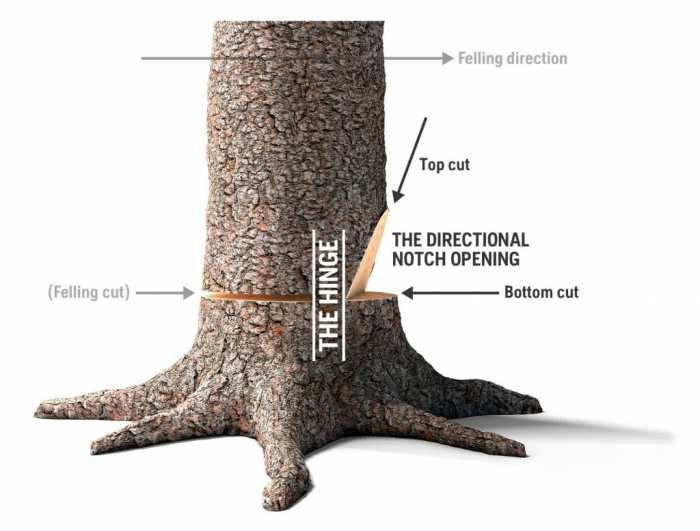
How to cut in electrical box safely is crucial for any electrical work. This comprehensive guide covers everything from essential safety precautions to detailed wiring procedures. Understanding the components, tools, and techniques is paramount to avoiding potential hazards. We’ll walk you through the steps to ensure a successful and safe electrical box installation or repair.
This guide details the critical steps for safely cutting into an electrical box, from initial power shut-off to final wire connections. We’ll also delve into various electrical box types and their specific applications.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical boxes requires meticulous attention to safety protocols. Ignoring these precautions can lead to serious injury or even death. This section details crucial safety measures, emphasizing the importance of power shut-off, grounding, and personal protective equipment. Understanding and consistently applying these safety procedures is paramount to preventing accidents and ensuring a safe working environment.Proper safety measures are essential when working with electrical boxes, and they prevent potentially hazardous situations.
The risks associated with electricity are significant, and they can be mitigated by following well-defined safety procedures. Understanding the hazards and taking the necessary precautions to avoid them is crucial for anyone working near electrical systems.
Power Shut-Off Procedures
Turning off the power supply at the circuit breaker is the single most critical safety step before any work on an electrical box. Failure to do so can result in electric shock, burns, or other serious injuries. The circuit breaker isolates the electrical circuit, preventing the flow of electricity to the area being worked on.
Always turn off the power supply at the circuit breaker before touching any electrical components.
Grounding Practices, How to cut in electrical box
Proper grounding is vital to prevent electrical shock. Grounding systems provide a safe path for electricity to flow to the earth, preventing it from building up and causing dangerous voltage differences. Grounding tools and equipment are crucial components of a safe work environment.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is critical to safeguarding yourself from electrical hazards. PPE such as insulated gloves, safety glasses, and rubber-soled shoes offer a vital layer of protection. This reduces the risk of electrical shock and protects against burns and other injuries.
- Insulated gloves: Protect hands from electrical shock.
- Safety glasses: Protect eyes from sparks and debris.
- Rubber-soled shoes: Prevent electrical shock by providing insulation from the ground.
- Non-conductive footwear: Avoid contact with grounded surfaces to prevent shock.
Importance of Safety Measures
Neglecting safety precautions when working with electricity can have devastating consequences. An electrical shock can cause muscle spasms, disrupt heart function, and lead to burns. These injuries can be life-altering or even fatal. The severity of the potential harm emphasizes the critical need for stringent safety procedures.
Safety Procedure Table
| Safety Procedure | Reason | Hazard if Not Followed |
|---|---|---|
| Turn off power at circuit breaker | Isolates the circuit, preventing electrical flow | Electric shock, burns, potential fire |
| Use insulated tools | Protects from electrical contact | Electrical shock, burns |
| Inspect tools and equipment | Ensures proper functionality and safety | Malfunctions leading to injury |
| Grounding tools | Provides a safe path for electricity to flow to earth | Electric shock, damage to equipment |
| Wear appropriate PPE | Protects from electrical hazards and physical dangers | Electrical shock, burns, cuts |
Identifying Electrical Components

Unveiling the secrets within electrical boxes is crucial for safe and effective work. Understanding the various components and their functions empowers you to handle electrical systems with confidence and precision. This section dives into the world of circuit breakers, fuses, wires, and the different types of electrical boxes, equipping you with the knowledge to identify and appreciate their roles.Knowing the components and their function in electrical boxes is vital for safe and efficient work.
