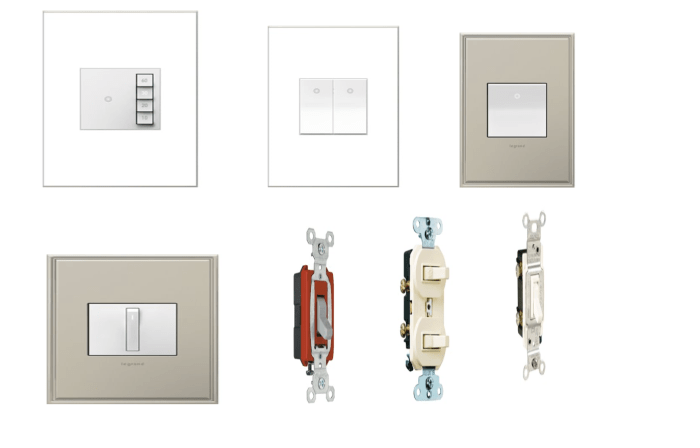
Types of electrical switches in the home are crucial for safely and effectively controlling lights and appliances. From simple single-pole switches to the more complex three-way and four-way options, each type has a specific purpose and method of operation within a home’s electrical system. Understanding these differences can prevent potential hazards and ensure efficient use of electricity. This guide will explore the various types, their applications, mechanisms, and safety considerations.
This exploration will begin with a fundamental overview of electrical switches, covering their basic functionalities and the critical safety aspects involved in their use and installation. We’ll then delve into the different types, from single-pole switches for basic lighting to the more intricate three-way and four-way systems, examining their specific applications and circuit connections. The comparison table will provide a quick overview of the key differences between each type.
Introduction to Electrical Switches

Electrical switches are fundamental components of any home’s electrical system, enabling us to control the flow of electricity to various appliances and lights. They are crucial for safety, convenience, and energy efficiency. Understanding their types and functions is essential for safe and effective use. From simple light switches to more complex circuits, these devices play a vital role in our daily lives.The fundamental purpose of a switch is to interrupt or complete an electrical circuit.
This allows us to turn appliances on or off, and control the flow of current to specific areas of the home. Properly functioning switches ensure the safe operation of electrical equipment, while faulty switches can lead to hazards.
Safety Considerations
Safe electrical practices are paramount when working with switches. Incorrect installation or improper use can lead to severe electrical shocks, fires, or equipment damage. Always ensure that you are working with the power off before handling any electrical wiring or components. Consult a qualified electrician for any installation or repair work that you are unsure about. Following established safety protocols is critical for preventing accidents.
Common Types of Switches
Several types of switches are commonly used in residential settings, each with specific functions and applications. These switches are crucial for managing electricity flow and controlling various electrical devices.
- Single-Pole Single-Throw (SPST) Switches: These are the most basic type of switch, controlling a single circuit. They are commonly found in simple light fixtures, where a single switch controls a single light. An example would be a switch that controls a single ceiling light. The SPST switch is known for its simplicity and reliability, making it a popular choice in numerous applications.
- Single-Pole Double-Throw (SPDT) Switches: These switches allow you to route current to one of two different circuits. A common example is a switch that controls a light fixture that has two different light bulbs. One switch can turn one light on and off, and the other light will turn on or off based on the position of the switch.
- Three-Way Switches: These are used to control a single light fixture from two different locations. For instance, you might have a switch at the top of the stairs and one at the bottom to control the light in a hallway. The three-way switch system allows you to turn the light on or off from either location, enabling flexibility in lighting control.
- Four-Way Switches: These are used in conjunction with three-way switches to control a single light from three or more locations. They are commonly used in larger rooms or hallways where multiple switches are needed to control a single light fixture. For instance, a large room with switches in various locations.
- Dimmer Switches: These switches allow for the control of the brightness of a light fixture. They gradually increase or decrease the amount of current flowing to the light, resulting in varying levels of illumination. Dimmers are used in many modern homes to provide energy efficiency and create adjustable lighting levels.
