How to grow and care for aluminum plant? This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of these captivating indoor plants. From understanding their unique needs to mastering propagation techniques, we’ll explore everything you need to cultivate a thriving aluminum plant. We’ll also discuss the different varieties, light requirements, watering schedules, and more, ensuring your plant thrives in your home or office.
Discover the secrets to keeping your aluminum plant healthy and happy. Learn about ideal soil composition, fertilization strategies, and how to identify and address common pests or diseases. With this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to nurture your aluminum plant into a beautiful, vibrant specimen.
Introduction to Aluminum Plants
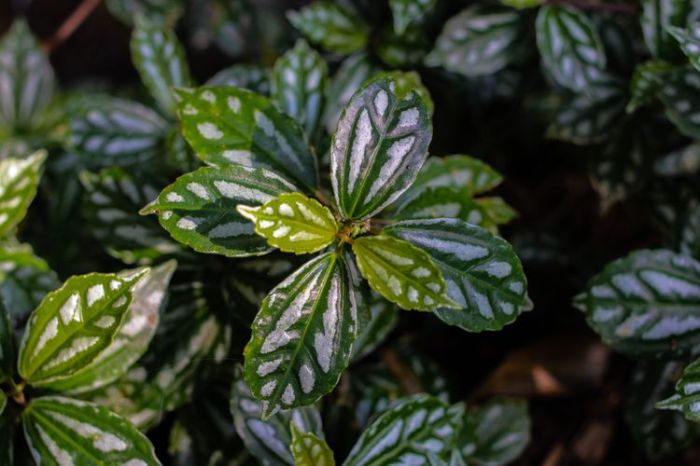
Aluminum plants, often mistaken for a specific species, are actually a group of plants with similar care requirements and aesthetic appeal. These popular houseplants, known for their striking foliage, offer a touch of tropical elegance to any indoor space. While the name might suggest a connection to aluminum, there’s no such direct correlation. Their name likely stems from their characteristic, silvery-grey, or sometimes bronze, leaves.
The appeal of these plants lies in their ability to thrive in various indoor environments, despite their unique needs.These plants aren’t demanding, but they do require specific care to maintain their vibrant beauty. Understanding their origins and unique characteristics is key to successfully nurturing these captivating plants. Different varieties within this group exhibit variations in size, leaf shape, and growth patterns.
Aluminum plants are surprisingly low-maintenance, thriving in bright, indirect light and well-draining soil. One common pest problem, though, is clover mites, which can wreak havoc on your foliage. To ensure your aluminum plant stays healthy and vibrant, regularly inspect your plant and if you find clover mites, be sure to check out this guide on get rid of clover mites.
By addressing these tiny critters, you can focus on nurturing the plant’s beautiful silvery foliage and enjoy its unique beauty in your home or garden.
Their resilience and adaptability to indoor conditions make them a rewarding choice for plant enthusiasts.
Origins and Popular Varieties
Aluminum plants, despite their name, encompass a range of species and cultivars. They are not a single, defined species but rather a collection of plants grouped together due to similar characteristics and care needs. Their origins lie in tropical and subtropical regions of the world, where they have evolved to thrive in humid environments. Commonly grown varieties often include those with deep green foliage and others with silvery-grey leaves, offering a spectrum of aesthetic options.
Unique Characteristics and Care Requirements
Aluminum plants, in contrast to many other common houseplants, prefer indirect, bright light rather than direct sunlight. Overexposure to direct sunlight can scorch their delicate leaves. Maintaining a consistent humidity level is also crucial for their well-being, as they are sensitive to dry air. Proper watering practices, avoiding both underwatering and overwatering, are essential to prevent root rot and leaf problems.
The soil’s composition should be well-draining to prevent waterlogging.
Symbolism and Cultural Significance
While aluminum plants haven’t garnered significant symbolism or cultural significance in most cultures, they’re appreciated for their visual appeal and relative ease of care, making them popular choices for home decor. Their ability to thrive in various indoor settings makes them a practical addition to any space.
