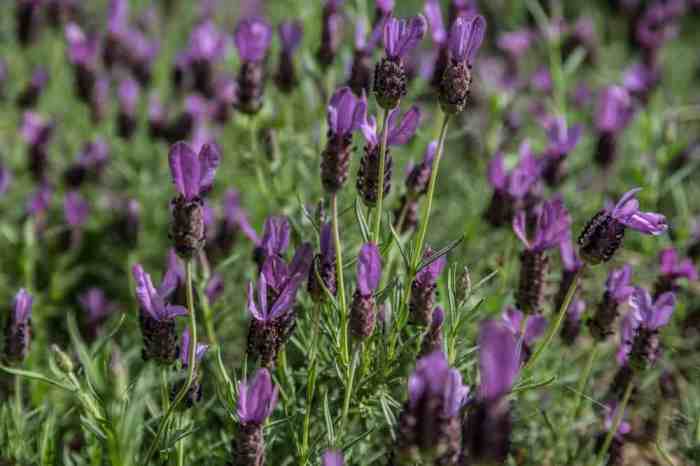
Spanish Lavender Growing Guide: Unlock the secrets to cultivating this stunning, fragrant herb. This comprehensive guide dives deep into everything you need to know, from understanding the plant’s unique characteristics to troubleshooting common growing challenges. We’ll explore optimal growing conditions, planting and care techniques, pest and disease management, propagation methods, and even practical uses for your beautiful Spanish Lavender.
Get ready to cultivate a fragrant oasis in your garden!
This guide will equip you with the knowledge and practical steps to cultivate thriving Spanish Lavender plants. We’ll cover everything from choosing the right soil and sunlight to proper watering and fertilization. Learn about various Spanish Lavender varieties, their growth habits, and the best time to plant for optimal results. We’ll also discuss propagation methods to expand your lavender collection and how to keep pests and diseases at bay.
Let’s embark on this journey to mastering the art of growing Spanish Lavender!
Introduction to Spanish Lavender
Spanish Lavender, scientifically known asLavandula stoechas*, is a captivating flowering plant renowned for its vibrant beauty and aromatic fragrance. This distinctive species, part of the mint family (Lamiaceae), boasts unique characteristics that set it apart from other lavenders. Its striking flower spikes and resilience make it a popular choice for gardeners and landscapers alike.This guide delves into the fascinating world of Spanish Lavender, exploring its botanical classification, diverse varieties, growth habits, and adaptability to different climates.
We’ll also highlight key features and origins, making it easier to understand and appreciate this exquisite plant.
Botanical Classification and Characteristics
Spanish Lavender, belonging to theLavandula* genus, displays a range of botanical characteristics. It is a perennial herb, meaning it lives for more than two years, and its woody stems contribute to its robust nature. The distinctive flower spikes are a hallmark of the species, often exhibiting a deep purple or bluish-violet color, though variations in hue exist. The leaves are typically silvery-gray and have a characteristic aromatic scent.
Varieties of Spanish Lavender
WhileLavandula stoechas* is the scientific name, several varieties and cultivars exist. These variations often differ in subtle nuances of flower color, size, and overall growth habit. ‘Alba’ is a popular cultivar known for its white flowers, while ‘Purple Knight’ displays a rich, deep purple. The variations add to the diversity of the plant, making it a visually appealing option for various garden designs.
Growth Habit and Mature Size
Spanish Lavender typically displays a rounded, bushy growth habit. The plants form a dense, attractive shape, often reaching a mature height and width of 2 to 3 feet. This moderate size makes it suitable for borders, containers, or as a part of a larger landscaping design. Their compact growth habit is a key feature for gardeners with limited space.
Native Region and Adaptability
Native to the Mediterranean region of Europe, Spanish Lavender is remarkably adaptable to various climates. It thrives in well-drained soil and tolerates periods of drought. While preferring full sun, it can tolerate partial shade in milder climates. Its resilience makes it a popular choice for gardeners in diverse locations, as long as the specific growing requirements are met.