Switch Configurations
A table detailing various switch configurations and their applications can further illuminate the different types of switches.
| Switch Type | Description | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| SPST | Controls a single circuit | Simple light switches |
| SPDT | Routes current to one of two circuits | Two-way lighting control |
| Three-Way | Controls a single light from two locations | Stairways, hallways |
| Four-Way | Controls a single light from multiple locations | Larger rooms, hallways |
| Dimmer | Controls the brightness of a light | Living rooms, kitchens |
Types of Electrical Switches
Electrical switches are fundamental components in any home’s electrical system. They provide a controlled and safe way to turn lights and other appliances on and off. Understanding the different types of switches allows for efficient and customized lighting control within a home, whether it’s for a simple single fixture or a more complex multi-switch arrangement.Different switch types cater to diverse lighting needs.
Knowing how each type works, and how it’s wired into the circuit, is key to ensuring proper function and safety.
Single-Pole Switches
Single-pole switches are the most basic type. They control a single light fixture from a single location. This is the simplest and most common type of switch, frequently used for individual lamps or small light clusters.
Single-pole switches are straightforward to install and are generally cost-effective. They are directly wired to the light fixture and the electrical supply. The switch itself interrupts the current flow, allowing the light to turn on or off at the location of the switch. This simple arrangement makes single-pole switches ideal for most standard light fixtures in a house.
Three-Way Switches
Three-way switches allow control of a single light fixture from two different locations. This is useful for hallways, stairwells, or rooms with multiple entry points.
Three-way switches work by forming a circuit with two switches. Each switch has two terminals, and these switches are connected in a series configuration. One switch controls the other. When one switch is flipped, the circuit is completed, and the light turns on. Flipping the other switch disrupts the circuit and turns the light off.
Ever wondered about the different types of electrical switches in your home? From simple toggle switches to more advanced dimmer switches, they all serve a purpose. Choosing the right switch can make a huge difference in your home’s functionality. Speaking of functionality, you might also be curious about the nuances of different wall repair solutions, such as understanding the difference between joint compound and spackle.
Learning about these options is helpful in getting a smooth finish when patching or repairing walls. For a deep dive into the world of joint compound vs spackle, check out this helpful guide: joint compound vs spackle. Ultimately, understanding your electrical switches is just as important as knowing your wall repair options. Different switch types offer different levels of control and style.
This allows the light to be controlled from either switch location.
Four-Way Switches
Four-way switches are used to control a single light fixture from three or more locations. They are commonly found in long hallways, stairwells, or areas requiring extensive light control from multiple points.
Four-way switches are part of a more complex circuit than three-way switches. They work by connecting the load (the light fixture) to a three-way switch. The three-way switch then connects to two four-way switches, which connect to the electrical supply and to each other. This allows a more intricate system where flipping a switch in one location can affect the light in multiple locations.
Comparison of Switch Types
| Switch Type | Application | Circuit Connection | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-pole | Single light fixture | One switch controls one light | Simple, inexpensive |
| Three-way | Two switches control one light | Two switches control a single circuit | Flexibility in location of switches |
| Four-way | Three or more switches control one light | Complex circuit with multiple control points | Flexibility in switch locations |
Examples of Switch Usage
In a long hallway, three-way switches allow you to turn the light on or off from either end of the hallway. A four-way switch system could be used to control the light in a larger area with multiple entrances, such as a long staircase or a wide hallway with multiple doorways. Single-pole switches are commonly found in individual rooms, controlling a single light fixture from a single switch.
Switch Mechanisms and Materials
Electrical switches are more than just simple on/off toggles. Their internal mechanisms and the materials used in their construction directly impact their performance, safety, and longevity. Understanding these components is crucial for appreciating the complexity behind a seemingly simple action. Different switch types employ various mechanisms to achieve their function, and the materials selected significantly influence their durability and operational characteristics.The choice of materials in electrical switches is paramount.
Factors such as conductivity, insulation, and resistance to wear and tear play a critical role in determining the switch’s overall reliability. The selection of suitable materials is vital to ensure the switch’s ability to handle the electrical load and prevent potential hazards.
Internal Switch Mechanisms
The internal mechanisms of switches vary significantly depending on the type of switch. A simple toggle switch uses a mechanical lever to make and break contact between two electrical conductors. More sophisticated switches, such as rotary switches, employ rotating mechanisms to connect different electrical circuits. A key feature of many switch designs is their ability to quickly and reliably interrupt electrical current without causing damage or sparks.
The design of the contact points is critical in ensuring smooth operation and preventing arcing.