Comparative Analysis of Aluminum Plant Types
| Plant Type | Light Requirements | Watering Frequency | Soil Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silver Aluminum Plant | Bright, indirect light | Water thoroughly when the top inch of soil is dry | Well-draining potting mix with perlite or coarse sand |
| Bronze Aluminum Plant | Bright, indirect light | Water when the top inch of soil is dry | Well-draining potting mix with peat moss or vermiculite |
The table above provides a concise comparison of common aluminum plant types, highlighting their similar yet distinct needs. Each type benefits from a well-draining soil mix that prevents waterlogging and ensures optimal root health. Consistent watering, according to the soil’s dryness, is essential for maintaining a healthy plant.
Light Requirements
Aluminum plants, despite their striking appearance, are surprisingly adaptable to various light conditions. Understanding their light preferences is crucial for maintaining their health and vibrant foliage. Providing the right amount and type of light will encourage robust growth and prevent common issues like leaf discoloration or stunted development.Optimal light conditions for aluminum plants are crucial for their overall well-being.
These plants thrive in bright, indirect light, which allows for healthy photosynthesis and prevents the intense sun damage that can lead to leaf burn. Mimicking their natural environment in a home or office setting is key to keeping these plants looking their best.
Optimal Light Conditions
Aluminum plants appreciate bright, indirect light. Direct sunlight, while providing energy, can lead to scorching and leaf damage. They are particularly sensitive to the intense midday sun, which can cause unsightly browning or wilting. Think of a location near a window that receives morning or afternoon sun, but not the harsh midday rays. An east-facing window or a location filtered by sheer curtains or blinds would be ideal.
Suitable Locations
A few examples of suitable locations for aluminum plants within a home or office environment include:
- East-facing windows, where morning sun filters through the glass.
- West-facing windows, provided the sun is diffused by curtains or blinds.
- South-facing windows, but with careful placement to avoid intense midday sun. Use sheer curtains to diffuse the light.
- Locations near a bright skylight or a large window that provides plenty of indirect light.
- Indoor grow lights can be used as an alternative to natural light, but the intensity should be adjusted to avoid burning the leaves.
Effects of Inadequate and Excessive Light
Insufficient light can lead to pale, yellowish leaves, stunted growth, and a general decline in the plant’s overall health. The plant may also lose its vibrant color, becoming dull and less appealing. Conversely, excessive light, particularly direct sunlight, can cause leaf burn, leading to brown spots or crispy edges on the leaves. Over time, this can severely damage the plant, potentially leading to its death.
Understanding these effects and providing the appropriate light conditions is crucial for maintaining the plant’s beauty and vitality.
Light Condition Comparison
The table below summarizes the effects of different light conditions on aluminum plants.
| Light Condition | Effect on Plant | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Low Light | Pale, yellowish leaves, stunted growth, loss of vibrant color. | Move the plant to a location with more indirect light or consider using grow lights. |
| Bright, Indirect Light | Healthy growth, vibrant foliage, optimal leaf color. | Maintain the plant in a location that receives this type of light. |
| Direct Sunlight (intense midday sun) | Leaf burn, brown spots, crispy leaf edges, potential for wilting. | Move the plant to a location with less intense or indirect light. |
Watering Techniques: How To Grow And Care For Aluminum Plant
Aluminum plants, despite their striking beauty, are quite sensitive to watering. Understanding the nuances of watering is crucial for their health and longevity. Consistent, appropriate watering prevents both overwatering and underwatering, which can lead to problems like root rot or wilting. Proper watering also ensures the plant receives the right nutrients and moisture to thrive.Watering frequency depends on various factors.
A plant in a small pot will need more frequent watering than one in a larger container. The type of soil also influences how quickly it dries out. Additionally, environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, play a significant role.
