Pawpaw plant growing guide: Unlocking the secrets to cultivating these delicious and unique fruit trees is easier than you think. This comprehensive guide delves into everything from choosing the right variety to harvesting your bounty. Discover the fascinating world of pawpaws, their unique characteristics, and the optimal growing conditions they need to thrive. We’ll explore their history, types, and the essential steps for a successful harvest.
This guide will cover everything from initial planting and propagation to ongoing care, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Learn how to identify ideal growing conditions, manage pests and diseases, and maximize your pawpaw plant’s productivity.
Introduction to Pawpaw Plants
The pawpaw, a fascinating fruit tree, holds a unique place in the botanical world. Its exotic flavor and intriguing history make it a worthwhile subject of study for any aspiring gardener or nature enthusiast. Originating in the forests of North America, this unique fruit tree offers a captivating blend of aesthetic appeal and delicious produce.The pawpaw plant, scientifically classified asAsimina triloba*, is a member of the custard apple family, Annonaceae.
This characteristic ties it to a wider group of tropical and subtropical plants, though its native habitat is uniquely temperate. This connection to tropical relatives hints at its surprising tolerance to a range of climates.
Botanical Classification and Origin
The pawpaw, scientifically classified asAsimina triloba*, belongs to the Annonaceae family. This classification places it alongside other plants known for their unique characteristics and often exotic fruits. Its origin lies within the forests of eastern North America, a testament to its adaptability to a variety of temperate conditions.
Characteristics of Pawpaw Plants
Pawpaw trees are generally medium-sized, typically reaching heights of 10 to 20 feet. Their broad, oval-shaped leaves, often a deep green, create a lush canopy. The tree’s overall structure is quite distinctive, with a rounded crown and a relatively straight trunk. Its growth pattern is fairly slow compared to other fruit trees, but its unique beauty makes it a rewarding plant to cultivate.
Types of Pawpaw Plants
WhileAsimina triloba* is the most common species, there are several cultivars and varieties. These variations might showcase subtle differences in fruit size, shape, or flavor. However, the core characteristics remain consistent across these various forms, making them all attractive additions to a home garden.
Uses and Cultural Significance
Pawpaws are primarily valued for their edible fruit. The fruit, a unique blend of custard-like texture and subtle sweetness, is a delicacy in some regions. In addition to consumption, the wood of the pawpaw tree is often used for carving and crafting. The tree itself provides a unique aesthetic value, creating a visually appealing element in any landscape.
So, you’re diving into pawpaw plant growing? It’s a fascinating journey, but sometimes, even the most meticulous gardeners overlook the essentials. Just like choosing the right bathroom fixtures, certain design elements in a pawpaw plant’s environment are crucial for optimal growth. For instance, consider these practical tips on bathroom items designers never thrift , which surprisingly, translate directly to the ideal growing conditions for your pawpaw plant.
Knowing which materials are best for your plants is key to a thriving garden.
Pawpaw Plant Overview
| Plant Name | Botanical Classification | Origin | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pawpaw | *Asimina triloba* | Eastern North America | Medium-sized tree (10-20 ft tall), broad oval leaves, slow growth, edible fruit |
Ideal Growing Conditions
Pawpaw trees, while relatively low-maintenance, thrive under specific environmental conditions. Understanding these conditions is crucial for successful pawpaw cultivation, ensuring a bountiful harvest of delicious fruit. Optimizing these factors leads to healthy growth, robust yields, and a more satisfying experience for the gardener.Pawpaw plants are adaptable but have specific needs for optimal growth. These needs include temperature, water, soil, sunlight, and pest management.
Addressing these factors directly impacts the health and productivity of the pawpaw tree.
Temperature Requirements
Pawpaw trees are sensitive to extreme temperatures. They thrive in a temperate climate, with optimal temperatures ranging between 65°F and 85°F (18°C and 29°C). Lower temperatures can stunt growth, while excessively high temperatures can lead to stress and reduced fruit production. Protecting pawpaw plants from frost during the winter months is crucial in cooler climates.