This knowledge will aid in the identification of issues and the implementation of proper solutions. A comprehensive understanding of the components and their arrangement allows for the efficient diagnosis and rectification of faults.
Circuit Breakers and Fuses
Circuit breakers and fuses are essential safety devices in electrical systems. They protect circuits from overcurrent, preventing fires and damage to appliances. Circuit breakers are reusable switches that automatically interrupt current flow when an overload or short circuit occurs. Fuses, on the other hand, are expendable components that melt and break the circuit when the current exceeds a safe limit.
Both serve the crucial role of safeguarding electrical systems.
Wire Types and Their Uses
Different wire types are designed for various applications, each with specific characteristics. Understanding these characteristics is essential for proper wiring. Solid core wires, for instance, are often used in permanent installations where flexibility isn’t a primary concern. Stranded wires, with their multiple strands, are more flexible and are commonly used in applications where movement or flexing of the wires might occur, such as in wiring for appliances or mobile equipment.
The gauge (thickness) of the wire is also important; thicker wires can handle higher currents, which are crucial in applications requiring greater power.
Electrical Box Types and Their Components
Electrical boxes come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific needs and configurations. Some boxes are surface mounted, while others are recessed into walls. The components housed within the boxes might differ depending on the application, such as a junction box, which is designed to connect multiple wires, or a panel box, which houses circuit breakers and other electrical devices.
Each type of box and its components work together to provide a safe and efficient electrical system.
Component Identification Table
| Component | Function | Location in Electrical Box |
|---|---|---|
| Circuit Breaker | Protects circuits from overloads and short circuits | Typically mounted in a panel box or electrical panel |
| Fuse | Protects circuits from overloads and short circuits | Located in various electrical boxes, often as part of a fuse block or holder. |
| Wire (Solid Core) | Conducts electricity in fixed installations | Connected to various components within the box, such as circuit breakers or devices. |
| Wire (Stranded) | Conducts electricity in flexible or movable applications | Used for connecting appliances, or where wires need to flex or move. |
| Junction Box | Connects multiple wires together | Used as a point for wire connections, often in areas with multiple branch circuits. |
| Panel Box | Houses circuit breakers and other electrical devices | Often a central location for the main electrical system, and where circuit breakers are installed. |
Tools and Materials Needed
Getting your hands dirty with electrical work requires meticulous preparation, especially when it comes to cutting into an electrical box. The right tools ensure not only a safe job but also a precise and efficient outcome. Improper tools can lead to damaged materials, injuries, and even electrical hazards. Let’s delve into the essential tools and materials for this task.
Learning how to cut into an electrical box safely is crucial. Proper preparation is key, just like when you’re getting ready to harvest potatoes, how to harvest potatoes requires careful planning, and so does working with electricity. You need the right tools and a clear understanding of the wiring. Always prioritize safety when handling electrical boxes.
Essential Cutting Tools
Properly selecting cutting tools is crucial for safe and effective work. Choosing the right tool for the job is paramount to preventing accidents and ensuring a clean cut. Different types of cutters excel in various situations, making the right choice a vital step in any electrical work.
- Wire Cutters: For cleanly severing wires, diagonal cutters, or side-cutters, are indispensable. These tools are designed for precise cuts on various wire gauges. The choice of wire cutters depends on the thickness of the wire being cut.
- Box Cutters: When dealing with electrical boxes, specialized box cutters are vital for controlled cuts. They are designed for cutting through materials like metal or plastic electrical boxes. The precise design of these cutters prevents damage to the surrounding materials and allows for clean, straight cuts.
- Utility Knives: For softer materials or preliminary cuts, utility knives with various blade sizes can be helpful. These knives are handy for making initial cuts or when working with less rigid materials, like certain plastic enclosures.
Essential Stripping Tools
Wire strippers are equally important for safely working with electrical wires. Proper stripping ensures a clean connection and prevents electrical hazards.
- Wire Strippers: These tools are designed to remove insulation from wires without damaging the conductor. They are available in various sizes to accommodate different wire gauges. Different wire strippers offer various levels of precision and convenience.
Other Necessary Tools
Besides the main cutting and stripping tools, a variety of supplementary tools enhance the job’s efficiency and safety.