Key Features of Spanish Lavender Varieties
| Plant Name | Common Name | Origin | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| *Lavandula stoechas* | Spanish Lavender | Mediterranean Europe | Showy flower spikes, aromatic foliage, drought tolerance, bushy growth habit, various flower colors. |
| ‘Alba’ | White Spanish Lavender | Cultivar | White flowers, similar growth habit to
Learning how to grow Spanish lavender is a rewarding experience, requiring specific conditions for thriving. While researching different plant care techniques, you might also be interested in how to grow and care for aluminum plants. This guide provides excellent tips for those, and ultimately, understanding these principles can help you master the intricacies of Spanish lavender’s needs, like well-drained soil and plenty of sun. Knowing the specific requirements of both plants can greatly enhance your gardening knowledge.
|
| ‘Purple Knight’ | Purple Spanish Lavender | Cultivar | Deep purple flowers, bushy growth habit, good drought tolerance. |
Growing Conditions
Spanish lavender, with its delicate beauty and fragrant blooms, thrives in specific growing conditions. Understanding these requirements ensures healthy plants and abundant blooms year after year. Careful attention to sunlight, soil type, and pH is crucial for successful cultivation.Optimal growing conditions for Spanish lavender are vital for its overall health and beautiful blooms.
So, you’re diving into the fragrant world of Spanish lavender? Great choice! Learning how to cultivate these beauties involves more than just planting them. For example, maintaining a clean washing machine is essential for keeping your clothes fresh, and using vinegar and baking soda, as detailed in how to clean a washing machine with vinegar and baking soda , can make a huge difference in the freshness of your laundry.
This, in turn, helps prevent lingering odors that can impact your Spanish lavender plants, making your garden truly aromatic!
Providing the right environment encourages robust growth and abundant flowering, allowing the plant to flourish.
Sunlight Requirements
Spanish lavender thrives in full sun, receiving at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight daily. Partial shade is acceptable, but the plant may produce fewer blooms and be more susceptible to diseases in consistently shaded areas. Exposure to direct sunlight promotes healthy growth and vibrant blooms. This sunlight exposure is critical for the plant’s photosynthetic process, enabling it to produce the energy necessary for growth and flowering.
Soil Type and Drainage
Lavender prefers well-drained soil that is sandy or loamy. Clay-heavy soil can lead to waterlogging, which harms the roots. The soil should not retain moisture, preventing root rot and promoting healthy growth. The key is aeration and rapid water drainage. Good drainage allows the roots to breathe and prevents the soil from becoming waterlogged, which can lead to root rot.
Ideal Soil pH
The ideal pH range for Spanish lavender is slightly alkaline, typically between 6.5 and 8.0. Acidic soil can inhibit the plant’s ability to absorb essential nutrients. Maintaining the appropriate pH level is important for overall health and growth.
Importance of Well-Draining Soil
Well-draining soil is crucial for the health of Spanish lavender. Waterlogged soil deprives roots of oxygen, leading to root rot and eventual plant death. To ensure excellent drainage, consider adding organic matter like compost or perlite to improve soil structure and aeration. This allows for the free flow of water, preventing waterlogging and promoting healthy root development.
This is vital for the plant’s survival and overall well-being.
Preparing the Planting Area
Thorough preparation of the planting area is essential for successful lavender cultivation. Dig the planting hole to be slightly wider than the root ball of the lavender plant. Amend the existing soil with organic matter to improve drainage and aeration. This creates an ideal environment for the lavender to establish itself and thrive.
Soil Type Suitability
| Soil Type | Suitability for Spanish Lavender | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Sandy Soil | Excellent | Excellent drainage, allows for rapid water absorption. |
| Loamy Soil | Good | Good drainage, holds moisture effectively. Ideal balance. |
| Clay Soil | Poor | Poor drainage, prone to waterlogging. Requires amendment. |
Well-draining soil is essential for lavender growth, preventing root rot.
Planting and Care
Bringing Spanish Lavender into your garden is an exciting endeavor! Proper planting and care are crucial for establishing a healthy and thriving lavender patch that will reward you with beautiful blooms and a lovely fragrance for years to come. Understanding the nuances of planting, watering, and fertilizing will significantly impact the plant’s overall health and appearance.
Planting Process
The process of planting Spanish Lavender should be approached with care and attention to detail, ensuring the plants have the best possible start. Proper spacing is key to healthy growth and allows for adequate air circulation to prevent diseases.
