Is mold remediation worth it? This question is crucial for anyone facing potential mold issues in their home or property. The answer isn’t always straightforward, as the decision depends on several factors, including the extent of contamination, the potential health risks, and the financial implications. This in-depth exploration will guide you through the process of evaluating the need for remediation, considering costs, health impacts, and available options.
From understanding the various types of mold and their health risks to assessing the extent of contamination, this article will walk you through the entire process of deciding whether mold remediation is the right choice for you. We’ll also delve into the pros and cons of DIY remediation versus hiring professionals, as well as the financial considerations and legal implications.
Ultimately, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to make an informed decision that prioritizes your health and your property’s well-being.
Defining Mold Remediation
Mold remediation is a critical process aimed at safely and effectively removing mold from affected areas. It’s more than just cleaning; it encompasses a comprehensive approach to eliminate the source of the problem, prevent future growth, and protect the health and well-being of occupants. This involves understanding the types of mold, the risks they pose, and the steps involved in a successful remediation project.A successful mold remediation strategy addresses the root cause of the moisture issue that fostered mold growth.
This preventative approach ensures that the problem doesn’t recur, avoiding costly and time-consuming future interventions. Understanding the process, from initial inspection to final cleanup, is crucial for homeowners and property managers alike.
Mold Types and Health Risks
Mold exists in a wide variety of forms, each with its own characteristics and potential health effects. Common types include Aspergillus, Penicillium, Stachybotrys chartarum (often called “black mold”), and Cladosporium. The severity of the health risks varies depending on the type of mold, the concentration, and an individual’s sensitivity.Some molds produce mycotoxins, which are toxic substances that can cause a range of symptoms, from mild allergic reactions to more serious respiratory issues and other health problems.
Exposure can trigger allergic reactions like sneezing, coughing, and skin irritation in sensitive individuals. In extreme cases, prolonged or heavy exposure to certain molds can lead to more serious health consequences. Knowing the potential health implications is critical to understanding the importance of prompt and effective mold remediation.
Stages of a Typical Mold Remediation Process
A typical mold remediation process follows a structured approach, ensuring safety and effectiveness. These steps are critical for preventing further spread and ensuring a thorough cleanup.
- Assessment and Inspection: The initial stage involves a thorough assessment of the affected area to identify the extent of mold growth, its type, and the source of moisture. This often involves visual inspection and potentially testing for the presence and type of mold. Accurate identification is critical for selecting the appropriate remediation method.
- Containment: The affected area is sealed off to prevent the spread of mold spores. This often involves using plastic sheeting, specialized barriers, and air filtration systems. This step is crucial to protecting the health of occupants and preventing contamination of unaffected areas.
- Cleaning and Removal: This stage involves removing the mold and contaminated materials. This might include scrubbing, vacuuming, or other cleaning methods, depending on the severity of the infestation and the material involved. Specialized equipment and procedures are often required for safety and effectiveness.
- Decontamination and Disinfection: This step involves cleaning and disinfecting the affected area to eliminate any remaining mold spores and prevent future growth. This typically involves applying specialized disinfectants and thoroughly cleaning surfaces.
- Air Quality Monitoring: Following remediation, monitoring air quality in the affected area is essential to ensure that mold levels have returned to safe limits. This might involve testing air samples and consulting with professionals to confirm that the area is safe for reoccupation.
Mold Remediation Methods Comparison
Different approaches are used for mold remediation, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Containment | Isolation of the affected area to prevent spread. | Protects unaffected areas, minimizes exposure. | Can be disruptive, may require temporary relocation. |
| Cleaning | Removal of mold from surfaces. | Cost-effective for minor infestations, less disruptive. | May not be effective for extensive or deep-seated mold. |
| Deconstruction | Removal of contaminated materials and structures. | Necessary for severe infestations, ensures complete removal. | Most disruptive, potentially expensive. |
Assessing the Need for Remediation
Knowing if you have a mold problem is the first step towards effective remediation. Ignoring potential mold can lead to health issues, structural damage, and increased costs in the long run. A proactive approach, involving thorough inspection and potential sample collection, is key to determining the extent of the problem and the need for professional help.