- Safety Glasses: Protecting your eyes is paramount. Safety glasses provide a protective barrier against flying debris, sparks, and potential electrical hazards. Always wear safety glasses when working with electrical equipment.
- Gloves: Protective gloves shield your hands from cuts, burns, and electrical shocks. Always wear appropriate insulated gloves when working with electrical components.
- Voltage Tester: Verifying the absence of voltage is crucial. A voltage tester ensures the circuit is de-energized before any cutting or stripping is performed. Failure to verify can lead to severe electric shock.
- Marking Tools: Marking tools like a pencil or marker aid in planning and precise cuts. Clear markings ensure accurate cutting and reduce the risk of errors.
Comparative Analysis of Cutting Tools
The effectiveness and safety of cutting tools vary. A comparison table highlights the pros and cons of different types of tools for electrical work.
| Tool | Use | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagonal Cutters | Cutting wires | Precise cuts, affordable | Can be less effective on thick wires |
| Box Cutters | Cutting electrical boxes | Designed for clean cuts on boxes | Can be less effective on very hard materials |
| Utility Knives | Cutting soft materials | Versatile, affordable | Can damage materials if not used correctly |
Cutting Techniques: How To Cut In Electrical Box
Opening up an electrical box safely and precisely requires careful consideration of the materials and tools involved. Improper techniques can lead to electrical hazards, damage to the box, and even injury. This section details the various methods for cutting into electrical boxes, emphasizing precision and safety, along with appropriate cutting techniques for different materials.Different cutting tools and techniques offer varying levels of control and precision.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each tool is crucial for choosing the best method for the job. This will help you avoid damaging the electrical box and ensure the safety of yourself and others.
Reciprocating Saw Techniques
Using a reciprocating saw for cutting into electrical boxes is a common and efficient method. The key to safety is understanding the limitations and operating procedures of the tool. Ensuring proper support and a controlled cutting motion will minimize the risk of damage and injury.
- Safety First: Always wear safety glasses, ear protection, and appropriate work gloves. Disconnect the power source to the electrical box before beginning any cutting work. Ensure a secure footing and work area. This will help you prevent accidents and injuries.
- Choosing the Right Blade: Select a blade specifically designed for the material of the electrical box. A metal-cutting blade is ideal for metal boxes, while a wood-cutting blade may be suitable for some plastic boxes. Using the incorrect blade can lead to blade breakage and create safety hazards.
- Proper Support: Position the electrical box securely on a stable surface. Support the box with your non-dominant hand while cutting. Use a vice or clamps if needed for added stability. This will help you avoid the box from shifting during the cutting process.
- Controlled Cutting: Make slow, controlled cuts, applying even pressure throughout the process. Avoid jerky movements, which can lead to inaccurate cuts and blade damage. A steady and consistent cutting motion helps maintain control.
- Avoiding Damage: Be mindful of the surrounding wiring and components. Try to avoid cutting through or damaging any electrical wires or components during the cutting process. Always take extra care to prevent damage.
Other Cutting Methods
While reciprocating saws are common, other methods exist for specific situations. These methods may include utility knives, hacksaws, or specialized cutting tools for specific materials.
- Utility Knives: Utility knives are excellent for precise cuts in plastic or non-metal materials. Use sharp blades and apply firm, controlled pressure for clean cuts. Sharp blades reduce the chance of tearing or damaging the material.
- Hacksaws: Hacksaws are ideal for cutting metal or tougher materials. Ensure the blade is properly tensioned and make gradual, controlled cuts. The hacksaw is effective for intricate and controlled cuts in metal.
- Specialized Cutting Tools: For specific materials or situations, specialized cutting tools may be necessary. Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions for these tools to ensure safety and proper usage. These tools may be used for more intricate or complex cuts.
Material-Specific Considerations
Different materials require different cutting techniques. Knowing the material type before starting the cutting process is crucial.
- Metal Electrical Boxes: Metal boxes often require a reciprocating saw or hacksaw with appropriate blades for effective cutting. Take care to avoid damaging the box’s integrity and ensure the box is securely supported.
- Plastic Electrical Boxes: Plastic boxes can be cut with utility knives or reciprocating saws with appropriate blades. Avoid using excessive force, as this can cause the plastic to crack or shatter. A sharp blade is key to avoid tearing or damaging the plastic box.
Wiring Procedures
Wiring procedures are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. Correct wiring prevents short circuits, electrical fires, and potential injuries. Understanding the proper techniques for connecting wires is essential for anyone working with electrical boxes. This section provides a comprehensive guide to safely connecting wires, covering procedures for circuit breakers and other components.
