Cement asbestos siding concerns are a serious issue, especially for homeowners with older properties. This comprehensive guide delves into the potential health risks associated with asbestos exposure from cement asbestos siding, exploring identification methods, health impacts, mitigation strategies, and legal aspects. Understanding these concerns is crucial for making informed decisions about your home and well-being.
This guide provides a concise overview of cement asbestos siding, highlighting its historical use, common applications, and potential health risks. It also details how to identify cement asbestos siding, Artikels the health impacts of exposure, and explores mitigation and remediation strategies. Furthermore, the guide addresses legal and regulatory aspects, safety measures, and resources for further information.
Introduction to Cement Asbestos Siding Concerns
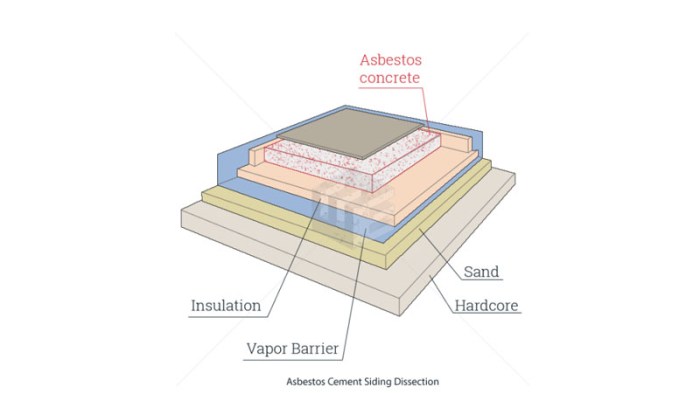
Cement asbestos siding, a common building material in the mid-20th century, was often used for its durability and resistance to weather. This material, a composite of cement and asbestos fibers, offered an attractive and long-lasting exterior finish for homes and commercial structures. However, the presence of asbestos fibers in this material presents significant health risks.The use of asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral, was widespread in various building materials due to its exceptional heat resistance, tensile strength, and insulating properties.
Unfortunately, this same combination of properties makes it incredibly dangerous when inhaled, leading to serious and often irreversible health complications. Cement asbestos siding, like other asbestos-containing materials, poses a substantial threat to human health when disturbed and released into the air.
Potential Health Risks of Asbestos Exposure
Asbestos fibers, when inhaled, can become lodged deep within the lungs and other organs. Prolonged exposure can lead to a range of serious health issues, including asbestosis, lung cancer, mesothelioma, and other respiratory diseases. Asbestosis is a progressive lung disease characterized by scarring of the lung tissue, while mesothelioma is a rare but aggressive cancer that typically affects the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart.
Lung cancer, a leading cause of cancer death worldwide, can also be linked to asbestos exposure.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Asbestos-Related Illnesses
The onset of asbestos-related illnesses can often be insidious, with symptoms developing gradually over many years. Symptoms can include persistent coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, and weight loss. Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for effective treatment and management of these conditions.
Importance of Addressing Concerns About Cement Asbestos Siding
The potential health risks associated with cement asbestos siding necessitate a proactive approach to address concerns. Identifying and safely managing asbestos-containing materials is critical to protecting public health. The health risks associated with asbestos exposure are significant and far-reaching, making it essential to prioritize safety and mitigation strategies.
Mitigation Strategies for Cement Asbestos Siding
Properly handling and removing asbestos-containing materials is crucial to prevent exposure. Professional asbestos abatement services should be utilized for safe removal and disposal of the material. Maintaining the integrity of the siding and preventing its deterioration are essential to avoid fiber release. This includes avoiding any actions that might disturb or damage the siding.
I’ve been researching cement asbestos siding lately, and the potential health risks are definitely concerning. While I’m trying to figure out the best way to address this, I’ve also been fascinated by the beauty of night blooming cereus, especially the different varieties like those found on types of night blooming cereus. Learning about their unique blooms has been a nice distraction from the more pressing issue of dealing with my old siding.
Hopefully, finding the right solution for my cement asbestos siding will be as rewarding as watching a night blooming cereus flower.
| Material Type | Asbestos Content | Potential Health Risks | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cement Asbestos Siding | Typically contains asbestos fibers | Asbestosis, Lung Cancer, Mesothelioma | Professional asbestos abatement, Avoid disturbing the siding, regular inspections. |
Identifying Cement Asbestos Siding
Knowing if your cement siding contains asbestos is crucial for your health and safety. Improper handling of asbestos-containing materials can lead to serious health risks. This section will guide you through various methods to identify potential asbestos presence, from visual inspections to professional testing.Identifying asbestos in cement siding requires a methodical approach. Visual clues can often point to a possible asbestos presence, but confirmation through professional testing is essential.
