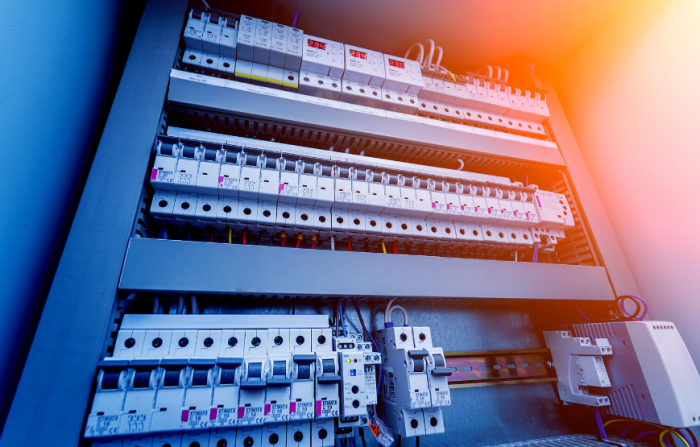
Fuses and fuse boxes 101: Understanding these crucial components of your home’s electrical system is key to safety and preventing costly repairs. From the different types of fuses to the proper maintenance procedures, this guide will walk you through the essentials of electrical safety, ensuring you’re well-equipped to handle any potential issues. This comprehensive overview covers everything from identifying blown fuses to upgrading your system to accommodate growing needs.
This in-depth exploration of fuses and fuse boxes will equip you with the knowledge to understand and maintain your home’s electrical safety. We’ll delve into the specifics of various fuse types, explaining their functions and applications. Furthermore, we’ll guide you through the steps of troubleshooting common problems and replacing fuses safely, providing practical insights to enhance your understanding of this critical aspect of home electrical systems.
Introduction to Fuses and Fuse Boxes
Fuses and fuse boxes are critical components in electrical systems, acting as safety devices to protect circuits from overloads and short circuits. They prevent excessive current flow that could damage appliances, wiring, and even pose fire hazards. Understanding their function, types, and proper selection is crucial for maintaining electrical safety and efficiency.A fuse is a safety device designed to interrupt current flow when it exceeds a predetermined limit.
This prevents damage to electrical components and protects the entire system. The fuse box, or breaker panel, provides a central location for these fuses, organizing and controlling the flow of electricity to different parts of the home or building.
Fuse Types and Applications
Different fuse types are designed for specific applications based on their amperage ratings and physical characteristics. Proper selection ensures the fuse can handle the load without failing prematurely or inadequately protecting the circuit. Choosing the wrong fuse type can lead to system damage or even safety hazards.
Fuse Type Comparison
| Fuse Type | Amperage Rating | Dimensions | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cartridge Fuse | Typically 1A to 63A | Cylindrical shape, varying lengths and diameters | Commonly used in household appliances, lighting circuits, and general electrical distribution panels. They are known for their compact size and ease of replacement. |
| Blade Fuse | Ranges from 1A to 60A | Two or more metal blades with a small gap. | Suitable for applications requiring higher current ratings, often found in automotive electrical systems, and in some industrial applications where space constraints may be an issue. These are also often used in circuit breakers due to their quick response time. |
| Miniature Fuse | Typically 0.5A to 30A | Very small in size, commonly used in electronic devices. | Suitable for protecting circuits in smaller electrical appliances and electronic equipment. Their compact size makes them ideal for densely populated circuit boards. |
| Panel Fuse | Usually 20A to 100A or higher | Large, typically mounted directly in electrical panels. | Used for high-current circuits in electrical panels, like those powering motors, heating systems, and larger appliances. These fuses have robust construction to handle substantial amperages. |
Importance of Proper Fuse Selection
Selecting the correct fuse for a specific circuit is vital for safety and performance. An undersized fuse will fail frequently, leading to circuit malfunctions and potentially exposing the system to damage. An oversized fuse will provide inadequate protection, potentially causing overheating and circuit failure. The amperage rating of the fuse must match the expected current demands of the circuit.