Knowing the different types of electrical switches in your home is handy, but before you start replacing anything, it’s crucial to identify if a wall is a load-bearing wall. This is essential to avoid any structural issues, which could potentially compromise the safety of your home. Understanding how to determine load-bearing wall determining load bearing wall is a vital step.
Once you’ve identified your load-bearing walls, you can confidently proceed with choosing the best electrical switches for your needs, ensuring both functionality and safety in your home’s electrical setup.
Switch Materials and Their Properties
The materials used in switch construction play a crucial role in determining the switch’s overall performance. Key properties include conductivity, insulation, strength, and resistance to corrosion. The selection of materials must balance these properties to ensure the switch’s durability, safety, and efficient operation. Material properties are essential to ensure that the switch can withstand the expected operating conditions, including temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress.
Common Materials in Electrical Switches
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal (e.g., copper, brass) | Excellent conductivity, high durability, and strength | Susceptibility to corrosion, can be heavy | Switch contacts, frames, and springs |
| Plastic (e.g., polycarbonate, nylon) | Excellent insulation properties, lightweight, and relatively inexpensive | Lower durability compared to metal, can be brittle in some cases | Switch housings, covers, and insulation components |
| Ceramics (e.g., alumina) | High thermal stability, excellent dielectric strength, and resistance to chemical attack | Can be brittle, may be more expensive than other materials | Insulating components in high-temperature applications |
| Silver | Extremely high conductivity, low contact resistance | High cost, prone to tarnishing | High-current switches, where minimizing resistance is critical |
The table above highlights the diverse materials employed in electrical switches and their respective advantages and disadvantages. The choice of material depends on the specific application and the desired performance characteristics. For example, high-conductivity materials are crucial in switches designed for high-current applications, while insulating materials are essential for preventing electrical shocks.
Smart Switches and Their Functionality
Smart switches are revolutionizing home electrical systems, offering a seamless blend of convenience, energy efficiency, and home automation. They go beyond the traditional on/off functionality, enabling users to control lights, appliances, and even entire rooms from anywhere, anytime. This increased control, combined with sophisticated features, makes managing and optimizing energy use much more manageable.Smart switches integrate seamlessly with home automation systems, creating a unified platform for controlling various aspects of the home.
Ever wondered about the different types of electrical switches in your home? From simple toggle switches to more sophisticated dimmer switches, each has its own function. Thinking about growing your own pineapple at home? Learning about the various types of electrical switches can help you understand the different electrical systems in your house and how they work.
And if you’re looking to grow a pineapple, how long to grow pineapple depends on several factors, but you’ll likely need a bit more than just a switch to get your own fruit-bearing plant. Ultimately, knowing your home’s electrical setup will help you make the right choices for your home improvement projects.
They allow users to automate tasks, such as turning lights on and off at specific times, or adjusting the temperature based on occupancy. This interconnectedness empowers users to optimize their home’s functionality and create a more responsive living environment.
Remote Control Capabilities
Smart switches enable remote control through various platforms. Users can utilize mobile applications, web interfaces, or voice assistants to operate switches from their smartphones, tablets, or computers, regardless of their location. This remote access enhances convenience, particularly for situations like forgetting to turn off lights before leaving home or adjusting lighting settings from a different room.
Energy Efficiency Enhancements
Smart switches contribute to energy efficiency by enabling users to monitor and manage their energy consumption. They provide detailed data on energy usage, helping identify areas for improvement and implement more energy-conscious habits. For example, a smart switch can be programmed to automatically turn off lights in unoccupied rooms, reducing energy waste. Real-time feedback and insights help users understand and modify their energy consumption patterns.
Integration with Voice Assistants
Smart switches often integrate with popular voice assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant. This integration allows users to control lights, appliances, and other connected devices using voice commands. Users can say “Turn on the living room lights” or “Dim the kitchen lights” to achieve the desired outcome without needing to physically interact with a switch. This voice control simplifies interactions, especially for users with limited mobility or those who prefer hands-free control.
Key Features of Smart Switches, Types of electrical switches in the home
- Remote Control: Smart switches allow users to control lights and appliances from anywhere via mobile apps or web interfaces. This eliminates the need to physically approach the switch, providing flexibility and convenience, such as remotely controlling lights while away from home or adjusting settings from a different room.
- Scheduling: Users can schedule lights and appliances to turn on or off at predetermined times. This is useful for tasks like automating morning wake-up lights or ensuring that lights are turned off when leaving for work or bed.