Watering Schedule
Determining the right watering schedule is essential for the well-being of your aluminum plant. Consider the size of the pot, the type of soil, and the surrounding environment. A general guideline is to water when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. Larger pots will require more frequent watering than smaller ones, as the soil will take longer to dry out completely.
Similarly, sandy soils drain more quickly than clay soils, requiring more frequent watering. Observe your plant; if it appears wilted or droopy, it might be time to water it. Conversely, if the leaves appear to be yellowing or have brown tips, it might be a sign of overwatering or underwatering.
Signs of Overwatering and Underwatering, How to grow and care for aluminum plant
Overwatering is a common problem that can lead to root rot and ultimately kill your aluminum plant. Look for signs like yellowing leaves, mushy stems, or a foul odor emanating from the soil. Underwatering, on the other hand, can cause the leaves to wilt and become crispy. The soil will feel extremely dry and the plant may appear dehydrated.
Recognizing these signs early can help you adjust your watering routine and prevent irreversible damage.
Importance of Water Type
The quality of water you use can significantly impact the health of your aluminum plant. Hard water, containing high levels of minerals, can accumulate in the soil and potentially harm the roots. Using distilled or filtered water is highly recommended for optimal plant health. These types of water lack the minerals that can build up in hard water and hinder the plant’s ability to absorb essential nutrients.
This will ensure that the plant gets the moisture it needs without any mineral build-up in the soil.
Caring for your aluminum plant is surprisingly straightforward! Just remember to avoid harsh chemicals, like those you’d find in some common outdoor furniture cleaning solutions. For example, check out this list of things things to never clean outdoor furniture with before tackling any cleaning jobs. This will help keep your aluminum plant thriving, and your other outdoor furniture looking its best.
Lots of sunlight and consistent watering will also help your aluminum plant flourish.
Watering Methods
Different watering methods can affect the plant’s health. Choosing the right method for your aluminum plant will contribute to its well-being.
Aluminum plants are surprisingly low-maintenance, thriving on bright, indirect light and infrequent watering. Knowing how to properly care for them can prevent issues, just like understanding the common reasons why you always strip screws when tightening them – often due to using the wrong tool or over-tightening. A good understanding of the appropriate torque and tool type can significantly reduce screw-stripping incidents.
This knowledge also translates to proper plant care, ensuring a healthy, thriving aluminum plant. For more on the frustrating issue of stripped screws, check out this helpful guide: why you always strip screws. Ultimately, both require a delicate touch and attention to detail for optimal results.
| Watering Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soaking | Ensures thorough watering of the entire root ball; allows water to reach the deeper roots. | Can be time-consuming, especially for larger pots. May lead to waterlogging if not done correctly. | Excellent for established aluminum plants in larger pots. |
| Top Watering | Simple and quick; easy to monitor the water absorption. | May not thoroughly water the entire root ball; water may run off without reaching the roots. | Suitable for smaller pots and newly established plants. |
| Bottom Watering | Minimizes water runoff; prevents leaf spotting; helps maintain a more consistent moisture level. | Requires a dedicated pot with a drainage hole; can be more time-consuming in some situations. | Good for aluminum plants with delicate leaves. |
Soil and Potting Mix

Aluminum plants, with their delicate beauty, thrive in specific soil conditions. Proper soil selection and potting mix are crucial for their health and longevity. A well-draining and aerated medium is key to preventing root rot, a common issue for these plants. Choosing the right potting mix and pot size ensures the plant has the support it needs to flourish.Aluminum plants appreciate a loose, well-draining potting mix that allows air to circulate around their roots.
This promotes healthy root growth and prevents the build-up of excess moisture, which can lead to root rot. The ideal soil composition should be balanced, providing adequate nutrients while maintaining optimal drainage and aeration.
Ideal Soil Composition
Aluminum plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral soil pH. The soil should be rich in organic matter, which improves drainage and water retention. A good balance between these two elements is essential for healthy growth.
Ingredients for a Homemade Potting Mix
Creating a custom potting mix allows for precise control over the soil’s composition. This approach allows you to tailor the mix to the specific needs of your aluminum plant.
