When to pick tomatoes? This isn’t just about harvesting; it’s about maximizing flavor and ensuring your homegrown tomatoes are at their peak. From identifying the perfect ripeness cues to understanding the impact of environmental factors, this guide delves into everything you need to know about harvesting the tastiest tomatoes possible.
This comprehensive guide covers everything from visual cues and tactile sensations to understanding the nuances of different tomato varieties and the role of environmental conditions in their ripening. We’ll explore how sunlight, temperature, and humidity influence your harvest, and provide a detailed step-by-step approach to harvesting, including the best tools and techniques for minimizing damage to your plants.
Identifying Ripeness
Picking the perfect tomato involves more than just a quick glance. Understanding the nuances of ripeness ensures you’ll enjoy the sweetest, juiciest fruit. From the vibrant color to the satisfying firmness, there’s a whole symphony of cues that signal a tomato’s readiness for harvest. Knowing these signals is crucial for maximizing flavor and preventing disappointment.A ripe tomato is a sign of a successful garden or a well-stocked market.
Knowing when to pick your tomatoes is key, but maintaining your footwear is just as important. For example, if you’re harvesting ripe tomatoes, you need to make sure your gardening shoes are in tip-top condition, which is why knowing how to clean your shoes properly is crucial. Properly cleaned shoes help you keep your gardening gear in good shape, making it easier to know when to pick those perfect tomatoes.
Knowing the ideal ripeness and when to pick them is a satisfying feeling! how to clean your shoes is a great guide for any gardener.
The right ripeness, beyond simply avoiding overly green or overly soft tomatoes, unlocks the best taste and texture. The subtle differences in visual and tactile cues, along with the variety of tomato types, all contribute to the perfect picking experience.
Visual Cues for Ripeness
Visual assessment is the first and most common method for determining tomato ripeness. Different varieties exhibit different color changes as they mature. Paying attention to the interplay of color, firmness, and stem characteristics is key to making the right selection.
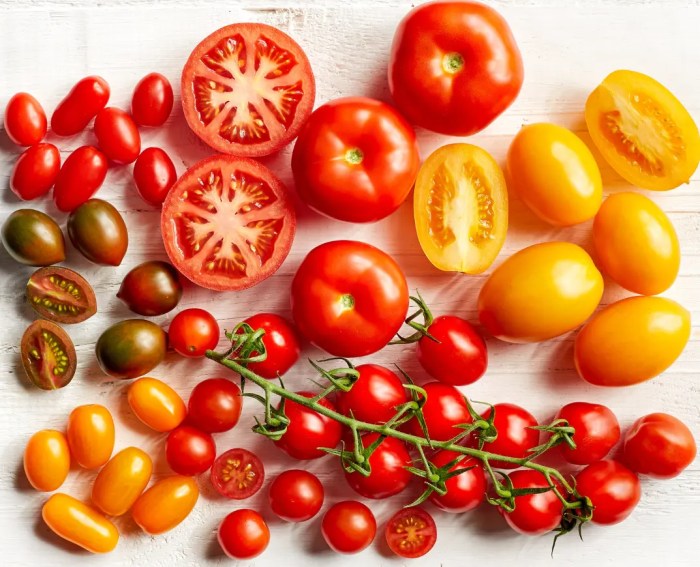
- Color Variation: Tomatoes, in general, change color as they mature. A common indicator is a shift from green to a deeper red, orange, or yellow, depending on the variety. For example, beefsteak tomatoes typically progress through a spectrum of green, then a rosy red, to a deep red, and finally, a slightly darker red. Cherry tomatoes often transition from green to a vibrant red.
Identifying these stages is crucial for picking at the optimal time.
- Firmness: A ripe tomato should exhibit a satisfying firmness. Avoid those that feel overly soft or mushy, as these likely have gone past their peak. Conversely, a tomato that’s too hard suggests it still needs more time to mature. Using gentle pressure to test the tomato’s firmness is important in the process.