- Energy Monitoring: Many smart switches provide detailed energy usage data, enabling users to track their consumption patterns and identify areas where they can reduce energy waste. Visualizations and reports allow users to pinpoint high-consumption periods and adjust usage accordingly.
- Integration with Home Automation Systems: Smart switches can integrate with broader home automation systems, enabling seamless control of various devices and creating a more interconnected and automated home environment. Users can create customized routines and automation tasks, such as adjusting lighting based on the time of day or the presence of people in the home.
Safety Considerations with Electrical Switches
Electrical switches, while seemingly simple, are crucial components in any electrical system. Their proper function and installation are paramount to ensuring safety within a home or workplace. Neglecting safety precautions can lead to electrical shocks, fires, and other potentially serious incidents. This section emphasizes the importance of safe practices when handling and maintaining electrical switches.Proper installation and maintenance are critical for minimizing risks.
Faulty switches can lead to electrical hazards, and even seemingly minor issues can escalate into major problems if not addressed promptly. Understanding potential hazards and implementing safe procedures are vital for preventing accidents and protecting individuals.
Potential Hazards Associated with Electrical Switches
Electrical switches, when improperly installed or maintained, can pose several hazards. These include electrical shocks, fire hazards, and potential injuries from falling objects or damaged components. Overheating, caused by faulty wiring or excessive current, is a serious risk that can lead to fires. Loose connections and exposed wires create opportunities for short circuits and electrical shocks.
Importance of Proper Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation of electrical switches is crucial for safety. A qualified electrician should always handle installations, ensuring that all wiring is correctly connected, insulated, and grounded. Regular maintenance, including visual inspections for damage or wear, is equally important. Addressing issues like loose connections or damaged insulation promptly can prevent potential accidents.
Safety Procedures for Troubleshooting Faulty Switches
When troubleshooting faulty switches, safety should be the top priority. Never attempt repairs without de-energizing the circuit. Consult an electrician for any complex issues or if you are unsure about the appropriate steps. Proper isolation techniques, such as using insulated tools and working in a well-lit area, should be followed. Always disconnect the power supply before performing any maintenance.
Importance of Using the Correct Tools and Techniques
Using the correct tools and following safe techniques when working with electrical switches is critical. Using insulated tools prevents accidental contact with live wires, minimizing the risk of electrical shocks. Proper grounding procedures ensure that any stray electrical current is safely directed to the ground. Carefully examining the wiring and switch mechanism for any damage or wear is essential before starting any repair work.
Safety Precautions When Working with Electrical Switches
- Always de-energize the circuit before any work is performed. Use a voltage tester to ensure the circuit is completely off.
- Use insulated tools and gloves to prevent electrical shocks. Ensure all tools are in good working order.
- Work in a well-lit area to minimize the risk of tripping or falling. Use proper lighting and ensure the workspace is free of obstructions.
- Never work alone when handling electrical work. A second person can provide assistance and act as a safety observer.
- If any part of the electrical switch or wiring is damaged, immediately disconnect the power and contact a qualified electrician. Do not attempt repairs if you are unsure about the procedure.
- Be mindful of potential hazards, such as exposed wires, loose connections, or damaged insulation. Report any potential hazards to a supervisor or other appropriate personnel.
- Follow all local electrical codes and regulations when working with electrical switches.
Troubleshooting Electrical Switches: Types Of Electrical Switches In The Home
Electrical switches, a fundamental part of any home’s electrical system, can sometimes malfunction. Understanding the common problems and troubleshooting techniques can save you time and money, preventing potentially hazardous situations. This section will detail various switch problems, provide diagnostic steps, and emphasize when professional help is necessary.
Common Electrical Switch Problems
Several issues can arise with electrical switches, ranging from simple loose connections to more complex internal component failures. Identifying these problems is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Common problems include:
- Light not working: A simple switch malfunction can lead to a non-functioning light. This could stem from a faulty switch, a loose connection, or a problem in the wiring itself.
- Flickering lights: Intermittent light output often indicates a loose connection or a problem with the switch’s internal components. This can be caused by corroded wires or a failing switch mechanism.
- Switch not turning on/off: A switch that fails to operate as intended could be due to a variety of factors. This could range from a simple obstruction to a more serious issue, like a damaged switch or a problem in the circuit.