Signs and Symptoms of Potential Mold Problems
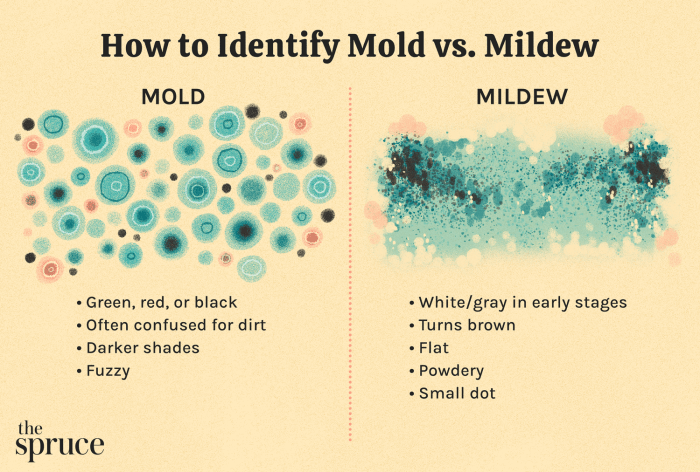
Mold growth often manifests with noticeable signs. Visual inspection is the first step in identifying potential problems. Common symptoms include musty odors, discoloration on walls, ceilings, or floors, and the presence of fuzzy or slimy spots. These spots can vary in color, from black and green to white or gray. Water damage, especially lingering moisture, is a significant factor in mold growth.
Be aware of persistent dampness in areas like bathrooms, basements, or attics, which could be a sign of hidden mold. If you experience allergy-like symptoms, such as sneezing, coughing, or eye irritation, in areas with suspected mold, it could be a strong indicator of mold presence.
Figuring out if mold remediation is worth the cost can be tricky. It really depends on the extent of the damage, but sometimes a good starting point is to consider how to best use the space. For example, if you have slanted walls in a room you’re looking to renovate, how to decorate a bedroom with slanted walls can often help maximize the room’s functionality and aesthetics, which in turn can affect whether or not remediation is a worthwhile investment.
Ultimately, it’s a case-by-case evaluation, weighing the potential health risks against the cost of remediation.
Identifying and Assessing the Extent of Mold Contamination
Thorough visual inspection is crucial for identifying the presence and extent of mold. Focus on areas prone to moisture accumulation, like bathrooms, kitchens, basements, and attics. Look for visible signs of mold growth, such as discoloration, musty odors, and any unusual textures. If you find mold, note its location, size, and color. A simple way to assess the severity is by considering the affected area’s size.
A small, localized patch of mold might only require surface cleaning, while extensive growth necessitates professional remediation.
Mold Inspection Checklist
This checklist provides a structured approach to inspecting your property for mold.
- Visual Inspection: Examine all areas with potential moisture issues (bathrooms, kitchens, basements, attics). Note any visible mold growth, its location, size, and color. Document the presence of water damage or leaks.
- Odor Assessment: Pay attention to any musty or unusual odors. If you detect such odors, investigate the source and potential mold presence. A strong, pungent odor might indicate significant mold growth.
- Moisture Inspection: Check for any signs of water damage, leaks, or standing water. Condensation on windows or pipes, for instance, can be a precursor to mold. Inspect caulking and sealing around windows and doors for cracks or gaps.
- Surface Inspection: Carefully inspect walls, ceilings, floors, and other surfaces for any signs of discoloration, discoloration, unusual textures, or water stains.
- Record Keeping: Document all findings, including the date, location, size, and color of any mold found. Photographs can be useful in documenting the extent of the problem.
Collecting Mold Samples for Professional Analysis
Collecting mold samples is crucial for professional analysis. A professional assessment will provide a detailed understanding of the mold type and its potential health risks.
Wondering if mold remediation is a worthwhile investment? It definitely depends on the extent of the problem, but checking out what designers consider the best home upgrades can offer some perspective. Designers share best home upgrades often prioritize preventative measures, highlighting how careful design choices can reduce the risk of future issues like mold. Ultimately, if you’re dealing with a severe mold problem, the cost of remediation might seem high, but long-term health and property value could make it a sound investment.