- Perlite: This volcanic glass provides excellent drainage and aeration, preventing waterlogging. It helps create a loose, porous structure that encourages healthy root development.
- Coco Coir: Derived from coconut husks, this natural fiber retains moisture while also providing excellent drainage. It is a sustainable alternative to peat moss.
- Potting Soil: A standard potting mix provides essential nutrients. Choose a mix formulated for indoor plants, as it is more likely to have the appropriate balance of nutrients.
- Worm Castings: These castings are a rich source of nutrients and beneficial microbes. They improve the soil structure, promote healthy root growth, and help the plant absorb essential nutrients more effectively.
Choosing the Right Pot Size
The pot size directly impacts the plant’s growth and health. A pot that is too small will restrict root growth, while a pot that is too large can lead to waterlogging. The pot should be just large enough to accommodate the plant’s root system, allowing for future growth. Over time, the plant’s root system will expand and require a larger pot to prevent it from becoming root-bound.
Comparison of Potting Mix Types
Different potting mixes have varying effects on plant health. A mix with excellent drainage is essential for aluminum plants to avoid root rot. A good balance between water retention and drainage is critical for their overall health and growth.
- Commercial Potting Mixes: These mixes often contain peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite. The balance of these ingredients varies between brands, so it’s important to choose a mix designed for indoor plants.
- Homemade Potting Mixes: These mixes allow you to precisely control the proportions of ingredients, ensuring optimal drainage and aeration. They can be tailored to the specific needs of your aluminum plant.
Ideal Potting Mix Components
A well-balanced potting mix is crucial for the success of aluminum plants. The right composition supports healthy root growth and prevents issues like overwatering or underwatering.
| Component | Role | Amount (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Perlite | Excellent drainage and aeration | 25% |
| Coco Coir | Moisture retention and drainage | 50% |
| Potting Soil | Essential nutrients | 20% |
| Worm Castings | Nutrient boost and soil structure | 5% |
Fertilizing Aluminum Plants
Aluminum plants, despite their resilience, benefit from regular fertilization. Proper feeding encourages robust growth, vibrant foliage, and overall plant health. Nutrients are essential for chlorophyll production, which is vital for photosynthesis, the plant’s primary food source.Aluminum plants thrive in a well-balanced nutrient environment, and feeding them the correct nutrients at the right time will result in healthy and happy plants.
A lack of essential nutrients can lead to stunted growth, pale leaves, and a weakened overall plant structure. Therefore, understanding the importance of fertilization is key to successful aluminum plant care.
Importance of Fertilizing
Aluminum plants require supplemental nutrients to maintain optimal growth and health. Without regular fertilization, plants may struggle to produce enough energy for healthy growth, flowering, and overall vitality. Fertilizers provide essential macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and micronutrients such as iron, zinc, and manganese, that support vital metabolic processes.
Appropriate Fertilizer Types
Choosing the right fertilizer is crucial for aluminum plants. A balanced, water-soluble fertilizer formulated for houseplants is ideal. These fertilizers often come in liquid form, making them easy to dilute and apply to the soil. Avoid using fertilizers high in nitrogen, as this can promote excessive leaf growth at the expense of root development.
Best Time to Fertilize
The optimal time to fertilize aluminum plants is during the growing season, typically spring and summer. These periods correspond to the plant’s increased metabolic activity, when they require more nutrients to support their growth and development. During the dormant period, typically fall and winter, reduced fertilization is necessary to prevent nutrient buildup and potential damage.
Risks of Over-Fertilizing
Over-fertilizing can have detrimental effects on aluminum plants. A high concentration of nutrients can lead to nutrient burn, manifesting as leaf discoloration, browning, or even leaf drop. Excess fertilizer can also disrupt the delicate balance of the soil’s microbial ecosystem, negatively impacting the plant’s ability to absorb nutrients effectively. Over-fertilization can also result in the accumulation of salts in the soil, hindering the plant’s water uptake.