Watering Needs
Consistent moisture is essential for pawpaw growth, particularly during the initial stages of development and fruiting. Young pawpaw trees require more frequent watering than established ones. During dry spells, water deeply to ensure moisture reaches the roots. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot. The frequency of watering depends on the soil type and local climate conditions.
Regularly checking the moisture level of the soil is a good practice to determine the appropriate watering schedule.
Soil Preferences
Pawpaw trees prefer well-drained, fertile soil with a slightly acidic to neutral pH. The ideal pH range is 6.0 to 7.0. Heavy clay soils can impede drainage and lead to waterlogging, while sandy soils may not retain moisture effectively. A rich loam soil, which combines the best qualities of clay and sand, is ideal. Soil amendment with compost or organic matter can improve soil structure and nutrient content.
Sunlight Requirements
Pawpaw trees require at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day for optimal growth and fruit production. Partial shade can be tolerated, but full sun exposure is essential for maximum yield. Insufficient sunlight can result in stunted growth and reduced fruit size. Planting in a location that receives ample sunlight is key to ensuring healthy development.
Pest and Disease Management
Pawpaw trees are susceptible to various pests and diseases. Regular monitoring and proactive measures are essential to prevent infestations. Common pests include aphids, spider mites, and caterpillars. Diseases like powdery mildew and fungal infections can also affect pawpaw trees. Early detection and appropriate treatment are critical for preventing widespread damage.
Implementing organic pest control methods, such as introducing beneficial insects or using neem oil, is a sustainable approach.
Soil Type Comparison
| Soil Type | Description | Suitability for Pawpaw |
|---|---|---|
| Sandy Soil | Loose, low in nutrients, drains quickly | Less suitable; needs regular watering and fertilization |
| Clay Soil | Heavy, dense, retains water poorly | Less suitable; prone to waterlogging and poor drainage |
| Loam Soil | Balanced mix of sand, silt, and clay; fertile and well-drained | Highly suitable; excellent for pawpaw growth |
Planting and Propagation
Pawpaw trees, with their unique fruit, require careful consideration during planting and propagation. Proper timing and technique are crucial for establishing a healthy and productive plant. Understanding the methods available, from planting seeds to grafting, allows you to tailor your approach to your specific needs and goals.
Best Time to Plant
The ideal planting time for pawpaw seeds or seedlings varies slightly depending on your climate zone. Generally, spring, after the last expected frost, is the best time to plant seedlings. For seeds, sow them indoors 6-8 weeks before the last expected frost. This allows the seedlings to establish a strong root system before transplanting outdoors.
Planting Pawpaw Seeds
Planting pawpaw seeds requires a bit of patience. Begin by preparing seed starting mix in small pots. Sow the seeds about 1/2 inch deep, keeping the soil consistently moist. Maintain a warm temperature (70-80°F) for optimal germination. Once seedlings emerge, gradually harden them off before transplanting them outdoors.
Planting Pawpaw Seedlings
Planting pawpaw seedlings is straightforward. Choose a sunny location with well-drained soil. Dig a hole twice the size of the root ball. Carefully remove the seedling from its container, and place it in the hole. Backfill the hole with soil, ensuring the root crown is slightly above the soil level.
Water thoroughly after planting.
Pawpaw Propagation Methods
Pawpaw plants can be propagated through several methods, including grafting and cuttings. Grafting is a technique used to combine desirable traits from different pawpaw varieties. Cuttings, typically stem cuttings, are another viable option for propagation, offering a relatively simple method for expanding your pawpaw collection.
Step-by-Step Guide for Planting Pawpaw Seedlings
- Site Selection: Choose a sunny location with well-drained soil. Pawpaws thrive in full sun, receiving at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Hole Preparation: Dig a hole twice the size of the root ball. Loosen the soil thoroughly to ensure good drainage.