A strong emphasis is placed on the importance of correct connections and the risks associated with improper connections.Correct wiring practices are vital to the safety and reliability of electrical systems. Improper connections can lead to a variety of problems, including overheating, short circuits, and electrical fires. Understanding the step-by-step procedures Artikeld below will ensure that wiring is performed safely and effectively, minimizing the risk of hazards.
Safe Wire Connection Procedures
Proper wire connections are critical to the functionality and safety of electrical systems. This section details a step-by-step procedure for safely connecting wires in an electrical box. Following these guidelines is essential to avoid electrical hazards.
Cutting in an electrical box requires precision, and understanding the measurements is key. First, you need to mark the cut lines accurately. Knowing what the black diamond on a tape measure means for your specific project ( what does the black diamond on a tape measure mean ) will ensure you’re using the right measurements. Then, carefully cut along the lines to get a perfect fit for your new box.
- Disconnect the power supply: Always disconnect the power supply to the electrical circuit before beginning any wiring procedures. This is the single most important safety precaution. Failure to do so can lead to severe electrical shock or even death. Verify the power is off by using a non-contact voltage tester.
- Prepare the wires: Strip the insulation from the ends of the wires to be connected, ensuring a clean, even cut. The length of the exposed wire should be consistent with the required connection method. Stripping the insulation too short or too long can affect the connection quality.
- Connect the wires: Connect the wires according to the wiring diagram and the specific requirements of the electrical box and components. Use appropriate wire connectors, such as wire nuts or terminal blocks, to ensure a secure and reliable connection. Ensure all connections are tight and secure. Over-tightening can damage the wire or the connector, while under-tightening can lead to loose connections and potential electrical hazards.
- Test the connections: After completing the connections, use a non-contact voltage tester to check that the power is not re-applied. Carefully inspect all connections for any signs of damage or looseness. This final inspection step is vital for preventing future problems.
- Reconnect the power supply: Only after all connections have been thoroughly inspected and verified can the power supply be safely reconnected. Reconnect the power supply in a methodical manner to prevent errors and ensure the circuit functions correctly.
Wiring Circuit Breakers and Other Components
Connecting wires to circuit breakers and other electrical components requires specific attention to detail. The correct procedures are essential for both the functionality and safety of the electrical system. Incorrect connections can lead to short circuits, overheating, and even fires.
- Circuit Breakers: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for connecting wires to circuit breakers. Different breaker types have unique connection methods. Incorrect connections can lead to the breaker malfunctioning or failing to provide the intended protection.
- Other Components: Consult the wiring diagrams for specific instructions on connecting wires to other electrical components. These diagrams will specify the correct wire colors and the order in which connections should be made.
Importance of Proper Wire Connections
Proper wire connections are paramount to ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. A poor connection can lead to overheating, potential short circuits, and in extreme cases, electrical fires. Improper connections can cause a wide range of issues, such as a malfunctioning circuit or damage to components.
| Step | Action | Safety Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Disconnect power | Always disconnect the power before any wiring work. |
| 2 | Prepare wires | Ensure proper insulation stripping to avoid damage or hazards. |
| 3 | Connect wires | Use appropriate connectors and tighten securely. |
| 4 | Test connections | Verify all connections using a voltage tester before reapplying power. |
| 5 | Reconnect power | Only reconnect power after thorough inspection. |
Electrical Box Repair and Maintenance
Keeping electrical boxes in good working order is crucial for safety and efficiency. Regular maintenance minimizes the risk of electrical hazards and ensures the longevity of your electrical system. Properly maintained boxes prevent potential fires, shocks, and other serious issues. This section details common problems, troubleshooting techniques, and preventative maintenance strategies.
Common Electrical Box Problems
Electrical boxes can face various issues, ranging from loose connections to damaged components. Identifying these problems early is key to preventing more significant problems.
- Loose connections are a frequent issue. Loose wires can cause overheating, sparking, and even fires. Identifying and tightening these connections is vital for preventing these risks.
- Damaged components, such as deteriorated insulation or broken wires, can lead to short circuits. Regular inspections can uncover these hidden problems before they cause significant damage.
- Overloading can put undue strain on the box and its components. Proper circuit sizing and careful wiring practices are essential to prevent overloading.
- Moisture ingress can cause corrosion and insulation breakdown, potentially leading to electrical shorts. Ensuring proper sealing and ventilation are critical to preventing moisture buildup.