It is crucial to adhere to the recommended fertilizer application rates to avoid these negative consequences.
Fertilizer Application Table
| Fertilizer Type | Benefits | Application Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Balanced Water-Soluble Fertilizer | Provides a comprehensive blend of essential nutrients. | Every 2-4 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer). Reduce to every 6-8 weeks during fall and winter. |
| Liquid Houseplant Fertilizer | Easy to dilute and apply; readily available in most garden centers. | Follow manufacturer instructions for dilution and application rates. |
| Organic Fertilizers (e.g., compost tea, fish emulsion) | Provides slow-release nutrients and improves soil health. | Every 4-6 weeks during the growing season. |
Propagation Methods
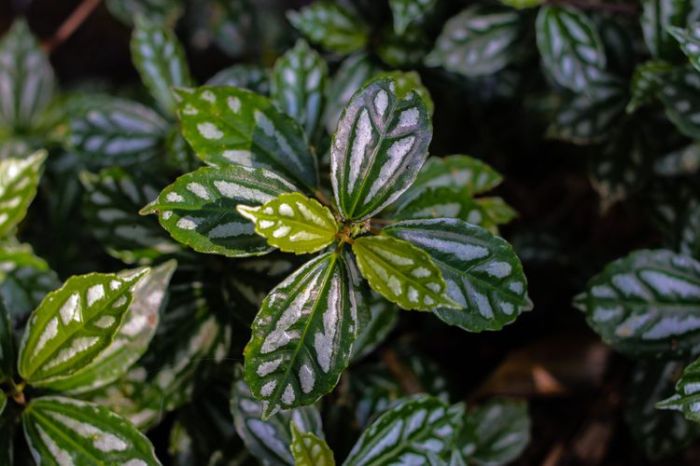

Aluminum plants, though beautiful, can be challenging to propagate. Understanding the different methods and their specific steps is crucial for successful propagation and expanding your collection. Different methods offer varying success rates, so choosing the right approach is key to growing more of these unique plants.Propagating aluminum plants allows you to create new plants from existing ones, expanding your collection and sharing the joy of these striking plants with others.
The methods described below provide detailed instructions to guide you through the process.
Cuttings
Cuttings are a common and relatively straightforward method for propagating aluminum plants. They involve taking a piece of the plant and encouraging it to develop roots and grow into a new individual.
- Selecting the Right Cutting Material: Choose a healthy, actively growing stem section. Avoid stems that are overly mature or show signs of disease. The cutting should be approximately 4-6 inches long, and have at least 2-3 nodes (where leaves attach to the stem). This ensures sufficient growing points for root development. Using sharp, clean pruning shears or a knife is essential to prevent the spread of disease and ensure a clean cut.
- Preparing the Cutting: Remove the lower leaves from the cutting, leaving only a few leaves at the top. This helps prevent rot and allows for better rooting. The exposed stem should be treated with a rooting hormone. This hormone encourages the growth of roots, significantly increasing the chances of successful propagation. Rooting hormone can be purchased at most garden centers.
- Planting the Cutting: Plant the cutting in a well-draining potting mix specifically designed for rooting cuttings. A mix of perlite and peat moss, or a commercial rooting mix, works well. Firmly press the cutting into the mix, ensuring it’s planted at the appropriate depth. Water the cutting thoroughly and keep the soil moist but not waterlogged. Maintain a humid environment by placing the pot inside a clear plastic bag or humidity dome.
- Maintaining the Cutting: Place the pot in a warm, well-lit location, but out of direct sunlight. Consistent humidity is essential during the rooting process. Check the soil moisture regularly and water as needed, keeping the soil consistently moist but not overly saturated. You can expect roots to develop in a few weeks to a few months, depending on the variety and environmental conditions.
Gradually increase the air circulation around the cutting to help it acclimate to the environment.