- Stem Attachment: The stem’s attachment is another indicator of ripeness. A firm attachment, which resists pulling, often signals a tomato that’s ready. A loose stem may indicate the tomato is overripe, while a stem that’s too tightly attached might mean it’s still underripe. This detail can offer a quick assessment to distinguish between underripe, ripe, and overripe tomatoes.
Tactile Assessment of Ripeness
Beyond visual cues, the feel of the tomato plays a vital role in determining its ripeness. Gentle pressure provides valuable information about the tomato’s internal structure and ripeness.
- Texture: A ripe tomato should yield slightly to gentle pressure, but not feel mushy or overly soft. A proper texture usually indicates a balanced internal structure and sufficient hydration. For instance, a beefsteak tomato, when pressed gently, should feel firm but not hard, providing a satisfying give. The texture should be consistent with the expected firmness for that type of tomato.
Varietal Differences in Ripeness
Different tomato types exhibit varying characteristics in their ripening process. Knowing these differences helps ensure optimal picking.
| Tomato Type | Color Progression | Firmness | Stem |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cherry Tomatoes | Green to deep red | Firm but slightly yielding | Firmly attached |
| Beefsteak Tomatoes | Green to deep red | Firm but slightly yielding | Firmly attached |
| Plum Tomatoes | Green to deep red or purple | Firm but slightly yielding | Firmly attached |
Understanding these variations in ripening cues for various tomato types is vital to achieving the best results. For example, a cherry tomato that is still green may not have reached its full flavor potential, while a beefsteak tomato that has turned too soft may be past its prime.
Methods for Visual Assessment
Comparing different visual assessment methods highlights their relative strengths and weaknesses.
- Color Comparison: Comparing the color of a tomato to a reference chart, or visually to a similar tomato of known ripeness, can provide a quick and easy way to determine its stage of ripeness. The reference can be an image, a ripe tomato from the same plant, or a similar tomato of known ripeness.
- Stem Inspection: Checking the stem’s attachment to the tomato provides a simple visual cue to its readiness. A firm attachment suggests a tomato that is likely ripe, while a loose attachment could indicate it’s past its prime. A strong, firm attachment, often considered a sign of a healthy tomato, is indicative of the optimal picking time.
Harvesting Techniques
Tomato harvesting is a crucial step in ensuring a bountiful and delicious harvest. Proper technique not only maximizes yield but also protects the plant’s health and longevity. Careful attention to detail in this stage will significantly impact the quality and quantity of your tomato crop.
Safe Harvesting Procedures
Careful harvesting is essential to maintain the health of your tomato plants. Gentle handling minimizes stress on the plants, promoting continued productivity and preventing potential diseases. A proper technique ensures the plant’s longevity and the quality of the fruit.
- Preparation is Key: Before you begin harvesting, ensure you have the necessary tools and are ready to work efficiently. This reduces the risk of injury and ensures you can handle the task with ease.
- Use Protective Gear: Wear gloves to safeguard your hands from thorns, scratches, or potential plant-borne pathogens. Eye protection is also advisable to prevent foreign objects from entering your eyes during the process.
- Tool Selection: Sharp scissors or pruning shears are recommended for harvesting tomatoes. A dull tool may damage the fruit or the plant. Avoid using your bare hands for delicate tomatoes.
Optimal Harvesting Time
Picking tomatoes at the right time is crucial for their flavor and ripeness. Overripe tomatoes tend to be softer and more prone to bruising during handling. The best tomatoes are firm and exhibit their characteristic color.
- Color Consistency: Pay close attention to the color of the tomatoes. The specific color varies depending on the variety, but the tomato should have reached its full color potential for optimal flavor. For example, a red tomato should be fully red, and a yellow tomato should be a deep yellow, not a pale yellow.
- Firmness: Gently press the tomato. A firm tomato resists pressure, while a soft tomato may be overripe. This is a reliable indicator of ripeness, and it avoids picking tomatoes that are still too green or too soft.