Troubleshooting Faulty Connections
Troubleshooting faulty connections involves systematically checking various points within the electrical box.
- Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting all connections for signs of damage, corrosion, or overheating. Look for any exposed wires, frayed insulation, or discolored components.
- Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of each wire connection. A continuous circuit indicates a good connection. A break in the circuit suggests a faulty connection that needs repair.
- Tightening Connections: If loose connections are found, use appropriate tools to tighten them securely. Ensure proper wire crimping for wire-to-wire connections. Use appropriate wire connectors where needed.
Identifying and Repairing Damaged Components
Damaged components in electrical boxes often manifest as issues with circuit breakers, fuses, or the box itself.
- Inspecting Circuit Breakers: Visually inspect circuit breakers for signs of damage, such as discoloration or melting. If a breaker trips repeatedly, it could indicate an overloaded circuit or a faulty component.
- Replacing Fuses: Replace blown fuses with the correct amperage rating to prevent further damage. Fuses act as safety devices; if they frequently blow, it indicates an underlying problem that needs investigation.
- Repairing or Replacing the Box: If the electrical box shows signs of water damage, cracks, or other structural issues, it might require repair or replacement to maintain safety and prevent future problems. Ensure the new box is correctly installed.
Proper Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance plays a significant role in preventing future electrical box problems.
- Routine Inspections: Schedule regular inspections to identify potential issues before they escalate. Look for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Visual checks are important to catch small problems early.
- Cleaning and Dust Removal: Regularly clean the electrical box to remove dust and debris, improving airflow and reducing the risk of overheating.
- Moisture Protection: Ensure the electrical box is properly sealed to prevent moisture ingress. This is particularly important in areas with high humidity or potential water exposure.
Different Types of Electrical Boxes
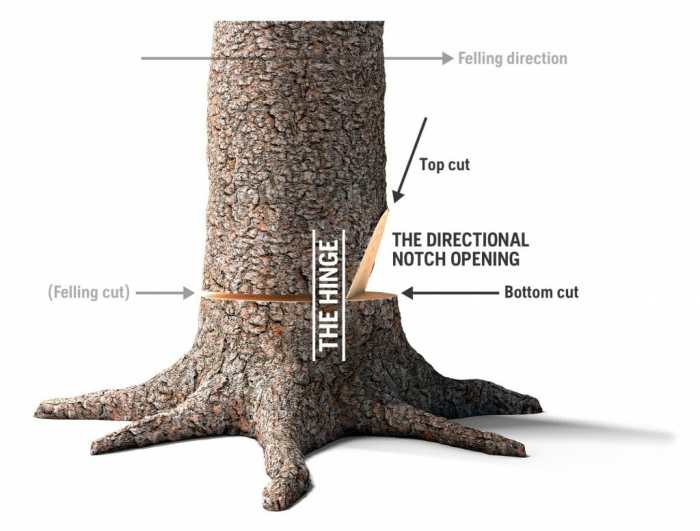
Electrical boxes are crucial components in any electrical system, providing a safe and organized enclosure for wiring connections. Understanding the various types and their specific applications is essential for proper installation and maintenance. Choosing the right box ensures both functionality and safety.Electrical boxes come in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and features, each tailored to a particular purpose.
The appropriate selection depends on the specific wiring needs and the environment where the box will be installed. From simple junction boxes to more complex panel boxes, the correct choice optimizes safety and efficiency.
Learning how to cut an electrical box is a crucial DIY skill. You’ll need the right tools and precise measurements, and remember safety first! Sometimes, a visually appealing project like faking a fireplace might require an electrical box modification. If you’re looking for ideas on how to fake a fireplace, check out this helpful guide: how to fake a fireplace.
Once you’ve got the fireplace design sorted, remember to carefully measure and cut the box to match your project’s needs for a professional finish.
Junction Boxes
Junction boxes are fundamental components in electrical systems. They provide a protected enclosure for connecting wires and devices. Their primary function is to facilitate the joining of multiple wires without exposing them to the elements or potential hazards. This allows for a neat and organized connection, improving safety and reducing the risk of short circuits. Junction boxes are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Panel Boxes
Panel boxes, often referred to as electrical panels, are central to electrical distribution systems. They house the main circuit breakers and fuses that control the flow of electricity to different parts of a building or structure. These boxes are designed with specific components, such as circuit breakers and disconnects, which are integral to safety and circuit protection. The design often includes mounting provisions for various electrical devices.