Historical records and material testing provide further insight, allowing you to take appropriate precautions.
Dealing with cement asbestos siding concerns can be a real headache, but thankfully, there are ways to tackle the issue head-on. Sometimes, a project like this requires a meticulous approach, and finding the perfect tools is key. For example, if you’re looking for the best beginner sewing machines to buy, you might find a great selection online here.
Ultimately, addressing cement asbestos siding safely and effectively is the top priority, so always prioritize expert advice and proper safety measures.
Visual Inspection Methods
Visual inspection is the first step in assessing potential asbestos content. While not definitive, visual cues can help pinpoint areas requiring further investigation. A careful examination can reveal subtle characteristics indicative of asbestos presence.
- Careful observation is key. Look for discoloration, variations in texture, or unusual patterns on the siding. Uneven color distribution or a speckled appearance might suggest asbestos-containing material.
- Pay attention to the siding’s age. Cement asbestos siding was commonly used in construction during specific time periods. Knowing the approximate age of your home can be a valuable indicator.
- Examine the condition of the siding. Damaged or deteriorated sections may exhibit signs of asbestos fibers or other unusual material properties. Look for signs of degradation, cracks, or crumbling.
- Consider the overall installation. How the siding is installed can also offer clues. For example, if the siding is installed in a specific pattern, it might indicate a particular manufacturing process.
Step-by-Step Visual Inspection Procedure
To effectively assess your siding for asbestos, follow these steps:
- Preparation: Gather protective equipment, including gloves, eye protection, and a dust mask. These precautions are crucial to prevent exposure to potential asbestos fibers.
- Inspection: Thoroughly inspect each section of the siding, paying close attention to color variations, textures, and any signs of damage or deterioration.
- Documentation: Take detailed photographs of any unusual features, noting specific locations and any observed discrepancies. Document the age of the building or siding, if known.
- Record Keeping: Note all observations in a log, including the date, location of the inspection, and any relevant details.
Visual Characteristics Suggesting Asbestos Presence
Some visual indicators might suggest the presence of asbestos. However, these indicators are not conclusive and professional testing is always recommended.
- Color Variations: Uneven color distribution, speckled patterns, or streaks of different shades might indicate variations in the material composition.
- Texture Differences: Unusual surface textures, such as roughness, bumps, or a granular feel, could suggest the presence of asbestos fibers.
- Cracks and Damage: Extensive cracking, crumbling, or degradation in specific areas might be a sign of asbestos-containing material.
- Age of the Building: Cement asbestos siding was prevalent in construction during specific time periods. Knowing the building’s age can be a helpful initial indicator.
Importance of Professional Testing
While visual inspection can provide valuable clues, professional testing is critical for definitive confirmation. A trained professional has the expertise and specialized equipment to accurately identify asbestos.
Professional testing provides conclusive results, allowing for informed decisions regarding asbestos management.
Visual Inspection Checklist
| Visual Cue | Possible Material | Asbestos Presence (Yes/No/Unknown) | Next Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discolored areas | Different types of cement | Unknown | Professional testing |
| Cracks and crumbling | Age-related deterioration | Unknown | Professional testing |
| Speckled texture | Cement-based material | Unknown | Professional testing |
| Installation pattern | Cement asbestos siding | Unknown | Professional testing |
Health Impacts of Exposure: Cement Asbestos Siding Concerns

Cement asbestos siding, while seemingly innocuous, poses significant long-term health risks. The presence of asbestos fibers, even in seemingly small quantities, can lead to severe and potentially fatal diseases. Understanding the mechanisms of asbestos’s harmful effects and the populations most vulnerable to these risks is crucial for preventative measures.The insidious nature of asbestos lies in its microscopic fibers.
These fibers, once inhaled, can become lodged deep within the lungs and other organs. The body’s attempts to eliminate these foreign particles can trigger an inflammatory response, which over time, can lead to serious health complications. Understanding this process is key to comprehending the long-term health impacts of asbestos exposure.
Respiratory Illnesses: A Detailed Look
Exposure to asbestos fibers, even from seemingly benign sources like cement siding, can trigger a cascade of respiratory problems. The fibers irritate the delicate lining of the lungs, leading to inflammation and scarring. This damage can impair lung function, making breathing progressively more difficult. Chronic respiratory issues are often the first visible symptoms of asbestos exposure.