- Preparation: Wear protective gear, including gloves, a mask, and eye protection. Collect the appropriate sampling tools. These might include sterile swabs, plastic bags, and a sharp knife (to cut a small piece of affected material).
- Sampling Procedure: Carefully collect samples from different areas of visible mold growth. Take samples from the edges of the affected area as well as the center. Ensure the sample is representative of the entire mold colony. Place the collected samples in a labeled, airtight container, ensuring they are not damaged or contaminated during transport.
- Labeling: Properly label each sample container with the date, location of the sample, and any relevant details. Clearly identify the type of material sampled (e.g., drywall, carpet).
- Transporting the Samples: Transport the samples to a certified laboratory or a qualified mold remediation professional for analysis. Follow all instructions given by the laboratory or professional regarding sample handling and transportation.
Cost Considerations
Mold remediation, while crucial for health and safety, often comes with a price tag. Understanding the potential costs involved is essential before undertaking any action. Knowing the range of expenses can help you budget effectively and make informed decisions about whether professional help is the best option.
Pricing Ranges for Mold Remediation Services
Mold remediation costs vary significantly depending on several factors. Generally, you can expect a range of expenses, but it’s crucial to get multiple quotes to ensure you’re getting a fair price. Labor costs for experienced mold remediation technicians are a substantial part of the total expense. The complexity of the job, including the size of the affected area and the type of mold present, significantly impacts the overall cost.
- Labor Costs: Expect labor costs to range from $50 to $150 per hour, depending on the technician’s experience and location. Experienced mold remediation professionals will typically charge more due to their specialized training and expertise.
- Materials: Mold remediation materials, including specialized cleaning solutions, protective gear, and air scrubbers, can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand, depending on the extent of the problem.
- Disposal Costs: Proper disposal of contaminated materials is critical. This often involves specialized waste removal and disposal, which can add significantly to the overall cost.
Factors Affecting Mold Remediation Costs
Several factors influence the final cost of mold remediation. Understanding these elements is vital for budgeting purposes. The extent of the mold problem directly affects the amount of time and resources required. Larger affected areas, intricate structural issues, and the presence of multiple types of mold will all drive up the overall cost.
- Severity of the Problem: The extent of mold infestation—from a small spot to a large-scale problem—dramatically influences the cost. A small, localized problem might be manageable with minimal expense, whereas a widespread issue will necessitate more extensive and costly measures.
- Size of the Affected Area: The larger the area affected by mold, the higher the cost. Larger remediation jobs require more labor hours, materials, and specialized equipment.
- Complexity of the Project: If the mold is embedded in drywall, behind walls, or in other hard-to-reach areas, the remediation process becomes more complex, thus increasing the cost. This includes factors like the need for specialized equipment or techniques to access and treat the mold.
DIY vs. Professional Remediation
While tempting to tackle mold remediation yourself, DIY methods often fall short of professional standards. Hiring qualified professionals is generally the safer and more effective approach. Improperly handled mold remediation can lead to further health risks and structural damage, potentially increasing the overall cost in the long run.
- DIY Remediation Risks: DIY mold remediation can lead to health problems for the homeowner, inadequate removal of the mold, and potential structural damage. Improper disposal of contaminated materials can also pose environmental risks.
- Professional Expertise: Professional mold remediation companies have the specialized training, equipment, and experience to handle various types of mold effectively and safely. They understand the proper procedures for containment, removal, and cleanup, minimizing the risk of further contamination and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Potential Expense Table
The following table provides a general overview of potential expenses for various mold remediation projects. Keep in mind that these are estimates and actual costs may vary significantly.