- Spacing Recommendations: For optimal growth, maintain a spacing of 18-24 inches between plants. This allows for adequate room for the roots to develop and prevents overcrowding, which can lead to issues with air circulation and potential disease. A well-spaced lavender patch is a healthy lavender patch.
- Ideal Planting Time: The best time to plant Spanish Lavender is during the spring or fall. In regions with harsh winters, spring planting is generally recommended. In regions with milder winters, fall planting can be an excellent choice. Spring planting gives the plant time to establish itself before the hot summer months. Fall planting provides time for the plant to root before the onset of winter.
So, I’ve been diving deep into Spanish lavender growing guides lately, and one crucial part of that is keeping the surrounding area clean. Properly cleaning outdoor furniture, like I detail in my post how i clean outdoor furniture and areas , is essential for healthy plant growth. This helps prevent pests and diseases that could affect my Spanish lavender.
A clean environment will contribute significantly to the success of your Spanish lavender garden!
Consider the specific hardiness zone and the expected weather patterns when making your decision.
Watering Techniques
Watering is a critical aspect of Spanish Lavender care. The frequency and amount of water required depend on various factors, including the climate, soil type, and the plant’s size. Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot and other problems.
- Watering Frequency and Amount: Young lavender plants need more frequent watering, especially during dry periods. Once established, they are more drought-tolerant. A general guideline is to water deeply and thoroughly once or twice a week, allowing the water to penetrate the soil. Avoid watering the foliage; instead, focus on the base of the plant to ensure proper hydration.
Observe the soil moisture; if it feels dry to the touch a few inches below the surface, it’s time to water.
- Importance of Appropriate Watering: Proper watering is essential for the health of your lavender plants. Consistent, deep watering encourages strong root development, making the plant more resilient to drought conditions. Overwatering can lead to root rot, which can significantly harm or kill the plant. It’s crucial to find the right balance to maintain healthy plant growth.
- Avoiding Overwatering: Overwatering is a common mistake that can be detrimental to lavender plants. Signs of overwatering include yellowing leaves, wilting, and the presence of fungal diseases. Ensure the soil has excellent drainage to prevent waterlogging. If you’re unsure about the soil’s drainage, you can improve it by adding perlite or other organic matter to increase drainage.
Proper drainage is a key component of successful lavender cultivation.
Fertilization
Fertilizing your Spanish Lavender plants can help promote healthy growth and abundant blooms. Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer formulated for flowering plants.
- Necessity of Fertilization: Regular fertilization is important for promoting healthy growth and encouraging abundant blooms. Lavender plants are not heavy feeders; over-fertilizing can harm the plant. A balanced, slow-release fertilizer tailored for flowering plants is typically sufficient.
- Appropriate Types of Fertilizer: A balanced, slow-release fertilizer formulated for flowering plants is the best choice. A balanced formula provides essential nutrients for healthy growth and blooming. A slow-release fertilizer ensures a steady supply of nutrients over time, reducing the need for frequent applications. Avoid using fertilizers high in nitrogen, as this can lead to excessive leaf growth at the expense of blooms.
Pruning and Shaping
Regular pruning and shaping is crucial for maintaining the shape and health of your lavender plants. Pruning helps to encourage bushier growth and promote flowering.
- Pruning for Optimal Growth and Appearance: Pruning removes dead or damaged stems, encouraging new growth and maintaining a neat appearance. It also helps to prevent the plant from becoming leggy and promotes bushier growth. Regular pruning is crucial for the overall health and aesthetic appeal of your lavender plants.
Step-by-Step Planting and Initial Care Procedure
- Preparation: Select a sunny location with well-drained soil. Ensure the planting hole is appropriately sized to accommodate the root ball.
- Planting: Carefully remove the lavender plant from its container and gently loosen the roots. Place the plant in the hole, ensuring the top of the root ball is level with the surrounding soil.
- Watering: Water thoroughly after planting, ensuring the soil is consistently moist.
- Mulching: Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the plant to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
- Ongoing Care: Continue to monitor watering needs, especially during dry spells. Fertilize according to the recommended schedule.