A fuse rated for a lower amperage than the load will repeatedly blow. A fuse rated for a higher amperage than the load may fail to protect the circuit if a fault occurs. The relationship between amperage and fuse rating is critical for system integrity.
Fuse Box Components and Layout
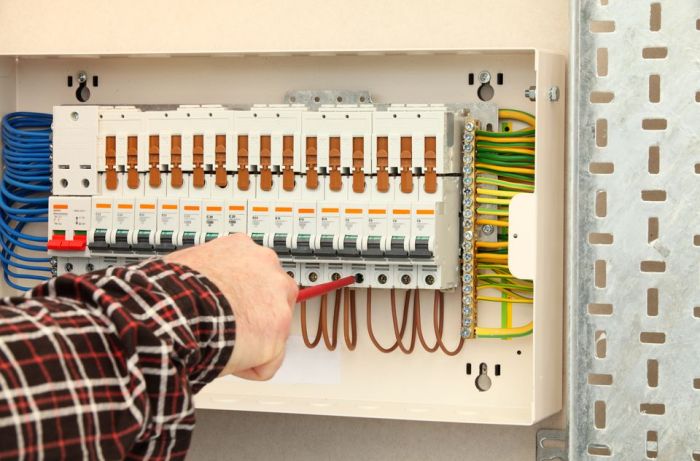
Fuse boxes are crucial safety components in any electrical system, protecting appliances and circuits from damage caused by overloads or short circuits. Understanding their components and layout is vital for safe and efficient use and troubleshooting. Knowing how to identify different components allows for quick and accurate repairs or replacements.The typical fuse box houses various components designed to safeguard your electrical system.
These components work together to regulate the flow of electricity, preventing potential hazards. Proper knowledge of these components and their placement is essential for safe and efficient maintenance and troubleshooting.
Fuse Box Components
The primary components within a fuse box are fuses, circuit breakers, and terminals. Fuses are designed to melt and break the circuit when excessive current flows, preventing further damage. Circuit breakers are similar in function, but they automatically reset, allowing for easy re-use. Terminals provide connections for wires carrying electricity to the various circuits.
Fuse Arrangement and Layout
Fuse boxes often employ a grid-like arrangement, with fuses or circuit breakers organized in rows and columns. This layout allows for easy identification of each circuit and its corresponding fuse or breaker. The specific layout varies based on the manufacturer and the electrical system’s complexity. A standard practice is to organize components by the circuits they protect.
The order of fuses and breakers is usually consistent and related to the electrical system’s functionality.
Identifying Circuit Breakers and Fuses
A step-by-step guide to identifying fuses and circuit breakers involves examining the labels on each component. These labels typically indicate the circuit they protect, along with the amperage rating. The amperage rating is crucial for matching the correct fuse or breaker to the circuit’s needs. Circuit breakers often have a visible handle or lever, allowing for manual resetting and providing a visual distinction.
So, you’re diving into fuses and fuse boxes 101? Knowing how to handle these electrical components safely is key, especially if you’re considering tasks like fixing a tripped circuit. But sometimes, tackling those tricky DIY projects leads you down unexpected paths, like wondering if you can use your steam cleaner to remove paint. Check out this helpful resource on can i use my steam cleaner to remove paint before you start blasting away! Understanding the basics of fuses and fuse boxes will help you avoid more significant electrical problems in the future.
Fuses, on the other hand, typically have a glass or ceramic casing.
A typical fuse box layout resembles a grid. Each slot holds a fuse or breaker, and each component has a unique identifier. Identifying the circuit protected by each fuse or breaker is essential. This involves matching the circuit label to the fuse or breaker.
Typical Fuse Box Layout Diagram
A visual representation of a typical fuse box layout is shown below. The diagram depicts a standard grid layout, with fuses and circuit breakers arranged in rows and columns. Labels indicate the circuit each component protects, and the amperage rating is shown alongside each component.
Imagine a grid of slots, each corresponding to a specific circuit. The labels identify the circuit each slot controls. The amperage rating is also displayed, ensuring correct fuse or circuit breaker selection. Each component is clearly labeled for easy identification. This layout ensures that the correct fuse or breaker is installed for the specific circuit.