| Project Type | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Small localized mold spot (e.g., bathroom) | $500 – $2,000 |
| Moderate-sized mold infestation (e.g., kitchen or basement) | $2,000 – $8,000 |
| Extensive mold problem (e.g., throughout a house) | $8,000 – $20,000+ |
Health Implications
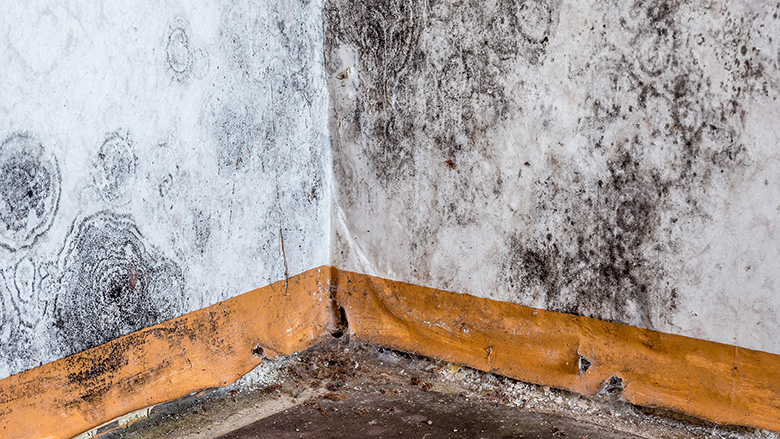

Mold exposure can be a serious health concern, impacting individuals in various ways. Understanding the potential risks, from immediate reactions to long-term health effects, is crucial for making informed decisions about remediation. This section delves into the potential health implications of mold exposure, focusing on sensitivities, demographics, and safety precautions.Mold exposure can trigger a range of reactions, from mild irritation to severe respiratory issues.
The severity of the reaction depends on several factors, including the type of mold, the concentration of mold spores in the air, and the individual’s sensitivity. People with pre-existing respiratory conditions like asthma or allergies are particularly vulnerable.
Potential Health Risks Associated with Mold Exposure
Mold spores are ubiquitous in the environment, but when present in high concentrations indoors, they can pose a significant health hazard. Exposure can lead to a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild irritation to serious health problems. Different individuals react differently to mold exposure due to factors like genetics, pre-existing conditions, and immune system function.
Impact on Different Demographics
Certain demographics are more susceptible to the adverse health effects of mold exposure. Children, the elderly, and individuals with compromised immune systems are at higher risk of developing more severe or prolonged symptoms. For example, children’s developing respiratory systems are particularly vulnerable to the effects of mold exposure.
Long-Term Health Effects of Mold Exposure
Prolonged exposure to mold can lead to a variety of long-term health issues. Some of these health issues include allergic reactions, respiratory problems, and in extreme cases, more severe conditions like asthma or chronic bronchitis. Asthma exacerbation is a common result of mold exposure, especially in individuals already diagnosed with the condition.
Importance of Safety Precautions During Mold Remediation
Safety is paramount during mold remediation. Improper procedures can expose workers and occupants to harmful mold spores, increasing the risk of health complications. Strict adherence to safety protocols is essential to minimize these risks.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for Mold Remediation, Is mold remediation worth it
Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial for minimizing exposure to mold spores during remediation. The following list Artikels the essential PPE components:
- Respirator: A high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) respirator is essential to filter out airborne mold spores. The respirator should be specifically designed for mold remediation and properly fitted to prevent leakage.
- Eye Protection: Safety glasses or goggles are necessary to protect the eyes from mold spores and other contaminants.
- Protective Clothing: Coveralls, gloves, and boots are needed to prevent mold spores from contacting skin. These items should be impervious to moisture and mold.
- Foot Protection: Waterproof and puncture-resistant boots protect the feet from exposure to mold and moisture.
- Hand Protection: Heavy-duty disposable gloves or specialized gloves made from impervious materials prevent contamination of the hands.
- Other Considerations: Proper sanitation and decontamination procedures for tools and equipment are vital to prevent cross-contamination.
Comparing Remediation Options
Mold remediation isn’t a one-size-fits-all process. Different methods tackle mold in various ways, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for homeowners to make informed decisions about the best course of action for their specific situation. Factors like the type and extent of mold, the affected materials, and the overall budget will all play a role in selecting the appropriate remediation approach.Different approaches vary significantly in their effectiveness, cost, and safety.
This section explores common remediation methods, delving into their efficacy, environmental impact, and associated costs. This will equip you with the knowledge necessary to make a well-informed choice.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation involves sealing off the mold-affected area to prevent further spread. This typically involves covering the affected surfaces with a sealant, such as paint or specialized coatings. This method is often a cost-effective solution for minor mold infestations.
Biocide Treatment
Biocide treatment employs chemicals to kill the mold. This method is often necessary for extensive mold infestations or when encapsulation isn’t feasible. Biocides can be effective at eliminating the mold but may pose environmental risks if not used properly.