- Look for Full Ripeness: The tomato should show signs of full ripeness. Consider the variety of the tomato and its expected characteristics to identify its full ripeness stage.
Gentle Detachment
Proper detachment techniques prevent damage to both the tomato and the plant. A gentle approach ensures a clean harvest and maintains the health of the vine. This method preserves the integrity of the fruit and avoids bruising.
- Grip the Stem: Position your hand firmly around the stem of the tomato. Avoid gripping the tomato itself directly.
- Twist and Gently Pull: Gently twist the tomato slightly to loosen its connection with the vine, then pull it straight away from the plant. This reduces the risk of tearing the stem or damaging the fruit. Use a firm but gentle tug.
- Inspect for Damage: After detaching, carefully inspect the tomato and the plant stem for any signs of damage. If any damage is visible, discard the tomato to maintain quality and avoid potential issues.
Avoiding Damage to the Plant
Minimizing plant damage during harvesting ensures the plant’s health and future productivity. By following proper procedures, you maintain a healthy plant for continued harvests. This prevents the spread of diseases and maintains the plant’s vigor.
- Avoid Over-Handling: Avoid unnecessary handling of the plant or the tomato. Limit your contact to the minimum required for the harvesting process. This reduces the risk of damage to the plant and the fruit.
- Appropriate Tools: Utilize the appropriate tools to prevent accidental damage to the plant or the fruit. Sharp tools are essential to minimize the risk of damaging the tomato or the plant.
- Pruning: If necessary, carefully prune the stem of the tomato after detaching the fruit. This prevents the plant from wasting energy on the stem. Follow proper pruning techniques to minimize the risk of damaging the plant.
Environmental Factors
Tomato ripening is a complex process heavily influenced by the environment. Understanding these external factors is crucial for achieving optimal harvest times and ensuring the best possible quality of your tomatoes. The interplay of sunlight, temperature, and humidity directly impacts the rate and uniformity of ripeness, influencing everything from the color development to the overall flavor profile.The specific environmental conditions in a given area play a significant role in determining when tomatoes are ready to be picked.
A nuanced understanding of these factors can help gardeners anticipate and adjust their harvest schedules, maximizing the yield and quality of their tomato crops.
Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which tomatoes produce energy. Sufficient sunlight promotes the development of sugars and pigments that contribute to the characteristic red color and sweetness of tomatoes. Tomatoes need ample sunlight to fully ripen. Areas with extended periods of cloudy weather or insufficient sun exposure may result in slower ripening and less intense coloration.
Different tomato varieties have varying sunlight requirements, with some needing more direct sunlight than others. Understanding these differences is important for ensuring optimal ripening in your specific growing conditions.
Temperature
Temperature directly impacts the rate of tomato ripening. Warmer temperatures generally accelerate the ripening process, while cooler temperatures slow it down. A consistent temperature range, ideally within a certain optimal window, is crucial for uniform ripening across the entire crop. Excessively high temperatures can lead to rapid ripening but may also result in smaller, less flavorful tomatoes.
Conversely, prolonged periods of cold weather can stunt growth and delay ripening significantly.
Knowing when to pick tomatoes is key for juicy, delicious results. But sometimes, when you’re busy with your garden, it’s hard to know what to do first. Finding the best beginner sewing machines to buy here can be a great way to pass the time while waiting for the perfect moment to harvest those tomatoes. Look for a firm, deep color – that’s the sign they’re ready to be picked, perfect for a summer salad.
Humidity
Humidity levels significantly influence tomato growth and ripening. Optimal humidity ranges vary depending on the specific tomato variety and the growing environment. High humidity can lead to fungal diseases and issues with blossom-end rot, impacting the health and quality of the tomatoes. Conversely, very low humidity levels can cause the fruit to dry out and crack, reducing yield and quality.
Maintaining appropriate humidity levels is essential for preventing these issues and promoting healthy tomato development.