Mechanisms of Asbestos-Induced Harm
Asbestos fibers, once inhaled, can become lodged deep within the lungs and other organs. The body’s attempts to eliminate these foreign particles trigger an inflammatory response. This inflammatory response, though initially designed to protect the body, can lead to the formation of scar tissue (fibrosis) over time. This scarring, particularly in the lungs, progressively restricts the lungs’ ability to function optimally.
Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations are more susceptible to the adverse effects of asbestos exposure. Children, whose lungs are still developing, are particularly vulnerable. Their developing respiratory systems are more susceptible to the damaging effects of asbestos fibers. Similarly, the elderly, whose immune systems may be compromised, are also at greater risk of developing serious complications from asbestos exposure.
Asbestos-Related Diseases
Exposure to asbestos can result in a range of serious and often fatal diseases. Asbestosis, a progressive lung disease, is characterized by scarring and inflammation in the lungs. Mesothelioma, a rare cancer affecting the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart, is a particularly aggressive form of cancer directly linked to asbestos exposure. Lung cancer, a common and devastating form of cancer, is also linked to asbestos exposure.
These diseases can manifest years after initial exposure, making early detection and preventative measures crucial.
Exposure Level, Symptoms, and Potential Diseases
| Exposure Level | Symptoms | Potential Diseases | Recommended Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-level, short-term | Mild respiratory irritation, occasional coughing | No immediate observable diseases, but ongoing exposure should be avoided. | Seek medical advice and avoid further exposure. |
| Moderate, long-term | Persistent coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue | Asbestosis, potential development of lung cancer | Seek immediate medical attention. Consider professional asbestos abatement. |
| High, long-term | Severe shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, significant chest pain, weight loss | Asbestosis, mesothelioma, lung cancer | Urgent medical attention required. Immediate professional asbestos abatement is necessary. |
Mitigation and Remediation Strategies
Dealing with cement asbestos siding requires careful planning and execution. Ignoring the presence of asbestos can lead to serious health risks, making proactive mitigation essential. Understanding the various remediation methods, their costs, and the importance of professional handling is crucial for homeowners and property managers.Effective mitigation strategies aim to minimize exposure to asbestos fibers, preventing their release into the air and protecting occupants.
These strategies range from containment methods to complete removal, each with specific considerations regarding cost, effectiveness, and required expertise. Choosing the right approach depends on factors like the extent of asbestos contamination, the building’s structure, and available resources.
Encapsulation Strategies
Encapsulation involves sealing asbestos-containing materials to prevent fiber release. This method is often a cost-effective solution for minor contamination or for situations where complete removal is impractical or excessively expensive. For example, encapsulation can be achieved by applying a thick layer of paint or sealant over the asbestos siding, effectively trapping the fibers within the material. While encapsulation can limit fiber release, it does not eliminate the asbestos.
It’s important to remember that encapsulation is not a permanent solution. The integrity of the encapsulation may eventually degrade, potentially releasing asbestos fibers.
Removal Strategies
Asbestos removal is the most comprehensive approach, completely eliminating the asbestos-containing material. This process requires specialized equipment and trained personnel, and it is generally more expensive than encapsulation. However, it offers the highest level of protection against future exposure. In cases where the asbestos siding is damaged or in poor condition, removal might be the only viable option to avoid potential fiber release.
Safe Handling Procedures
Safe handling procedures are critical during any asbestos abatement project. These procedures are designed to prevent the release of asbestos fibers into the air, protecting both workers and the surrounding environment. Strict adherence to these procedures is crucial, as inhalation of asbestos fibers can cause serious health problems. A crucial step involves the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including respirators, gloves, and coveralls, to protect the workers from asbestos exposure.
The proper disposal of asbestos-contaminated materials is also vital to prevent environmental contamination.
Comparison of Remediation Methods
| Remediation Method | Cost | Effectiveness | Required Expertise |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encapsulation | Generally lower | Relatively low in terms of complete removal; limits exposure | Specialized knowledge in asbestos handling, but less intensive than removal |
| Removal | Generally higher | Highest level of protection against future exposure; eliminates the source | Licensed and certified asbestos abatement professionals are absolutely essential |
Importance of Licensed and Certified Professionals
Hiring licensed and certified asbestos abatement professionals is paramount. These professionals possess the necessary training, experience, and certifications to handle asbestos-containing materials safely and effectively. They are knowledgeable about local regulations and safety protocols, ensuring compliance with legal requirements. Using unqualified individuals for asbestos abatement is dangerous and potentially illegal, leading to increased health risks and legal ramifications.