So, you’re tackling fuses and fuse boxes 101, huh? Knowing how to safely manage electrical systems is key, especially when getting creative with holiday decorations. For instance, if you’re planning a DIY wall Christmas tree, you’ll need to ensure your electrical setup is sound. This guide will walk you through the process, but remember, always check your fuse box before plugging anything in! Understanding fuses and fuse boxes is crucial for preventing potential hazards, no matter your project.
Fuse Box Safety Procedures
Working with electrical systems, especially fuse boxes, requires meticulous attention to safety procedures. Ignoring these precautions can lead to serious electrical hazards, including fire, electrocution, or personal injury. This section details the critical safety measures to ensure a safe and efficient approach to fuse box maintenance and troubleshooting.
Importance of Safety Procedures
Safe procedures are paramount when handling fuses and fuse boxes. Improper techniques can expose individuals to electrical shocks, burns, and even fatalities. Adhering to these safety guidelines minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures the integrity of the electrical system. Following these precautions is crucial for both professional electricians and homeowners undertaking DIY repairs.
Safe Fuse Replacement Procedure
Before attempting any fuse replacement, ensure the power to the circuit is turned off. This is the most crucial step in preventing electrical shocks. Never replace a blown fuse with one of a higher amperage rating. Using an incorrect amperage fuse can cause overheating and potential fire hazards. Always use the correct amperage fuse specified by the manufacturer or the electrical panel markings.
- Turn off the circuit breaker: Locate the circuit breaker associated with the faulty fuse. Turn the breaker switch to the “off” position. This isolates the circuit, preventing any electrical flow.
- Safety Precautions: Wear insulated gloves and eye protection to prevent accidental electrical shocks or flying debris.
- Identify the blown fuse: Carefully examine the fuse box. Look for a fuse that has a visibly damaged or melted element. Note the amperage rating of the blown fuse.
- Obtain a replacement fuse: Acquire a replacement fuse with the exact same amperage rating as the blown fuse. Never substitute with a fuse of a different rating.
- Replace the fuse: Gently grasp the fuse holder and remove the blown fuse. Insert the new fuse into the holder, ensuring it is seated securely. Double-check for proper alignment and secure placement.
- Turn on the circuit breaker: Carefully turn the circuit breaker switch back to the “on” position. Test the circuit to ensure it is functioning correctly.
Proper Grounding Practices
Proper grounding is essential in electrical systems. Grounding provides a safe path for electrical current to flow in the event of a fault, preventing electric shocks. Grounding systems should always be correctly installed and maintained to ensure their integrity.
Risks of Bypassing or Tampering with Fuses
Bypassing or tampering with fuses is extremely dangerous. Fuses are designed to protect electrical circuits from excessive current. Bypassing a fuse, you are essentially removing this vital safety mechanism, potentially leading to circuit overload, overheating, and fire. This practice could also cause damage to electrical components and create a severe risk to the user and the house.
Fuse Box Maintenance Checklist
Regular maintenance of your fuse box is crucial for ensuring its longevity and safety. This checklist provides a structured approach to routine maintenance.
| Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect fuses | Monthly | Visually check all fuses for damage or discoloration. |
| Check circuit breakers | Monthly | Ensure circuit breakers operate smoothly and are not loose. |
| Check grounding connections | Annually | Verify the integrity of all grounding connections. |
| Clean fuse box | Semi-annually | Remove dust and debris from the fuse box. |
| Replace worn parts | As needed | Replace any damaged or worn components. |
Troubleshooting Fuse Box Issues: Fuses And Fuse Boxes 101
Troubleshooting fuse box issues is a crucial skill for anyone working with electrical systems. A blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker can indicate a variety of problems, from a simple loose connection to a more serious short circuit. Understanding the causes and the steps to diagnose these problems can prevent further damage and ensure the safe operation of your electrical system.Identifying the root cause of a blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker is essential to restoring power safely.
By systematically checking connections, identifying overloaded circuits, and isolating faulty components, you can quickly and effectively resolve the issue. This process not only safeguards your electrical system but also helps you understand the underlying causes of these incidents, leading to more proactive maintenance practices.