Climate Effects on Harvest Times
Different climates dictate optimal tomato harvest times. In warmer climates, tomatoes may ripen more quickly, potentially allowing for multiple harvests throughout the season. In cooler climates, the ripening process takes longer, and harvest seasons may be shorter. For example, a warm, sunny California spring will typically produce earlier and more abundant harvests than a cooler, wetter spring in the Pacific Northwest.
Frost and Other Weather Conditions
Frost and other extreme weather conditions can severely impact tomato crops. Frost can damage or destroy developing fruit, significantly reducing the harvest. Sudden temperature drops or freezes can halt the ripening process altogether. Similarly, prolonged periods of heavy rainfall can lead to fungal diseases, impacting the overall health and ripeness of the tomatoes. Understanding the potential impacts of these weather events on tomato plants allows for the development of strategies for mitigating potential damage and loss, such as frost protection measures.
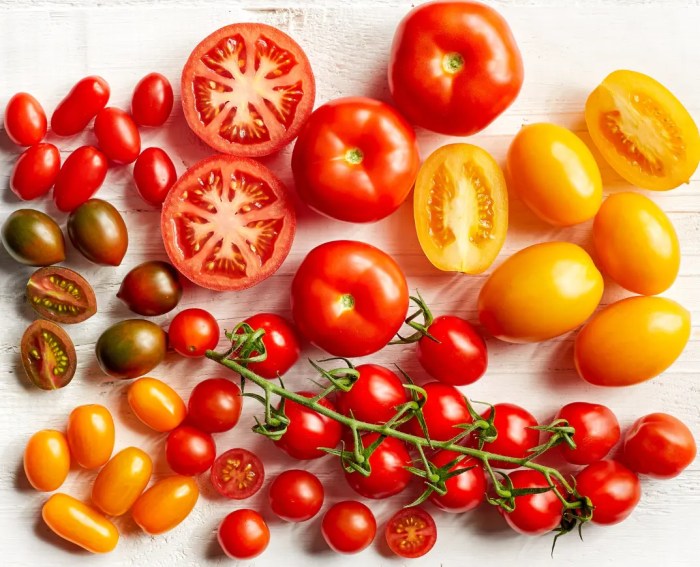
Tomato Variety Impact

Picking the perfect tomato depends not only on its ripeness but also on the specific variety. Different tomato types have varying growth habits, maturation rates, and sensitivities to environmental conditions. Understanding these nuances allows for a more precise and successful harvest. Knowing the ideal picking time for each variety ensures you’re enjoying the peak flavor and texture of your homegrown tomatoes.
Tomato Variety Picking Time Comparison
Different tomato varieties mature at different rates. This table provides a general guideline for picking times, but remember that specific conditions can influence these timelines. Factors like sunlight exposure, soil moisture, and temperature all play a role.
| Tomato Variety | Ideal Picking Time (Days from Planting) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Beefsteak | 70-90 days | Large, meaty tomatoes; often require more time to mature. |
| Roma | 65-80 days | Ideal for sauces and canning; usually ready sooner than beefsteak varieties. |
| Cherry | 55-70 days | Small, sweet tomatoes; mature relatively quickly. |
| Grape | 60-75 days | Tiny, sweet tomatoes; often ready earlier than other varieties. |
| Heirloom | 60-80 days | Unique shapes and colors; individual varieties have varying maturation times. |
Average Ripening Time for Tomato Types
This table Artikels the typical ripening period for common tomato types, providing a general expectation for when to anticipate your harvest.
| Tomato Type | Average Ripening Time (Days) |
|---|---|
| Determinate | 55-75 |
| Indeterminate | 60-90 |
| Hybrid | 65-80 |
Variety Response to Environmental Conditions
Tomato varieties differ in their tolerance to various environmental factors. Some varieties are more susceptible to heat stress, while others are more prone to fungal diseases. Understanding these responses is crucial for successful cultivation. For example, some varieties are better suited to hot, sunny climates, while others thrive in cooler conditions.