Furthermore, unqualified contractors may compromise the effectiveness of the remediation process.
Safety Precautions During Asbestos Abatement
- Strict adherence to all safety protocols, including proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). This includes respirators, gloves, and coveralls.
- Proper ventilation and containment measures are essential to prevent airborne asbestos fibers.
- Proper disposal of asbestos-contaminated materials is critical to minimize environmental contamination.
- Regular monitoring of worker exposure levels is crucial to ensure safety.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Navigating the legal landscape surrounding asbestos abatement is crucial for homeowners and property owners. Understanding the regulations, responsibilities, and potential liabilities associated with asbestos-containing materials is paramount to ensuring safety and compliance. Ignoring these aspects can lead to costly legal issues and jeopardize public health.
Legal Framework Governing Asbestos Abatement
The legal framework governing asbestos abatement and remediation is complex and varies by jurisdiction. Federal regulations, such as those established by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), often serve as a baseline, while state and local regulations can impose more stringent requirements. This complex web of regulations aims to protect public health by controlling asbestos exposure during demolition, renovation, or removal projects.
Homeowner and Property Owner Responsibilities
Homeowners and property owners who discover asbestos-containing materials in their buildings have specific responsibilities. These responsibilities typically include proper identification of the material, adhering to regulatory guidelines for handling and removal, and engaging qualified professionals for asbestos abatement. Failure to adhere to these guidelines can result in significant legal repercussions.
Government Agencies and Regulations
Several government agencies play a vital role in regulating asbestos handling and removal. The EPA, with its extensive regulations, provides national guidelines, while state environmental agencies often enforce more specific standards. Local jurisdictions might also have ordinances that impact asbestos abatement. Understanding the interplay between these different levels of regulation is crucial for compliance.
Potential Legal Liabilities
Improper handling of asbestos-containing materials can lead to significant legal liabilities. Penalties can range from fines to lawsuits. Failing to follow proper procedures can expose property owners and contractors to liability for health issues arising from asbestos exposure. For example, a contractor who removes asbestos improperly, leading to a neighbor’s exposure and subsequent illness, could face substantial legal repercussions.
Table: Regulatory Agencies, Regulations, Responsibilities, and Penalties
| Regulatory Agency | Regulations | Responsibilities | Penalties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) | Comprehensive guidelines on asbestos identification, handling, and removal. | Ensuring compliance with federal regulations, including proper training and certification for asbestos abatement professionals. | Significant fines for non-compliance, potentially including criminal charges in severe cases. |
| State Environmental Agencies | State-specific regulations that may supplement or supersede federal guidelines. | Enforcing state regulations regarding asbestos abatement, issuing permits, and inspecting work sites. | Fines and penalties tailored to state laws, potentially including suspension or revocation of licenses. |
| Local Jurisdictions | Local ordinances and regulations on asbestos handling and removal. | Implementing local regulations and ensuring compliance with building codes related to asbestos. | Fines, injunctions, and other penalties specific to the local jurisdiction. |
| Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) | Regulations focusing on worker safety during asbestos abatement. | Ensuring worker safety through training, protective equipment, and adherence to health and safety standards. | Fines and penalties for failing to provide safe working conditions, which could include worker injury or illness resulting from improper handling. |
Prevention and Safety Measures
Protecting yourself and your family from asbestos exposure when dealing with cement asbestos siding requires a proactive and cautious approach. Ignoring these safety measures can lead to serious health risks. This section details crucial preventative steps and safety procedures to follow during home maintenance or renovation projects involving asbestos-containing materials.Cement asbestos siding, while a common building material, poses a significant health risk if not handled properly.
The crucial aspect is understanding and implementing preventive measures to avoid exposure and protect oneself and others. Thorough preparation and adherence to safety protocols are essential for minimizing risks and maintaining a safe environment.
Preventing Asbestos Exposure
Proper planning and execution are essential to prevent asbestos exposure. Understanding the potential hazards associated with cement asbestos siding is the first step. This involves recognizing the material’s presence and the potential for asbestos fibers to become airborne.
- Thorough Inspection: A comprehensive inspection of the property, particularly areas with cement asbestos siding, is necessary. This inspection should be conducted by a qualified professional familiar with asbestos identification and handling procedures. The inspection should cover not only the siding itself but also areas where the material may have been used, such as flashing or roofing.