Pests and Diseases

Spanish Lavender, while generally resilient, can be susceptible to certain pests and diseases if growing conditions are not optimal. Understanding these potential issues and how to address them is crucial for maintaining healthy and thriving lavender plants. Early detection and appropriate management strategies are vital for preventing significant damage and ensuring the long-term health of your lavender garden.
Common Pests
Understanding the common pests that affect Spanish Lavender is the first step to effective management. Recognizing their presence and characteristics allows for timely intervention.
- Aphids: These small, soft-bodied insects often appear in colonies on new growth and stems. They suck sap from the plant, causing distortion and stunting. Identifying aphids involves looking for small, pear-shaped insects that are typically green, yellow, or black. They can be found clustered on leaves, stems, and buds.
- Spider mites: These tiny arachnids create a fine webbing over leaves, particularly noticeable on the undersides. The webbing, combined with a stippled or bronzed appearance on the leaves, helps with identification. They also suck plant juices.
- Whiteflies: These tiny, white insects are often found on the undersides of leaves, particularly in warm, dry conditions. They leave a sticky residue on the plant. Look for small, white, winged insects on the undersides of leaves.
- Snails and Slugs: These mollusks feed on the leaves and stems at night. Identifying their presence involves searching for gnawed holes or damaged leaves, especially during or after rainfall.
Common Diseases
Identifying diseases is equally important. Early diagnosis can prevent extensive damage and guide the most appropriate treatment.
- Powdery mildew: This fungal disease appears as a white, powdery coating on the leaves, stems, and flowers. It can severely impact plant vigor and aesthetics. Properly identifying the symptoms is crucial for effective treatment. The powdery appearance and its distribution over the plant’s surface are key indicators.
- Root rot: Caused by fungal pathogens, root rot leads to yellowing and wilting of the plant. This occurs when the soil is overly moist or poorly drained. Diagnosing root rot involves careful examination of the root system, looking for discoloration, rot, and decay. Improper watering practices often contribute to the development of root rot.
- Leaf spot: This fungal disease causes brown or black spots on the leaves, which may expand and merge. Recognizing the distinct pattern of these spots is essential for proper diagnosis. Identifying the specific shape and size of the lesions can help determine the precise type of leaf spot.
Preventative Measures
Implementing preventative measures is often more effective than treating existing issues.
- Proper Watering: Avoid overwatering, as this creates a conducive environment for fungal diseases. Water deeply and allow the soil to dry out between waterings. Allowing for proper drainage in the planting area is also vital.
- Good Air Circulation: Ensure adequate air circulation around plants to prevent moisture buildup, which can promote fungal growth. Spacing plants appropriately and avoiding overcrowding can greatly assist with air circulation.
- Sanitation: Remove and destroy any diseased plant parts to prevent the spread of diseases. Regularly removing dead or decaying plant material helps control the spread of pathogens.
- Resistant Varieties: Choose lavender varieties that are known for their disease resistance. Select the best type for your specific environment.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment depends on the severity and type of the problem.
- Pests: For mild infestations, insecticidal soaps or neem oil can be effective. For more severe infestations, systemic insecticides may be necessary. Consult with a local gardening expert for specific recommendations. These treatments often need to be repeated at regular intervals to ensure efficacy.
- Diseases: Fungal diseases often require fungicides. Follow the product instructions carefully and apply them when the disease is detected. In many cases, the best approach to controlling diseases is preventative care.
Identifying and Treating Common Fungal Diseases
A thorough understanding of fungal diseases is key to their effective treatment.
- Powdery mildew: Control with a sulfur-based fungicide. Proper timing is important; apply before the disease becomes widespread.
- Leaf spot: Treat with a broad-spectrum fungicide, targeting the specific fungus causing the issue. Correcting environmental conditions, such as improving air circulation and reducing humidity, can also prevent future outbreaks.
Pest Control Methods Comparison
Comparing pest control methods helps in selecting the most effective approach.
| Method | Effectiveness | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insecticidal Soap | Moderate | Environmentally friendly, safe for beneficial insects | Less effective against hard-shelled insects, may require multiple applications |
| Neem Oil | Good | Environmentally friendly, effective against various pests | May need multiple applications, not as potent as chemical insecticides |
| Systemic Insecticides | High | Effective against a wide range of pests | Can harm beneficial insects, may have environmental impact |
Propagation: Spanish Lavender Growing Guide
Expanding your Spanish lavender collection doesn’t have to be difficult. Propagation allows you to create new plants from existing ones, preserving desirable traits and increasing your garden’s fragrant beauty. Whether you’re aiming for a larger display or simply want to share your favorite lavender variety, propagation is a rewarding process.Propagation techniques for Spanish lavender, like cuttings and division, are efficient and straightforward.