- Seedling Removal: Carefully remove the seedling from its container, being mindful not to damage the roots.
- Placement: Gently place the seedling in the hole, ensuring the root crown is slightly above the soil level.
- Backfilling: Fill the hole with soil, firming it gently around the roots.
- Watering: Water thoroughly after planting to settle the soil and encourage root establishment.
Tools and Materials for Planting Pawpaw
| Tool/Material | Description |
|---|---|
| Spade or Shovel | For digging the planting hole. |
| Hand Trowel | For preparing the soil and transplanting seedlings. |
| Gardening Gloves | For protecting hands during planting. |
| Measuring Tape | For accurate hole sizing, especially for larger seedlings. |
| Watering Can | For watering the newly planted pawpaw. |
| Potting Mix (Optional) | For preparing the planting mix, especially when starting from seeds. |
Care and Maintenance: Pawpaw Plant Growing Guide
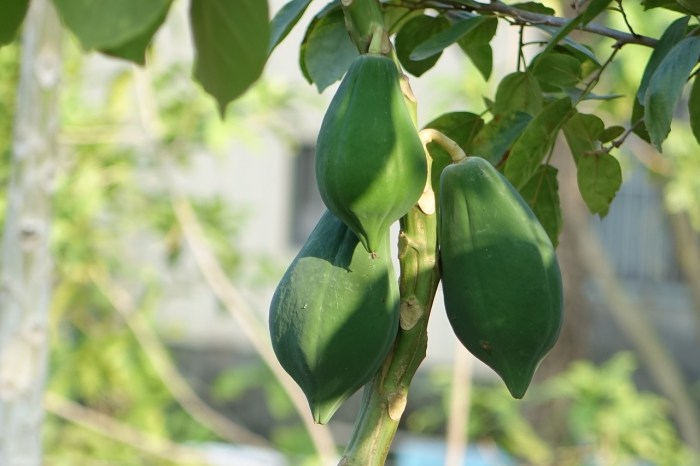

Pawpaw plants, with their impressive size and delicious fruit, require ongoing care to thrive. Regular maintenance, including pruning, fertilization, and pest control, ensures optimal growth and abundant yields. Ignoring these aspects can lead to stunted development, disease, and a lower fruit production. Understanding and implementing these practices will significantly contribute to the success of your pawpaw garden.Maintaining a healthy pawpaw plant involves a proactive approach, focusing on preventative measures rather than reactive solutions.
Addressing potential issues early minimizes damage and promotes robust growth. Consistent monitoring and prompt action are crucial for maintaining the health and productivity of your pawpaw tree.
Pruning
Regular pruning is essential for maintaining the shape and size of the pawpaw plant, as well as promoting air circulation and sunlight penetration. Proper pruning techniques encourage healthy growth and improve fruit production. Removing dead, diseased, or damaged branches helps prevent the spread of infections and maintains the plant’s overall health. Prune during dormant periods, typically late winter or early spring.
- Remove any branches that cross or rub against each other, as this can lead to damage and disease.
- Thin out crowded areas to allow for better light penetration and air circulation. This promotes healthier growth and minimizes competition for resources.
- Cut back any branches that are growing towards the center of the plant, promoting outward growth and a more open canopy.
Fertilization
Pawpaw plants require specific nutrients to flourish. Regular fertilization, tailored to the plant’s needs, promotes healthy growth, vigorous fruiting, and overall resilience. Applying fertilizer during the growing season, typically spring and summer, ensures the plant has the necessary nutrients for optimal development. It is important to use a balanced fertilizer formulated for fruit trees, to ensure the right proportions of nutrients for the plant.
Pest and Disease Control
Pawpaw plants are susceptible to various pests and diseases. Proactive pest control measures, including regular inspections and prompt treatment, prevent widespread infestations and diseases. Identify pests early to prevent major outbreaks. Effective prevention methods and early detection can help minimize damage.