Early, Mid-Season, and Late-Season Varieties
Tomato varieties are often categorized by their maturity timing. Early varieties provide an earlier harvest, while mid-season and late-season varieties offer a longer harvest window. Knowing the maturity group helps plan your garden accordingly.
- Early Season Varieties typically mature in 55-70 days. These varieties are often compact and produce smaller tomatoes, but they are perfect for a quick harvest and are suitable for cooler climates. Examples include certain cherry and grape varieties.
- Mid-Season Varieties mature in 65-80 days. They offer a balance of yield and time, making them a popular choice for many gardeners. Examples include many hybrid varieties and some heirloom types.
- Late Season Varieties mature in 75-90 days or more. These varieties are often larger and have a longer growing season, providing a late harvest of tomatoes, perfect for climates with a longer growing season. Examples include beefsteak and certain heirloom tomatoes.
Importance of Variety Selection
Considering the specific variety is vital when determining the best time to pick. Different varieties have unique characteristics that affect their ripening and ideal harvest time.
Pre-Harvest Considerations

Before you reach for the first ripe tomato, several factors play a crucial role in ensuring a bountiful and high-quality harvest. Understanding these pre-harvest considerations will help you maximize your yield and ensure the best possible taste and texture for your homegrown tomatoes. These steps help optimize the plant’s resources for producing the most flavorful and attractive tomatoes.Careful attention to pre-harvest conditions can lead to more robust plants, fuller harvests, and better-tasting tomatoes.
This involves understanding the plant’s needs and recognizing the signs that indicate a tomato plant is ready for harvesting.
Signs of Harvest Readiness
Tomato plants exhibit distinct visual cues that signal ripeness. Careful observation is key to identifying the perfect time for harvesting. Different varieties of tomatoes will display varying characteristics at their peak ripeness.
Picking tomatoes at the perfect moment is key for the best flavor. Knowing when to harvest them depends on the variety, but generally, you’ll want to pick them when they’re firm and the color is vibrant. This reminds me of the best houseplants for sun, which need bright light to thrive, just like a ripe tomato. So, if you’re aiming for the tastiest tomatoes, keep an eye out for those plump, brightly colored beauties! They’ll be ready for a delicious meal soon.
- Color Change: The most common indicator is a change in color. For example, red tomatoes should exhibit a deep, vibrant red hue. Other varieties, like yellow or orange tomatoes, will display their specific, fully mature colors. The color change signifies the completion of the ripening process and the accumulation of sugars and acids that give tomatoes their characteristic taste.
- Firmness: A firm, slightly yielding tomato is typically a sign of ripeness. Avoid tomatoes that feel soft or mushy, as these may have begun to overripen or are past their prime.
- Shape and Size: Most varieties will exhibit their mature shape and size when ripe. Look for the correct size and shape for your specific tomato variety. Differences in size are common across various types of tomatoes, reflecting their unique characteristics.
- Stem Attachment: A tomato that is firmly attached to the stem is often a good sign that the fruit has finished ripening. A loose or easily detachable stem could indicate that the tomato is not yet fully developed.
Ideal Conditions for Optimal Ripeness
Providing optimal growing conditions is crucial for ensuring that your tomato plants produce the best possible fruit.
- Sunlight: Tomato plants require ample sunlight to produce high-quality fruit. Aim for at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Adjusting the position of the plant or using supports to ensure adequate sunlight can significantly affect the tomato’s quality and flavor.
- Temperature: Ideal temperatures for tomato growth are between 70-85°F (21-29°C). Temperatures outside this range can negatively impact the plant’s development and fruit production. Monitoring the temperature regularly is essential for maintaining the best possible conditions for ripening.
- Watering: Consistent watering is vital, but avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot. Water deeply and less frequently, allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings. This encourages strong root development and healthy fruit growth.
Watering and Fertilization, When to pick tomatoes
The right balance of water and nutrients is essential for healthy tomato growth and optimal ripeness.