Proper execution, considering factors like the best time of year and suitable conditions, leads to high success rates. This section will guide you through the various methods, emphasizing best practices for each.
Taking Cuttings
Taking cuttings is a popular and effective way to propagate Spanish lavender. This method involves selecting healthy stems and encouraging them to root independently. The goal is to create a new plant from a section of the parent plant. Choose healthy, vigorous stems, ideally from the current year’s growth, that are not flowering. These stems are more likely to produce roots.
- Selecting the Right Cuttings: Look for stems that are firm, free of diseases or pests, and approximately 4-6 inches long. Avoid stems that are too woody or too soft. Remove any leaves from the lower inch of the cutting to reduce moisture loss during rooting.
- Preparing the Cutting Medium: Use a rooting hormone to encourage root development. A mixture of perlite and vermiculite, or a commercial rooting mix, provides good drainage and aeration. Keep the medium consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Rooting the Cuttings: Place the cuttings in the prepared medium, ensuring they are buried at an angle. Cover the container with a clear plastic bag or a humidity dome to maintain humidity. Keep the cuttings in a warm, bright location, but out of direct sunlight.
- Monitoring and Care: Regularly check the moisture level of the medium. Mist the cuttings as needed to maintain humidity. Once roots begin to form, gradually reduce the humidity. This is usually after a few weeks. Transplant the cuttings into individual pots once they have developed a robust root system.
Dividing Established Plants
Dividing established lavender plants is another effective propagation method, particularly for expanding an existing collection. This method allows for the creation of new plants from a single mature plant. This is beneficial for controlling plant size and spreading lavender to new areas.
- Timing is Key: Divide established plants in the spring or fall, when the plant is dormant or actively growing. Avoid dividing during periods of extreme heat or cold.
- Preparation: Carefully dig up the plant, being mindful not to damage the roots. Gently shake off excess soil.
- Division Process: Use a sharp knife or spade to divide the plant into sections, each with its own set of roots and shoots. Ensure each division has a healthy amount of roots and shoots.
- Replanting: Replant the divisions in individual pots or directly in the garden. Water thoroughly and provide consistent moisture until the plants are established.
Best Time for Propagation
The ideal time for propagation varies depending on the climate. In temperate regions, spring and fall are generally the best times to take cuttings or divide plants. The optimal temperature for rooting is typically between 65-75°F (18-24°C). In warmer climates, propagation may be possible during the cooler parts of the year. In colder climates, spring or early fall are best to avoid harsh weather.
Propagation Methods Comparison
| Method | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Cuttings | Preserves desirable traits, relatively easy, inexpensive |
| Division | Fast and effective way to expand your collection, economical, creates multiple plants from a single source |
Uses and Benefits
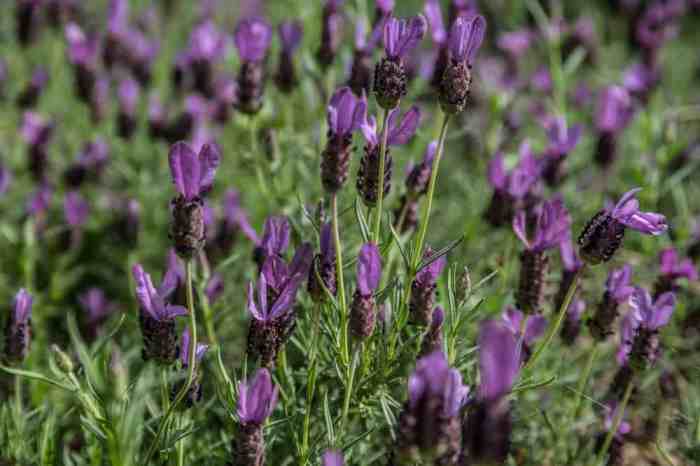

Spanish Lavender, with its captivating fragrance and resilience, offers a wealth of practical and aesthetic applications. Beyond its visual appeal, this versatile plant boasts a rich history of use in various cultures, from traditional medicine to culinary arts. Its ability to thrive in diverse climates and its ease of propagation make it a valuable addition to any garden.Spanish Lavender’s numerous uses extend far beyond simply adding beauty to a landscape.