Dealing with cement asbestos siding can be a real headache, right? It’s a serious concern, but luckily, sometimes a little green thumb can help you feel a bit better about your home improvement projects. Learning how to propagate mint, for instance, can be a rewarding experience. how to propagate mint is a great way to grow your own herbs, and you’ll be surprised how that can take your mind off of those potentially hazardous siding materials.
Of course, addressing the asbestos issue is still crucial. Proper removal and disposal are paramount, but hopefully, a little home gardening can ease the stress a bit.
- Avoid Disturbing the Material: Avoid any activities that could disturb or damage the cement asbestos siding. This includes hammering, sawing, sanding, or any other actions that could release asbestos fibers into the air. If repairs are absolutely necessary, consult with an asbestos abatement specialist.
- Encapsulation: If the siding is in good condition and there are no visible signs of damage, encapsulation might be an option. This involves applying a protective coating to the siding to prevent the release of asbestos fibers.
Safety Procedures During Home Maintenance
Following established safety procedures is critical during any home maintenance or renovation project involving cement asbestos siding. Proper preparation and adherence to these protocols will significantly reduce the risk of asbestos exposure.
- Professional Assistance: For any work involving the removal or disturbance of cement asbestos siding, hire qualified and licensed asbestos abatement contractors. These professionals possess the expertise and equipment to handle the material safely and effectively.
- Designated Work Area: Create a designated work area, ideally in an enclosed space. If this isn’t feasible, take steps to contain the area, minimizing the spread of asbestos fibers to other parts of the house or the environment.
- Airborne Containment: Implement measures to contain airborne asbestos fibers, such as using air filtration systems and ensuring proper ventilation. The area should be well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of asbestos dust.
Safe Handling and Disposal of Asbestos-Contaminated Materials
Safe disposal of asbestos-contaminated materials is critical to prevent environmental contamination and public health risks.
- Proper Packaging: Asbestos-contaminated materials must be carefully packaged in sealed containers to prevent the release of fibers. Special disposal bags or containers are required. The material must be double-bagged and labeled as asbestos-containing material.
- Specialized Disposal: Asbestos-containing materials should be disposed of through licensed and certified disposal facilities. Never attempt to dispose of asbestos-contaminated materials in regular trash bins or landfills.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhere to all local, state, and federal regulations regarding asbestos disposal. These regulations dictate the appropriate procedures for handling and disposal.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount for preventing asbestos exposure. This equipment forms a critical barrier between the worker and the potential hazard.
- Specialized Clothing: Wear specialized clothing, including disposable coveralls, gloves, and respirators, when working with cement asbestos siding. This clothing should be designed to prevent the penetration of asbestos fibers.
- Respiratory Protection: Respirators are essential to prevent the inhalation of asbestos fibers. The type of respirator needed depends on the level of asbestos exposure anticipated.
- Eye Protection: Eye protection, such as safety glasses or goggles, is also necessary to shield the eyes from airborne particles.
Safety Procedures Table
| Task | Safety Equipment | Procedures | Potential Hazards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inspecting cement asbestos siding | Safety glasses, dust mask | Inspect from a safe distance, avoid touching the surface | Exposure to asbestos fibers (minimal if surface is intact) |
| Repairing damaged siding | Full body suit, respirator, gloves, eye protection | Enclose the work area, wet the surface before working, vacuum thoroughly after | Significant exposure to asbestos fibers, potential for inhalation |
| Removing cement asbestos siding | Full body suit, respirator, gloves, eye protection, disposable coveralls, specialized disposal containers | Hire licensed asbestos abatement contractors, follow their instructions meticulously, proper disposal of materials | High risk of asbestos exposure, potential for environmental contamination |
| Cleaning up asbestos-contaminated debris | Full body suit, respirator, gloves, eye protection, disposable coveralls, wet mops, specialized disposal containers | Wet the area, use vacuum with HEPA filter, dispose of debris according to regulations | Exposure to asbestos fibers during cleanup, potential for environmental contamination |
Resources and Further Information
Navigating the complexities of asbestos and cement asbestos siding requires access to reliable information. This section provides crucial resources for understanding the risks, testing procedures, and remediation options. Knowing where to turn for expert guidance is essential for protecting your health and property.