- Watering Frequency: Watering deeply and less frequently encourages the roots to grow deeper, making the plant more resilient to drought conditions. This deep watering also contributes to a more flavorful and firm tomato.
- Fertilization: Regular fertilization with a balanced tomato fertilizer is necessary for fruit development. Using an appropriate fertilizer, tailored to your specific tomato variety, can enhance the fruit’s quality and increase yields. A soil test can help you determine the specific needs of your soil and tailor your fertilization plan accordingly.
Plant Support and Pruning
Proper support and pruning help the plant to focus its energy on producing fruit.
- Plant Support: Tomato plants tend to be heavy, especially as they mature. Providing adequate support, such as stakes or cages, prevents the plants from bending or breaking under the weight of the fruit. Proper support promotes the healthy development of the plant and prevents stress that could impact fruit production.
- Pruning: Pruning involves removing excess foliage, particularly suckers (new shoots that grow from the main stem), to improve airflow and sunlight penetration. Pruning also concentrates the plant’s resources towards fruit production. This will ensure optimal growth and prevent the plant from becoming overly dense.
Impact of Pests and Diseases
Pests and diseases can negatively affect the timing of harvesting.
- Pest Management: Regular monitoring for pests like aphids, tomato hornworms, and spider mites is crucial. Early detection and control measures can prevent significant damage and ensure that the plant remains healthy and productive.
- Disease Prevention: Diseases such as blight and blossom-end rot can impact the quality and timing of harvest. Implementing preventative measures, such as proper spacing, good air circulation, and disease-resistant varieties, is important for maintaining a healthy crop.
Post-Harvest Handling
From the vine to your table, tomatoes require careful handling to maintain their quality and freshness. Proper post-harvest procedures are crucial for maximizing their shelf life and preventing undesirable changes in texture and flavor. This meticulous attention to detail ensures that the delicious fruits of your labor reach consumers in optimal condition.Careful handling after harvest is essential to preserve the quality of tomatoes.
Neglecting this stage can lead to rapid deterioration, impacting both their visual appeal and overall taste. Proper handling techniques, along with appropriate storage conditions, are key to maximizing the lifespan and maintaining the integrity of these vibrant fruits.
Handling Procedures
Thorough handling of harvested tomatoes is paramount for maintaining their quality and extending their shelf life. A systematic approach, from picking to packaging, is essential. Clean hands and sanitized tools are critical to prevent the spread of pathogens and maintain the aesthetic appeal of the produce.
- Gently remove tomatoes from the vine, avoiding excessive pressure that can bruise the fruit.
- Handle tomatoes with clean hands or gloves, ensuring no dirt or other contaminants come into contact with the surface.
- Avoid dropping or tossing tomatoes, as this can cause bruising and reduce their quality.
- Inspect tomatoes for any visible damage before storing. Discard any with significant damage or blemishes.
Storage Conditions
Optimizing storage conditions is critical for preserving the quality and freshness of tomatoes. Maintaining the ideal temperature and humidity levels is key to preventing spoilage and preserving the desirable flavor profiles. The storage environment plays a significant role in extending the shelf life and ensuring the optimal quality of tomatoes.
- Ideal temperature for storing tomatoes is between 50-55°F (10-13°C). Temperatures above this range accelerate ripening and lead to rapid deterioration.
- Maintain humidity levels between 85-90% to prevent dehydration. This prevents the tomatoes from losing moisture, which can affect their texture and overall quality.
- Store tomatoes away from ethylene-producing fruits like apples, bananas, and pears. Ethylene gas accelerates ripening and can shorten the shelf life of tomatoes.
Damage Prevention
Preventing bruising and other damage is crucial for preserving the quality of harvested tomatoes. The sensitivity of the tomato skin to impact necessitates careful handling throughout the process.
- Avoid placing tomatoes directly on hard surfaces. Use cushioning materials or containers to prevent bruising.
- Do not stack tomatoes tightly. Allow adequate space between each fruit to prevent bruising and maintain airflow.