So, you’re tackling fuses and fuse boxes 101? Knowing how to safely maintain your electrical system is crucial, especially when considering exterior upgrades like those discussed in articles about ways to modernize a split level home exterior. Modernizing your home’s exterior can be exciting, but remember to check your fuses and fuse box before making any electrical modifications.
Understanding your electrical system will ensure a smooth and safe project, keeping your home’s electrical integrity intact.
Common Fuse Box Issues
Common issues include blown fuses and tripped circuit breakers. These often stem from overloaded circuits, faulty wiring, or short circuits. Understanding the specific symptoms associated with each problem can help you identify the potential cause.
Steps to Troubleshoot Blown Fuses
First, locate the blown fuse. This is often visually evident by a broken or melted element within the fuse. Once you’ve identified the problematic fuse, use a non-contact voltage tester to ensure the power to the affected circuit is off before proceeding. Carefully replace the fuse with one of the correct amperage rating. If the fuse blows again, the issue lies beyond a simple replacement.
Diagnosing the Cause of Blown Fuses
Several factors can lead to a blown fuse. Overloading a circuit with too many appliances or devices drawing too much current is a frequent cause. Faulty wiring, including loose connections or damaged insulation, can also cause excessive current flow, leading to a blown fuse. Short circuits, where the current takes an unintended path, are another common culprit, often resulting in a rapid and significant surge of current.
Isolating Faulty Circuits
To isolate the faulty circuit, systematically turn off the power to each circuit and check if the fuse blows again. This methodical process helps pinpoint the specific circuit responsible for the problem. If the fuse blows again after turning off one circuit, you’ve narrowed the problem to a component or connection within that circuit. Consider checking for loose connections or damaged wiring in that particular circuit.
Methods for Troubleshooting Blown Fuses
Various methods exist for isolating the problem. A visual inspection of the circuit and connections is often the first step. Checking for loose connections or damaged wiring is crucial. Using a multimeter to test the continuity of the circuit can identify potential short circuits. Comparing the current draw of appliances on the affected circuit with the circuit’s amperage rating can determine if the load is exceeding the circuit’s capacity.
These combined methods help you understand the nature of the fault and its exact location within the circuit.
Fuse Box Maintenance and Replacement

Fuse boxes are vital components of any electrical system, ensuring the safe and efficient distribution of power. Proper maintenance and timely replacement of components are crucial for preventing electrical hazards and maintaining the longevity of your electrical system. Regular checks and upkeep can help prevent costly repairs and ensure the continued reliable operation of your home or business.Maintaining your fuse box is not rocket science, but it’s a critical task that shouldn’t be taken lightly.
A well-maintained fuse box safeguards your property and protects you from electrical dangers. Knowing how to inspect, clean, and replace fuses is essential for everyone’s safety.
Recommended Maintenance Frequency
Regular inspections of your fuse box are vital. A general inspection, including visual checks for damage and loose connections, should be conducted at least twice a year. More frequent inspections are recommended if you experience unusual electrical issues or have experienced recent electrical surges or outages. For example, if you live in an area prone to thunderstorms, quarterly inspections are a good practice.
Safe Fuse Box Replacement Procedures
Replacing a fuse box is a complex task that should only be undertaken by qualified electricians. Improper replacement can lead to serious electrical hazards. If you notice damage to your fuse box, contact a qualified electrician to perform the replacement. Do not attempt to replace the fuse box yourself if you are unsure of the procedure or lack the necessary experience.
Fuse Box Inspection and Cleaning
Inspecting and cleaning your fuse box is a simple process that helps maintain its functionality and prevent potential hazards. First, turn off the power supply to the fuse box at the main breaker. Next, visually inspect all components for signs of damage, such as discoloration, melting, or loose connections. Look for any signs of water damage or corrosion, which can indicate a potential electrical issue.
Use a soft-bristled brush to gently remove dust and debris from the fuse box components. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials, as these can damage the components. If you notice any significant damage or have concerns, contact a qualified electrician.