Reputable Organizations and Resources
Comprehensive information about asbestos and its related hazards is available from various organizations. These resources provide detailed information on identification, testing, and remediation procedures. Understanding the different types of asbestos and their associated risks is vital. This knowledge empowers informed decision-making when dealing with potential asbestos exposure.
- The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): The EPA is a primary source of information on asbestos, including its identification, handling, and safe removal. They offer guidelines and regulations for asbestos abatement and provide crucial resources for understanding the risks associated with asbestos exposure. Their website is a valuable tool for staying informed about current regulations and best practices.
- The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): OSHA provides critical standards and guidelines for workers handling asbestos, emphasizing safety protocols and proper procedures to mitigate exposure risks. They offer resources and training materials for businesses and individuals who may be exposed to asbestos.
- The American Industrial Hygiene Association (AIHA): AIHA is a professional association dedicated to promoting industrial hygiene, including asbestos safety. Their resources offer a wealth of information about asbestos identification, exposure assessment, and control strategies. They often provide educational materials and support for professionals working in this field.
Local Government Agencies
Contacting local government agencies can provide valuable information about asbestos regulations in your area. These agencies often have detailed information on permitting requirements for asbestos abatement projects. This ensures compliance with local regulations and avoids potential legal issues.
- Local Health Departments: Local health departments can provide information on asbestos regulations, testing requirements, and resources for remediation in your area. They can also offer guidance on how to report potential asbestos exposure concerns.
- Building Departments: Building departments can offer information on permitting requirements for asbestos abatement and remediation work. They often have specific guidelines for handling asbestos-containing materials within building structures.
Testing Laboratories
Reliable testing laboratories are crucial for accurate asbestos identification and quantification. This information is critical for developing appropriate remediation strategies. Choosing a certified laboratory is essential for ensuring the validity and reliability of the test results.
- Certified Asbestos Testing Laboratories: Finding a certified asbestos testing laboratory is essential for accurate identification of asbestos-containing materials. These laboratories utilize validated methodologies and adhere to strict quality control procedures. Their expertise is vital for ensuring accurate assessment of asbestos levels.
Abatement Companies
Selecting qualified abatement companies is critical for safe and effective asbestos removal. Professional abatement companies possess the necessary expertise, equipment, and safety protocols to handle asbestos removal safely.
- Certified Asbestos Abatement Contractors: Certified asbestos abatement contractors are equipped with the specialized training and equipment necessary for safely removing asbestos-containing materials. They adhere to strict safety protocols and follow regulations to minimize risks during remediation procedures. Ensuring their certification is essential for a safe and effective abatement process.
Online Resources
Numerous online resources offer valuable information about asbestos and its related hazards. These resources provide detailed information on identification, testing, and remediation procedures.
- EPA Website: The EPA website provides comprehensive information on asbestos, including identification guides, regulations, and resources for remediation.
- OSHA Website: The OSHA website offers valuable resources for understanding asbestos safety standards, including guidelines for worker protection and proper handling procedures.
- ASBESTOS.COM: This website is a dedicated resource for information about asbestos-related issues, including identification, health effects, and remediation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This section addresses common questions about cement asbestos siding and asbestos exposure. These questions and answers offer a comprehensive understanding of the relevant issues.
- How can I determine if my cement asbestos siding contains asbestos? Professional testing by a certified laboratory is the only reliable way to confirm the presence of asbestos in cement asbestos siding.
- What are the health risks associated with asbestos exposure? Asbestos exposure can lead to serious health problems, including lung cancer, mesothelioma, and asbestosis.
- What are the legal and regulatory aspects of asbestos abatement? Specific regulations and laws vary by jurisdiction and should be reviewed for compliance.
Table of Resources, Cement asbestos siding concerns
| Organization | Contact Information | Services | Website |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) | (Insert Contact Information Here) | Asbestos information, regulations, and resources. | (Insert Website Here) |
| Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) | (Insert Contact Information Here) | Asbestos safety standards, worker protection. | (Insert Website Here) |
| American Industrial Hygiene Association (AIHA) | (Insert Contact Information Here) | Industrial hygiene, asbestos safety resources. | (Insert Website Here) |
Last Recap
In conclusion, navigating cement asbestos siding concerns requires a multi-faceted approach. By understanding the risks, identification methods, and mitigation strategies, homeowners can make informed decisions to protect their health and well-being. This guide serves as a starting point for learning about asbestos, but professional consultation is crucial for any concerns or actions regarding asbestos-containing materials. Remember, safety is paramount.