- Regularly inspect the leaves, stems, and fruit for signs of pests, such as aphids, spider mites, or caterpillars. Early detection can help prevent significant infestations.
- Use organic pest control methods whenever possible, like introducing beneficial insects or using insecticidal soaps.
- Monitor for fungal infections, like powdery mildew or anthracnose. Early detection is key; address the infection with appropriate fungicides if needed.
Mulching
Mulching is a crucial aspect of pawpaw care. Applying a layer of mulch around the base of the plant helps regulate soil temperature, retain moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil structure. A layer of mulch helps maintain consistent soil conditions, preventing moisture loss and extreme temperature fluctuations. Proper mulch application protects the roots from extreme temperatures.
Support Structures
Some pawpaw varieties can become quite large and heavy. Providing support, such as stakes or trellises, ensures the plant remains upright and prevents breakage, particularly during periods of heavy fruit load. A proper support system will improve the overall health of the plant and reduce potential damage to branches or stems. This is particularly important for larger varieties.
So, you’re diving into pawpaw plant growing? That’s awesome! But before you get completely swept up in the thrill of cultivating this amazing fruit, take a moment to consider if you might be heading towards a situation like the signs you have way too many plants. Knowing the right time to pull back is just as crucial as knowing how to water a pawpaw seedling.
After all, the goal is a thriving pawpaw plant, not a jungle! Focusing on a few well-maintained pawpaw plants will result in a better outcome than trying to manage a sprawling collection.
Maintenance Schedule, Pawpaw plant growing guide
| Task | Frequency | Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Pruning | Yearly (late winter/early spring) | Remove dead, diseased, or damaged branches; thin out crowded areas; prune crossing branches. |
| Fertilizing | Twice a year (spring and summer) | Apply a balanced fruit tree fertilizer according to package instructions. |
| Pest/Disease Monitoring | Weekly | Inspect the plant for pests and signs of diseases. Take action if necessary. |
| Mulching | Annually (as needed) | Apply a layer of mulch around the base of the plant. |
| Support Installation/Maintenance | As needed | Install stakes or trellises to support the plant if necessary. Ensure support remains secure. |
Harvesting and Storage
Pawpaw fruit, a delicious and nutritious treat, reaches its peak flavor and texture at a specific point in its ripening process. Understanding the ripening stages and knowing the signs of ripeness allows for optimal harvesting, maximizing the enjoyment of this tropical fruit. Proper storage techniques are equally important to prolong the pawpaw’s freshness and prevent spoilage, ensuring a longer window for savoring this unique fruit.The journey from a vibrant green fruit to a sweet, aromatic treasure is fascinating, and recognizing the stages of ripening is key to harvesting at the perfect moment.
Once harvested, understanding storage methods will preserve the fruit’s quality and flavor, allowing you to enjoy pawpaws for days to come.
Pawpaw Fruit Ripening Process
Pawpaw fruit goes through several stages of development before reaching its peak ripeness. The fruit begins as a vibrant green, gradually transitioning through various shades of yellow and orange before reaching full maturity. This color change is a significant indicator of the fruit’s ripeness and eating quality.
Signs of Pawpaw Fruit Ripeness
Several key indicators can help determine when a pawpaw is ready for harvest. The color change is the most obvious sign, moving from a deep green to a yellowish-orange hue. The fruit should also exhibit a soft, yielding texture when gently pressed. A sweet aroma emanating from the ripe fruit is another telltale sign of ripeness. Avoid picking fruit that appears overly soft or mushy, as this often indicates overripeness.
Figuring out the best pawpaw plant growing guide can be tricky, but understanding the needs of similar plants like the zz zanzibar gem plant profile zz zanzibar gem plant profile can help. Both thrive in similar light conditions and appreciate consistent watering, though the pawpaw plant needs a bit more space to truly flourish. Learning about the growing requirements of these types of plants will ultimately help you better understand the pawpaw plant’s needs.