Division
Dividing is another common method for propagating aluminum plants. This technique is often successful with mature plants that have developed multiple stems or clumps.
- Preparing the Plant: Carefully remove the plant from its pot. Gently loosen the soil around the roots to separate the plant into individual sections. Ensure each section has a healthy portion of roots.
- Repotting: Repot each division into its own pot containing fresh, well-draining potting mix. Water thoroughly and maintain consistent moisture until the plants establish themselves. Provide appropriate light and care conditions to support their growth.
Seeds
Although less common, aluminum plants can be propagated through seeds. This method often takes longer and requires careful attention to detail.
- Seed Collection: Collect seeds from mature, healthy aluminum plants. Allow the seeds to dry completely before storing them in a cool, dark, and dry place.
- Seed Starting: Sow seeds in a well-draining seed-starting mix. Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Cover the container with plastic wrap to maintain humidity. Place the container in a warm, well-lit location.
- Seedling Care: Once seedlings emerge, gradually acclimate them to the surrounding environment. Provide appropriate light and care conditions to support their growth.
Common Pests and Diseases
Aluminum plants, despite their resilience, are susceptible to various pests and diseases. Understanding these potential issues and how to address them proactively is crucial for maintaining healthy and thriving plants. Proper identification and swift action are key to preventing widespread damage and ensuring the long-term health of your aluminum plant.Aluminum plants are often grown in relatively humid environments.
This can create ideal conditions for certain pests and fungal diseases to flourish. Recognizing the signs of infestation or disease early is critical, as timely intervention can prevent the problem from escalating and potentially harming the plant.
Identifying Pests
Aluminum plants can attract several common houseplant pests. Early detection is essential to preventing widespread infestations.
- Spider mites: These tiny arachnids create fine webbing, often visible on the leaves and stems. Leaves may appear yellowed or mottled. Severe infestations can cause leaf drop.
- Mealybugs: These pests appear as small, white, cottony masses on the leaves, stems, and roots. Mealybugs feed on the plant’s sap, causing stunted growth and leaf discoloration.
- Scale insects: Scale insects are tiny, immobile pests that appear as raised bumps or shields on the leaves or stems. They often secrete a honeydew substance that attracts ants and can lead to sooty mold.
- Aphids: Aphids are small, soft-bodied insects that feed on plant sap. They can appear in clusters on leaves, causing yellowing and distortion.
Recognizing Diseases
Several fungal diseases can affect aluminum plants, particularly in humid environments.
- Root rot: Overwatering or poor drainage can lead to root rot, causing the roots to become mushy and dark brown. Affected plants may exhibit wilting, yellowing leaves, and stunted growth.
- Leaf spot: Fungal leaf spot diseases manifest as spots on the leaves, ranging from small and circular to larger and irregular shapes. The spots can be dark brown, black, or yellow, and may have a distinct border. These diseases are often spread by splashing water.
- Powdery mildew: This fungal disease creates a white, powdery coating on the leaves, stems, and sometimes flowers. The affected leaves may also turn yellow and drop prematurely.
Prevention and Treatment Methods
Proper care is crucial in preventing pest and disease issues.
- Prevention: Regularly inspect your plant for signs of pests or diseases. Maintain good air circulation around the plant to prevent fungal issues. Ensure proper drainage to prevent root rot. Avoid overwatering.
- Treatment: For minor infestations, gently remove visible pests with a cotton swab dipped in rubbing alcohol. For more serious infestations, use insecticidal soap or neem oil, following the product instructions carefully. Fungal diseases may require fungicides. Always research and follow product labels carefully before using any treatment.