Tools Required for Fuse Box Maintenance and Replacement
Proper tools are essential for safe and efficient fuse box maintenance and replacement. The specific tools required will depend on the nature of the maintenance. However, a basic toolkit is usually sufficient.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead) | Used for disassembling the fuse box and securing components. |
| Wire strippers/cutters | Used for safely cutting and stripping wires, if needed. |
| Gloves | Essential for protecting your hands from electrical hazards and potential cuts. |
| Voltage tester | A critical tool for confirming the power is off before working on the fuse box. |
| Fuse puller (optional) | Facilitates safe removal and installation of fuses. |
Fuse Box Upgrade and Expansion
Upgrading or expanding your fuse box is a necessary step when your electrical needs grow beyond its current capacity. This often occurs with the addition of new appliances, renovations, or simply the need for more circuits to manage the load. Understanding the process and factors involved can prevent potential electrical hazards and ensure a safe and efficient electrical system.Modern homes often rely heavily on electricity for various functions, and the demand for more electrical outlets, lighting, and appliances continuously increases.
This necessitates a careful evaluation of the existing fuse box’s capacity to handle the increased load. Expanding or upgrading the fuse box is a crucial aspect of maintaining a safe and reliable electrical system.
Factors to Consider When Upgrading, Fuses and fuse boxes 101
The decision to upgrade a fuse box hinges on several factors. Firstly, the current electrical load and the anticipated future needs must be carefully assessed. A professional electrician can perform a load analysis to determine the existing amperage usage and the potential for future increases. Secondly, the existing electrical panel’s capacity and type need evaluation. Older fuse boxes might not be compatible with modern electrical devices or wiring configurations.
Thirdly, the available space for the new fuse box or expansion components is essential to consider. A cramped space can hinder proper installation and maintenance. Lastly, the cost of the upgrade must be weighed against the potential benefits and the long-term cost savings.
Process for Upgrading or Expanding a Fuse Box
The upgrade process typically involves several steps. First, a thorough inspection of the existing electrical system by a qualified electrician is paramount. This inspection should assess the wiring, connections, and overall condition of the electrical system to ensure compatibility with the upgrade. Secondly, the required amperage for the additional circuits must be calculated. The electrician will determine the appropriate size and type of fuses or circuit breakers for the new circuits.
Thirdly, the new fuse box must be installed and connected according to local electrical codes and regulations. Fourthly, the new circuits need to be wired and tested for proper functionality and safety.
Adding Additional Circuits
Adding additional circuits involves several crucial steps. Before starting, ensure that the necessary permits and inspections are in place. Secondly, determine the appropriate location for the new circuits based on the electrical load and the existing layout. Thirdly, the electrician must install the necessary wiring, ensuring compliance with all local electrical codes. Fourthly, the new circuits need to be tested and verified for proper functionality and safety.
Examples of Fuse Box Upgrades
Different needs may require varying degrees of upgrade or expansion. A homeowner adding a few more outlets in a new room might only need to add one or two new circuits, possibly by replacing a single fuse or breaker. A homeowner planning a large addition or a home renovation project requiring numerous appliances and lighting might necessitate a significant upgrade, including a larger electrical panel with more circuits.
A commercial space undergoing expansion might require a complete electrical system overhaul with increased amperage and more sophisticated circuit control systems.
Fuse Box Upgrade Considerations
The decision to upgrade a fuse box requires careful planning and consideration. A comprehensive assessment of the existing electrical load, anticipated future needs, and compliance with local electrical codes is vital. Upgrading a fuse box can ensure the safety and reliability of your electrical system for years to come. Hiring a qualified electrician is highly recommended to prevent costly errors and ensure a proper installation.
Epilogue
In conclusion, understanding fuses and fuse boxes is paramount for maintaining a safe and efficient electrical system in your home. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, equipping you with the knowledge to handle common issues and ensure the proper maintenance of your fuse box. Remember, safety is paramount; always follow proper procedures and consult a professional if needed.
With this knowledge, you’re now better prepared to navigate the intricacies of your home’s electrical network, ensuring both safety and efficiency.