Harvesting Methods
Proper harvesting techniques are essential for minimizing damage to the fruit and the plant. Gently twist or cut the fruit from the stem, taking care not to bruise or puncture the skin. Avoid pulling or yanking, which can damage the fruit and the plant. Using sharp, clean pruning shears or a knife is ideal for this purpose. A small incision is generally sufficient for harvesting, ensuring minimal damage to the stem and fruit.
Storage Methods
Pawpaw fruit is best enjoyed when consumed shortly after harvesting, as its shelf life is relatively short. To extend its shelf life, storing the fruit properly is crucial. For best results, store ripe pawpaws in the refrigerator at 35-40°F (2-4°C). A cool, dry environment is optimal. Avoid storing pawpaws in direct sunlight or near heat sources, as these can accelerate spoilage.
Table of Harvesting and Storage Methods
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Harvesting | Gently twist or cut from stem, avoiding bruising | Minimizes damage to fruit and plant | Requires care and attention |
| Refrigeration (35-40°F/2-4°C) | Store in a crisper drawer or airtight container | Extends shelf life significantly | Fruit may lose some flavor and texture over time |
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Pawpaw plants, while generally resilient, can face various challenges. Understanding the common problems and their solutions is crucial for successful cultivation. Knowing the causes and how to address them will prevent significant yield loss and maintain the health of your pawpaw trees. This section provides a comprehensive guide to diagnosing and resolving issues.Troubleshooting pawpaw problems requires a methodical approach.
Careful observation, understanding of potential causes, and a willingness to implement appropriate solutions are key to successful management.
Identifying Common Pawpaw Issues
Pawpaw plants, like any other fruit tree, are susceptible to various problems, impacting their growth, yield, and overall health. Recognizing these issues early is crucial for timely intervention. Common problems include pest infestations, diseases, and environmental stresses.
Pest Infestations
Pawpaw plants can be vulnerable to a range of pests, which can lead to significant damage if not addressed promptly. Identifying the specific pest is the first step to effective control. Common pests include aphids, caterpillars, and spider mites.
- Aphids: These small insects feed on the sap of leaves and stems, causing yellowing and distortion. They can be controlled by spraying with insecticidal soap or neem oil.
- Caterpillars: These chewing insects can defoliate plants. Hand-picking or using Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) spray can help control them.
- Spider mites: These tiny arachnids create webs on leaves and suck sap, leading to stippling and yellowing. A strong spray of water can dislodge them, and insecticidal soaps can also be effective.
Disease Issues
Pawpaw plants are susceptible to fungal and bacterial diseases that can severely impact their health and productivity. Prompt identification and treatment are essential. Common diseases include anthracnose, powdery mildew, and bacterial spot.
- Anthracnose: This fungal disease manifests as dark lesions on leaves, stems, and fruit. Proper sanitation and fungicides can control it.
- Powdery mildew: This fungal disease appears as a white powdery coating on leaves. Improving air circulation and using fungicides can help.
- Bacterial spot: This bacterial disease shows up as small, dark spots on leaves and fruit. Preventing the spread of the bacteria is key, often involving pruning and sanitation.
Environmental Stress
Environmental factors can significantly impact pawpaw growth and health. Understanding the needs of the plant and addressing any environmental stressors is vital for success. Common environmental issues include insufficient water, extreme temperatures, and poor soil quality.
- Insufficient Water: Pawpaw plants require consistent moisture, especially during dry spells. Regular watering, especially during establishment, is crucial.
- Extreme Temperatures: Pawpaw trees are sensitive to both frost and extreme heat. Protecting them from harsh conditions is essential.
- Poor Soil Quality: Pawpaw trees thrive in well-drained, fertile soil. Amendments can improve soil quality if necessary.