Its fragrant flowers and leaves are a treasure trove of potential, offering a diverse range of benefits for both practical and decorative purposes.
Practical Uses
Spanish Lavender’s practicality stems from its diverse applications. Its strong aroma and subtle medicinal properties have led to its incorporation in various products, from cleaning solutions to aromatherapy.
- Cleaning Solutions: The essential oil extracted from Spanish Lavender possesses potent antibacterial properties, making it a valuable addition to cleaning products. Its natural antiseptic qualities can effectively disinfect surfaces and eliminate unwanted odors. This natural cleaning agent is an environmentally friendly alternative to harsh chemicals, providing a safe and effective solution for households seeking natural cleaning alternatives.
- Aromatherapy: The calming fragrance of Spanish Lavender is widely used in aromatherapy. Its essential oil is believed to have a relaxing effect, promoting a sense of calm and well-being. Inhaling the scent is a simple yet effective way to relieve stress and anxiety, making it a popular choice for creating a tranquil atmosphere.
- Potpourri: Dried Spanish Lavender flowers can be used to create beautiful and fragrant potpourri. The dried flowers can be arranged in decorative bowls or vases, diffusing their lovely aroma throughout the home and adding a touch of elegance.
Medicinal Properties
Spanish Lavender, thanks to its chemical composition, has a history of use in traditional medicine. While modern medicine often investigates and validates these claims, many find relief and comfort from using it topically for its calming and antiseptic properties.
- Skin Care: Spanish Lavender is known for its soothing and antiseptic properties. Topical applications of lavender oil can help alleviate skin irritations, such as insect bites and minor burns. The oil can also promote skin healing and reduce inflammation.
- Insect Repellent: The strong scent of Spanish Lavender can act as a natural insect repellent. This is a natural and safe alternative to harsh chemical-based repellents, providing a solution for keeping insects away from the home and garden. Adding lavender plants around the garden is a good practice for this purpose.
Culinary Uses
While not as extensively used in cooking as other herbs, Spanish Lavender can add a unique flavor to certain dishes.
- Flavoring: Spanish Lavender can add a subtle, floral note to baked goods, jams, and teas. Its delicate flavor pairs well with other herbs and spices, creating a unique and aromatic experience for the palate.
Aesthetic Value, Spanish lavender growing guide
Spanish Lavender’s visual appeal makes it a desirable addition to any garden or landscape design. Its vibrant purple flowers provide a pop of color, while its delicate foliage adds texture and depth.
- Landscaping: Spanish Lavender’s drought tolerance and low-maintenance nature make it a popular choice for landscaping projects. Its compact growth habit makes it suitable for borders, edging, and containers. The visual appeal of the plant’s flowers is also a great addition to floral arrangements and bouquets.
- Decorative Arrangements: The vibrant purple flowers of Spanish Lavender add a touch of elegance and sophistication to various decorative arrangements. Dried lavender flowers can be incorporated into bouquets, wreaths, and centerpieces, adding a fragrant and visually appealing element.
Table of Uses
| Category | Use |
|---|---|
| Practical | Cleaning solutions, aromatherapy, potpourri |
| Medicinal | Skin care, insect repellent |
| Culinary | Flavoring (baked goods, jams, teas) |
| Aesthetic | Landscaping, decorative arrangements |
Troubleshooting
Keeping your Spanish Lavender healthy and thriving often involves addressing potential problems. This section delves into common issues and provides practical solutions to help you maintain your lavender’s beauty and vitality. Understanding these problems and their causes is crucial for effective care and ensures your lavender thrives in your garden.Troubleshooting involves identifying and addressing issues that may arise during the growth cycle of your Spanish Lavender.
This section provides a structured approach to dealing with common problems, enabling you to maintain optimal growing conditions.
Common Growing Problems and Solutions
Identifying and addressing issues promptly is key to ensuring healthy plant growth. A proactive approach to problem-solving will prevent minor issues from escalating into more significant problems.