Meter Boxes
Meter boxes are specifically designed to house electrical meters. These meters measure the electrical energy consumed by a building or area. Meter boxes are typically installed outdoors or in utility rooms, and are designed to protect the meter and its associated wiring. Their construction often includes weatherproofing features to withstand the elements.
Wiring Devices Boxes
Wiring device boxes are designed to house various electrical devices, such as switches, receptacles, and dimmers. They offer a protected environment for these components, ensuring proper installation and preventing damage. Their design often incorporates mounting provisions for the specific devices they are intended to hold.
Table of Electrical Box Types
| Box Type | Dimensions (Approximate) | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Junction Box | Various sizes, typically 4×4 inches to 12×12 inches | Connecting wires, distributing power, splicing cables, creating branch circuits. |
| Panel Box | Larger sizes, varying with amperage rating, typically 12×18 inches to 24×36 inches | Housing circuit breakers, fuses, and other protective devices. Central control point for electrical distribution. |
| Meter Box | Standardized sizes, depending on meter type. | Protecting electrical meters, often installed outdoors or in utility rooms. |
| Wiring Device Box | Various sizes, typically 2×2 inches to 4×4 inches. | Housing electrical switches, receptacles, and dimmers. Supporting and protecting these components. |
Illustrative Examples
Understanding the intricacies of electrical boxes is crucial for safe and efficient work. This section delves into practical examples, showcasing the components, materials, and cutting techniques involved. Visual representations and detailed descriptions are provided to guide you through the process.The following examples illustrate the common procedures for working within electrical boxes, highlighting the safety precautions and precision required for each step.
From identifying critical components to correctly cutting through different materials, these examples provide practical insights into electrical box maintenance and repair.
Typical Electrical Box and Components
Electrical boxes are enclosures designed to protect and organize electrical wiring. A typical box typically contains various components, including junction boxes, conduit entries, and mounting provisions. These components often need to be accessed and/or modified during repair and maintenance procedures. Elements needing attention frequently include wires, conduit, and mounting plates.
Visual Representation of Cutting Process
A safe and efficient cutting process within an electrical box involves careful planning and execution. Precise cuts minimize damage to the box and surrounding components. The process should be documented and followed in a step-by-step manner to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
A well-executed cutting procedure ensures the safety and integrity of the electrical system. This involves using appropriate tools and techniques to avoid damaging wires or other critical components.
 The image shows a junction box with wires, conduit, and mounting plates. Different tools, such as wire strippers, a utility knife, and a hacksaw, are shown being used safely. Note the clear separation of working areas and the attention to avoiding damage to the wiring and components. Proper grounding is also evident, showcasing the importance of safety precautions.
The image shows a junction box with wires, conduit, and mounting plates. Different tools, such as wire strippers, a utility knife, and a hacksaw, are shown being used safely. Note the clear separation of working areas and the attention to avoiding damage to the wiring and components. Proper grounding is also evident, showcasing the importance of safety precautions.
Materials Used in Electrical Boxes
Electrical boxes are typically constructed from metal (often steel or aluminum) or plastic (often ABS or polycarbonate). The choice of material depends on the specific application and environmental conditions.
- Metal boxes provide durability and protection from environmental elements. However, they may be more challenging to cut than plastic boxes.
- Plastic boxes are lighter and often more cost-effective. They offer a degree of flexibility, which can be advantageous in certain situations, but their durability might be lower than metal.
Cutting Procedures for Different Materials
The cutting procedure for metal and plastic differs due to the inherent properties of each material.
- Metal: Metal boxes require more robust cutting tools, such as a hacksaw or reciprocating saw, to achieve precise cuts. Using a grinder with a cutting wheel is also an option for metal. Always ensure proper safety precautions, such as wearing safety glasses and gloves, when working with metal.
- Plastic: Plastic boxes can be cut with a utility knife or a sharp blade. Care should be taken to avoid tearing or cracking the plastic. Precise cuts are achievable using these tools, and they’re often easier to manage than metal cutting. Note that some plastic boxes might require specialized tools or techniques depending on their specific composition.
Last Recap
In conclusion, this guide has provided a step-by-step approach to cutting into electrical boxes, emphasizing safety throughout the process. By following the detailed instructions, you can confidently and correctly install or repair electrical boxes, mitigating risks and ensuring a safe electrical system. Remember, safety is paramount in all electrical work. Always prioritize safety measures and seek professional help when necessary.