- Avoid storing tomatoes in direct sunlight or near heat sources. Heat can accelerate ripening and lead to spoilage.
Storage Containers
The choice of container significantly impacts the storage life of tomatoes. Consider the type of tomato and its intended use when selecting a container. Different types of tomatoes require different handling to prevent damage and maintain their quality.
| Tomato Type | Suitable Container | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Beefsteak Tomatoes | Cardboard boxes lined with paper towels | Provides cushioning and prevents bruising during transport and storage. |
| Cherry Tomatoes | Plastic containers with perforated lids | Allows for air circulation and prevents moisture buildup. |
| Roma Tomatoes | Mesh bags | Facilitates air circulation, prevents moisture buildup, and maintains the fruit’s shape. |
Illustrative Examples
Picking the perfect tomato involves more than just color; it’s about understanding the subtle nuances of ripeness. Different varieties display ripeness in unique ways, and knowing what to look for in each type is key to achieving the best flavor. This section provides detailed descriptions of various tomato types at different stages of ripeness, aiding you in making informed harvesting decisions.Different tomato varieties exhibit unique characteristics when they reach optimal ripeness.
Recognizing these distinctions is crucial for achieving the best flavor and texture. By understanding these visual cues, you can identify the perfect time to harvest your tomatoes, ensuring you enjoy the best possible taste.
Ripe Heirloom Tomato
Heirloom tomatoes, known for their diverse shapes and colors, exhibit distinct characteristics when ripe. A perfectly ripe heirloom tomato displays a deep, vibrant color, reflecting the specific variety. Its skin is firm but yields slightly to gentle pressure. The stem will be a rich, dark color, firmly attached to the tomato. A healthy heirloom tomato will have a uniform color and texture, without any blemishes or soft spots.
The aroma of a ripe heirloom tomato will be pleasant and sweet.
Slightly Under-Ripe Cherry Tomato
A slightly under-ripe cherry tomato will often still have a vibrant green or red hue, depending on the variety. Its skin will be firm to the touch and not yield readily to pressure. The stem will still be green or a light shade of the final color. The flavor of a slightly under-ripe cherry tomato might be less intense compared to a fully ripe one.
The interior of the tomato will not be fully developed yet.
Bruised Tomato
A bruised tomato is easily identifiable by its visual cues. A bruise is a discoloration, often appearing as a dark spot or area on the tomato’s skin. The area around the bruise may also appear slightly sunken or soft. The bruise can be dark red, purple, or black, depending on the extent and nature of the damage. The texture of the affected area will be softer than the surrounding healthy skin.
A bruised tomato is best avoided for eating, as it can have an unpleasant flavor and texture.
Beefsteak Tomato Ripeness
Beefsteak tomatoes, with their large size, can be tricky to assess for ripeness. A ripe beefsteak tomato will have a deep, rich color, often a deep red or a deep orange depending on the variety. The skin should be firm but slightly yielding to gentle pressure. The stem will be firmly attached, but a bit more flexible compared to a cherry tomato.
The aroma of a ripe beefsteak tomato will be strong and rich, with a hint of sweetness. A slight firmness to the touch, and a good color, indicate ripeness.
Ripe, Vibrant Orange Tomato
A perfectly ripe, vibrant orange tomato is a testament to the unique colors that some tomato varieties can achieve. The skin will be a uniformly deep orange color. The texture will be firm but yield slightly to pressure, indicating that it is not overly hard or soft. The stem will be attached firmly, often with a slight darkening of the stem color, indicating ripeness.
The aroma of a perfectly ripe orange tomato will be distinctive and sweet, with a slightly tangy undertone, characteristic of its variety.
Last Word: When To Pick Tomatoes
In conclusion, knowing when to pick tomatoes is a crucial aspect of gardening success. By understanding the factors that influence ripeness, you can ensure you’re harvesting the most flavorful and vibrant tomatoes possible. Remember to consider the variety, environmental conditions, and proper handling techniques for the best results. Happy harvesting!