- Yellowing Leaves: Yellowing leaves can indicate several underlying problems. Nutrient deficiencies, overwatering, underwatering, or pests are common causes. Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
- Stunted Growth: Slow or stunted growth in lavender can be attributed to several factors. Insufficient sunlight, poor soil quality, or an inadequate watering schedule can hinder the plant’s development. Addressing these issues will promote healthy growth.
- Insufficient Drainage: Poor drainage can lead to root rot and other problems. Waterlogged soil deprives roots of oxygen, leading to stress and disease. Improper soil composition and inadequate drainage holes in pots are common causes.
- Root Rot: Root rot is a serious fungal disease that affects the roots of the lavender plant. Overwatering, poor drainage, and high soil moisture levels are primary contributing factors. Addressing these conditions is critical for saving the plant.
Yellowing Leaves: Causes and Remedies
Yellowing leaves are a common issue, often caused by a combination of environmental factors and plant care practices.
- Nutrient Deficiency: Insufficient nutrients in the soil can lead to yellowing leaves, particularly in older leaves. A soil test can help determine the specific nutrients lacking and suggest appropriate corrective measures. Amendments like compost or fertilizer are often necessary.
- Overwatering/Underwatering: Both extremes can lead to yellowing. Overwatering deprives roots of oxygen, while underwatering stresses the plant, causing leaves to turn yellow. A consistent watering schedule, tailored to the specific needs of your plant, is crucial.
- Pest Infestation: Pests like aphids or spider mites can cause yellowing or distorted leaves. Inspect the plant thoroughly and treat infestations with appropriate pest control methods.
Stunted Growth: Possible Solutions
Several factors can contribute to stunted growth in Spanish Lavender. Addressing the underlying causes is essential for promoting healthy growth.
- Insufficient Sunlight: Lavender thrives in full sun. Insufficient sunlight can limit photosynthesis and hinder growth. Ensure your lavender receives at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Poor Soil Quality: Compacted or poor-quality soil restricts root development and water absorption. Amend the soil with organic matter like compost or well-rotted manure to improve its structure and drainage.
- Inadequate Watering: Consistent but not excessive watering is vital. Water deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between waterings.
Insufficient Drainage: Strategies
Insufficient drainage can be a significant problem for lavender, leading to waterlogged soil and root rot.
- Soil Composition: Heavy clay soils often have poor drainage. Improve drainage by adding perlite, sand, or other amendments to the soil.
- Potting Mix: Use a well-draining potting mix for potted lavender. Avoid using heavy soils that retain too much water.
- Drainage Holes: Ensure adequate drainage holes in pots to allow excess water to escape.
Root Rot: Causes and Solutions
Root rot is a common fungal disease in lavender, often caused by overwatering and poor drainage. Prompt action is crucial for preventing further damage.
- Overwatering: Overwatering saturates the soil, depriving roots of oxygen and creating an environment conducive to fungal growth. Adjust your watering schedule to allow the soil to dry out between waterings.
- Poor Drainage: Waterlogged soil is a primary cause of root rot. Improve drainage by amending the soil or adjusting the planting location.
- High Soil Moisture: Maintaining consistently high soil moisture levels creates an ideal environment for fungal pathogens. Adjust watering practices to allow for proper drying of the soil.
Troubleshooting Table
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Yellowing Leaves | Nutrient deficiency, overwatering, underwatering, pests | Soil testing, adjusted watering schedule, pest control |
| Stunted Growth | Insufficient sunlight, poor soil quality, inadequate watering | Ensure sufficient sunlight, amend soil, consistent watering |
| Insufficient Drainage | Heavy clay soil, poor potting mix, lack of drainage holes | Amend soil, use well-draining potting mix, ensure adequate drainage holes |
| Root Rot | Overwatering, poor drainage, high soil moisture | Adjust watering schedule, improve drainage, avoid overwatering |
Closure
We’ve explored the captivating world of Spanish Lavender, from its captivating beauty to its practical uses. This guide provided a comprehensive overview of everything from selecting the perfect growing conditions to mastering propagation techniques. Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently cultivate your own fragrant Spanish Lavender garden. So, get your hands dirty, and watch your lavender flourish!