessary tools and materials, including new parts if a replacement is required. Preparation and having the right tools ensures efficiency.
- Turn off the water supply at the main shut-off valve and the specific valve to be worked on. This prevents water damage and ensures a safe working environment.
- Disconnect any connections to the valve and carefully remove the faulty valve. Thorough disconnection avoids potential water damage.
- Install the new valve according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Proper installation ensures a leak-free connection.
- Turn the water supply back on slowly to check for leaks. Careful monitoring prevents water damage.
Safety Considerations
Working with water shut-off valves requires meticulous attention to safety protocols. Improper handling or maintenance can lead to serious injuries and property damage. Understanding potential hazards and adhering to safety procedures is crucial for both personal well-being and preventing costly accidents.Proper safety precautions are paramount when working with water shut-off valves. Neglecting these precautions can result in severe consequences, including water damage, electric shock, and physical injuries.
A comprehensive understanding of potential hazards, coupled with the use of appropriate safety equipment, is essential for safe and efficient valve operations.
Safety Precautions When Working with Valves
Safe valve handling begins with recognizing potential hazards. These hazards include the risk of slips, trips, and falls due to wet floors, potential electric shock from faulty wiring, and the inherent danger of high-pressure water jets. Ensuring a safe working environment is paramount.
- Always shut off the water supply completely before working on any valve.
- Inspect the valve for any signs of damage or leakage before attempting any maintenance.
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, safety glasses, and sturdy footwear.
- Work in well-lit areas to minimize the risk of accidents.
- Never work alone when performing complex maintenance tasks.
Potential Hazards Associated with Water Shut-off Valves
Water shut-off valves, if not handled correctly, can present various hazards. These hazards often stem from improper installation, lack of maintenance, or failure to follow safety procedures.
- Water Leaks: A common hazard is water leakage. This can lead to significant property damage, mold growth, and even electrical hazards.
- High-Pressure Water Jets: Unexpectedly releasing high-pressure water from a faulty valve can cause serious injuries.
- Electrical Hazards: Valves often have electrical components. Faulty wiring or exposed wires can result in electrical shock.
- Physical Injuries: Improper lifting or handling of valves can lead to strains, sprains, and other physical injuries.
Importance of Proper Safety Equipment
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is critical for preventing injuries during valve installation and maintenance. The right equipment can significantly reduce the risk of accidents.
- Gloves: Protect hands from cuts, abrasions, and potential exposure to chemicals.
- Safety Glasses/Goggles: Protect eyes from flying debris or water spray.
- Sturdy Footwear: Provide protection against slips, trips, and falls.
- Harness and Fall Protection Equipment: Necessary when working at heights.
Steps to Take in Case of a Water Leak or Valve Malfunction
A water leak or valve malfunction can have serious consequences. Understanding the steps to take in these situations is critical for minimizing damage and ensuring safety.
- Shut Off the Water Supply: Immediately isolate the affected valve or the main water supply.
- Assess the Situation: Determine the extent of the leak or malfunction and the potential risks involved.
- Contact a Qualified Professional: If the problem is beyond your capabilities, call a licensed plumber or water service technician.
- Document the Incident: Record the details of the incident, including the date, time, and nature of the problem, for future reference.
Examples of Accidents Related to Improper Valve Handling and Installation
Accidents related to improper valve handling and installation can have severe consequences. These accidents frequently stem from a lack of adherence to safety protocols.
- Valve Explosion: Improper maintenance or faulty valves can lead to explosions, causing significant property damage and potential injuries.
- Water Damage: Improper installation or failure to shut off the water supply can result in extensive water damage, affecting both homes and businesses.
- Electrical Shock: Working with valves that have electrical components without proper safety precautions can result in electrical shock.
Summary
In conclusion, selecting the right water shut-off valve is critical for a safe and functional plumbing system. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of various valve types, materials, sizing, installation, and maintenance. By understanding the intricacies of each component, you can ensure your water system operates smoothly and efficiently for years to come. Remember, safety should always be your top priority when working with water shut-off valves.