Comparison of Treatments
| Pest/Disease | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Spider mites | Fine webbing, yellowing/mottling leaves | Insecticidal soap, neem oil, or horticultural oil |
| Mealybugs | Cottony masses on leaves/stems | Rubbing alcohol, insecticidal soap, or neem oil |
| Root rot | Mushy, dark brown roots; wilting, yellowing leaves | Reduce watering, improve drainage, fungicides (if fungal) |
| Powdery mildew | White powdery coating on leaves | Fungicide spray, improving air circulation |
Troubleshooting
Aluminum plants, while generally low-maintenance, can sometimes present challenges. Understanding common problems and their solutions is crucial for maintaining healthy, thriving specimens. This section will delve into troubleshooting techniques, covering everything from leaf discoloration to stunted growth, providing actionable steps for successful aluminum plant care.
Identifying Leaf Discoloration
Leaf discoloration in aluminum plants can stem from various factors. A yellowish hue, for instance, could signify nutrient deficiencies, while brown spots or edges might point towards overwatering or underwatering. Identifying the specific type of discoloration and its pattern is key to pinpoint the root cause and implement the correct corrective measures.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Yellowing leaves, particularly interveinal chlorosis (yellowing between the leaf veins), often indicate a lack of essential nutrients like magnesium, iron, or nitrogen. Correcting this involves using a balanced fertilizer formulated for houseplants and adjusting watering practices to avoid nutrient leaching. Regular soil testing can help determine precise nutrient levels and guide fertilization strategies.
- Overwatering: Excessive watering can lead to root rot, resulting in brown or black leaf tips and overall leaf discoloration. The solution involves adjusting watering frequency, ensuring proper drainage in the pot, and repotting with fresh, well-draining soil if necessary.
- Underwatering: Insufficient watering can cause the leaves to become dry and brown. This issue is resolved by increasing the frequency and amount of waterings, ensuring the soil is consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Pests and Diseases: Certain pests and diseases can cause leaf discoloration as a symptom. For example, spider mites may leave tiny yellow or brown spots on the leaves, while fungal infections can cause browning or spotting. Treating any visible pest infestation with appropriate methods is essential. If the discoloration persists despite other interventions, consult a gardening professional for a definitive diagnosis.
Addressing Wilting Issues
Wilting in aluminum plants often signals a problem with watering or environmental conditions. A drooping plant may indicate inadequate watering, excessive heat, or insufficient humidity. Precise diagnosis is crucial to resolve the wilting effectively.
- Insufficient Watering: A wilting plant may simply need more water. Ensure the soil is consistently moist, but not waterlogged. Allow the top inch or two of soil to dry out between waterings, adjusting watering frequency according to the plant’s needs and the environment.
- Overwatering: Overwatering can also lead to wilting, as it causes root rot, depriving the plant of essential nutrients and water. Adjust watering schedule and ensure proper drainage.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to intense sunlight or excessively dry air can cause wilting. Adjust the plant’s location to a more shaded area, or increase humidity levels using a humidifier or pebble tray.
Troubleshooting Stunted Growth
Slow or stunted growth in aluminum plants can result from several factors. These include insufficient light, poor soil quality, nutrient deficiencies, or pests. A thorough evaluation of the plant’s environment and care practices is crucial to identify the underlying issue.
- Insufficient Light: Aluminum plants require bright, indirect light. If the plant is not receiving enough light, its growth will be hindered. Move the plant to a location with more indirect sunlight, or use grow lights to supplement the natural light.
- Poor Soil Quality: Poorly draining or nutrient-poor soil can impede root development and growth. Repot the plant in a well-draining potting mix to ensure optimal nutrient uptake and water drainage.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients can stunt growth. Use a balanced fertilizer formulated for houseplants, and adjust watering practices to prevent nutrient leaching.
- Pests and Diseases: Pest infestations or diseases can also lead to stunted growth. Identify and treat any visible pests or diseases promptly.
Last Word
In conclusion, cultivating a healthy aluminum plant requires understanding its specific needs and providing the right environment. By following the guidelines in this guide, you can successfully nurture your plant from seedling to thriving specimen. Remember, consistent care and attention to detail are key to achieving a lush, happy aluminum plant. We hope this guide empowers you to create a beautiful indoor oasis with your new aluminum plant.