Diagnosing Pawpaw Plant Diseases
Careful observation is crucial in diagnosing pawpaw diseases. Identifying the specific symptoms and patterns of the disease is the first step. Look for patterns of leaf spots, wilting, or discoloration. Also note the presence of any unusual growths or abnormal textures on the plant.
Troubleshooting Table
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Leaf spots | Fungal infection (e.g., anthracnose) or bacterial infection | Apply appropriate fungicides or bactericides. Improve air circulation to prevent further infection. |
| Wilting leaves | Insufficient water, root damage, or pest infestation | Increase watering frequency. Inspect for pests. Ensure proper drainage. |
| Yellowing leaves | Nutrient deficiency, pest infestation, or environmental stress | Amend soil with appropriate nutrients. Address pests. Improve watering and light exposure. |
Pawpaw Plant Varieties
Pawpaws, with their unique flavor profile and versatility, come in a delightful array of varieties. Choosing the right variety for your garden depends on factors like your climate, desired fruit characteristics, and personal preferences. This section delves into the diverse world of pawpaw cultivars, highlighting their distinct traits and suitability for different growing regions.Understanding the nuances of different pawpaw varieties empowers gardeners to select plants that thrive in their specific microclimates, ultimately leading to a rewarding pawpaw-growing experience.
Different Types of Pawpaw Plants
Various pawpaw cultivars exhibit unique characteristics, impacting fruit size, flavor, and growing requirements. Some varieties are better suited for specific regions or climates, ensuring optimal growth and yield. Understanding these distinctions allows for a more informed decision when selecting pawpaw plants for your garden.
Unique Characteristics of Each Variety
Different pawpaw varieties exhibit a spectrum of characteristics. Some produce larger fruits, while others offer a more intense flavor profile. Certain varieties might be more cold-hardy, tolerating lower temperatures better than others. This variation in traits is key to selecting the ideal pawpaw for a particular location.
Comparison of Pawpaw Varieties
Comparing pawpaw varieties based on fruit size, flavor, and growing requirements provides valuable insight. A larger fruit size might be desirable for commercial purposes, while a sweeter flavor might appeal to home gardeners. Consider the specific climate of your region when selecting a variety, ensuring its ability to thrive in the local conditions. For example, a variety known for its cold hardiness is ideal for areas with frequent frost.
Best Pawpaw Varieties for Specific Regions
Choosing the best pawpaw variety for your region involves careful consideration of the specific climate and growing conditions. A variety adapted to a specific region will likely exhibit superior growth and yield. Local agricultural extension offices or experienced gardeners in your area can provide valuable insights into the most suitable pawpaw varieties for your climate.
Pawpaw Variety Table
This table summarizes various pawpaw varieties, their fruit descriptions, and their recommended growing zones. Note that specific growing zones can vary depending on microclimates. This table is a general guideline and further research is recommended.
| Variety Name | Fruit Description | Growing Zone |
|---|---|---|
| ‘Autumn Gold’ | Medium-sized fruits, golden yellow color, sweet and mild flavor. | 6-9 |
| ‘Sunrise’ | Large fruits, vibrant orange-yellow color, juicy and sweet flavor. | 6-9 |
| ‘Stark Early’ | Early-bearing variety, medium-sized fruits, good for areas with shorter growing seasons. | 6-9 |
| ‘Pawnee’ | Large fruits, good flavor, and cold-hardy. | 5-9 |
| ‘Missouri’ | Medium-sized fruits, sweet flavor, relatively easy to grow. | 6-9 |
Closing Summary

In conclusion, cultivating pawpaw plants can be a rewarding experience. By understanding their needs and following the guidelines in this comprehensive guide, you’ll be well-equipped to grow thriving pawpaw trees and enjoy their delicious fruit. Remember to research your specific climate and region for optimal results. With a little care and attention, your pawpaw plants will flourish, bringing joy and delicious fruit to your garden.