- Strange noises: Unusual noises emanating from the switch, such as grinding or popping sounds, can signal a mechanical problem within the switch mechanism.
- Burning smell: A burning smell emanating from a switch is a significant indicator of a potential electrical hazard. This typically points to an overload or a short circuit, and immediate action is required.
Troubleshooting Techniques for Switch Issues
Troubleshooting electrical switches requires a methodical approach. Safety precautions are paramount. Before beginning any work, ensure the power to the circuit is off at the breaker box.
- Visual Inspection: Thoroughly inspect the switch for any visible damage, loose wires, or unusual signs. Look for signs of burning or overheating. Ensure all connections are tight and secure. If loose connections are present, tightening them could resolve the issue.
- Checking Connections: Verify all wire connections at the switch are secure and properly soldered or crimped. Loose connections are a frequent cause of intermittent problems. Inspect for signs of corrosion on the terminals. Clean connections with a wire brush or sandpaper if needed.
- Testing the Switch: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the switch. This will confirm the switch itself is operating correctly. Ensure the multimeter is set to the correct range for testing electrical components.
- Circuit Breaker Check: If a switch is causing the circuit breaker to trip repeatedly, the problem may be with the switch or the circuit itself. Ensure the breaker is rated correctly for the load and that there are no overloaded circuits. Checking the amperage rating of the switch and the load it’s intended to handle is critical.
Diagnosing and Fixing Common Switch Malfunctions
A methodical approach to diagnosing and fixing switch malfunctions can save time and prevent further damage.
- Light not working: If a light is not working, first ensure the power is off at the breaker. Visually inspect the switch for any visible issues. Check the connections at the switch and at the light fixture. If the connections are secure and the switch appears normal, replace the switch.
- Flickering lights: Flickering lights often indicate a loose connection. Verify all connections are tight and secure. If the problem persists, check for corroded wires and clean them if necessary. Consider replacing the switch if the problem persists.
Importance of Seeking Professional Help
While many switch problems can be tackled by homeowners with basic electrical knowledge, some situations require professional intervention. If you encounter burning smells, electrical shocks, or if you feel uncomfortable working with electricity, immediately contact a qualified electrician. Their expertise can prevent further damage and ensure your safety.
Troubleshooting Steps for Different Switch Problems
| Problem | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light not working | Faulty switch, loose connection, blown fuse/ tripped breaker | Check switch, verify connections, check breaker box for tripped breakers or blown fuses | Replace switch, tighten connections, reset breaker/replace fuse |
| Flickering lights | Loose connection, damaged switch, poor wiring | Check connections, inspect switch for damage, check for exposed wires | Tighten connections, replace switch, repair or replace wiring |
| Switch not turning on/off | Obstruction, damaged switch mechanism, loose connections | Remove any obstructions, inspect switch for damage, check wire connections | Remove obstruction, replace switch, tighten connections |
Closure
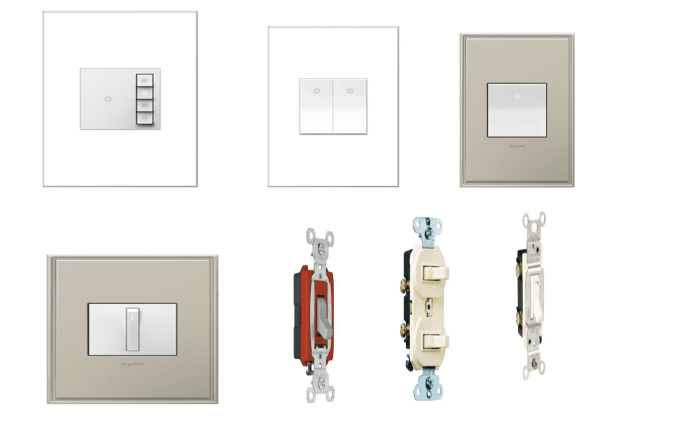
In conclusion, understanding the different types of electrical switches in the home is essential for both safety and efficient use of electricity. From the fundamental single-pole switch to the more complex smart switches, each serves a specific purpose. Knowing how they work, how to install them safely, and how to troubleshoot potential issues is crucial for any homeowner. This exploration of switch mechanisms, materials, and safety considerations provides a comprehensive understanding of this often-overlooked aspect of home electrical systems.