Combination Approaches
In some cases, a combination of methods proves most effective. For instance, encapsulation might be used to contain the mold, followed by biocide treatment to eliminate it completely. This approach allows for a targeted and comprehensive solution, optimizing both the effectiveness and efficiency of the process.
Effectiveness and Efficiency of Each Method
The effectiveness of a remediation method hinges on the specific circumstances of the mold problem. Encapsulation is usually sufficient for superficial mold growth, while biocide treatment is often necessary for deep-seated or extensive infestations. The efficiency of each method can vary depending on the extent of the infestation, the type of materials affected, and the experience of the remediation professionals.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of each method is crucial to consider. Encapsulation, while generally less disruptive, may not fully eliminate the mold, potentially leading to future problems. Biocide treatment, while effective at killing mold, can introduce harmful chemicals into the environment if not managed properly. Proper ventilation, disposal of contaminated materials, and adherence to safety protocols are vital to minimizing environmental risks associated with both methods.
Comparative Analysis
| Remediation Technique | Effectiveness | Cost | Safety |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encapsulation | Good for minor infestations, but may not fully eliminate mold | Generally lower | Relatively safe, especially if properly executed |
| Biocide Treatment | Effective for extensive infestations, but requires careful handling of chemicals | Generally higher | Requires careful handling of chemicals, potential for health risks |
| Combination Approach | Highly effective, addresses various levels of infestation | Moderate to high, depends on the scope of the work | Requires careful execution and adherence to safety protocols |
Legal and Insurance Aspects: Is Mold Remediation Worth It
Navigating the legal and insurance landscape surrounding mold remediation can be complex. Understanding your rights and responsibilities, as well as the role insurance plays, is crucial for a smooth and effective resolution. This section delves into the legal implications and insurance coverage aspects of mold remediation.
Property Owner Responsibilities and Liability
Property owners have a legal obligation to maintain safe living conditions for tenants and occupants. This includes addressing potential health hazards like mold. Failure to do so can lead to liability issues if a health problem arises. The extent of responsibility varies based on local regulations and the specific circumstances. For instance, if a leak is discovered and not immediately addressed, the property owner could face legal action if mold-related health problems arise.
Insurance Coverage for Mold Remediation
Insurance policies often include coverage for mold remediation, but the specifics depend on the policy type. Homeowners insurance, renters insurance, and commercial insurance policies can potentially cover mold remediation costs if the mold is caused by a covered event. For example, if a pipe bursts and causes water damage leading to mold growth, the damage and remediation costs might be covered by the homeowner’s insurance policy.
However, it’s essential to review the policy details thoroughly to understand the scope of coverage and any exclusions.
Filing a Mold-Related Insurance Claim
The process for filing a mold-related insurance claim typically involves several steps. First, document the mold problem thoroughly. Take photos, videos, and record the dates of any repairs or attempts to address the mold. Then, contact your insurance provider to report the damage and request a claim form. Provide all necessary documentation to support your claim.
If possible, have a professional mold inspection performed to gather detailed information. This will assist the insurance company in assessing the extent of the damage.
Deciding if mold remediation is worthwhile often hinges on the severity of the issue. Sometimes, a seemingly small problem can quickly escalate, especially if ignored. For instance, when tackling a DIY project like replacing baseboards, choosing the right technique, like coping or mitering baseboards , can make a huge difference in the overall look and longevity of your work.
Ultimately, whether remediation is worth it depends on the extent of the damage and the potential long-term costs.
Relevant Legal Resources and Regulatory Bodies
Several legal resources and regulatory bodies can provide guidance and support in mold-related issues. Local building codes and health departments often have specific regulations related to mold remediation. Your state’s attorney general’s office or consumer protection agency can also offer assistance. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides valuable information on mold and remediation. Consulting with an attorney specializing in property law can be beneficial for navigating complex legal situations.
- Local Building Codes: Local building codes often Artikel specific standards and procedures for mold remediation, ensuring the safety and health of occupants. Understanding these regulations can help avoid future issues.
- Health Departments: Health departments provide crucial information and guidance regarding mold remediation. They can offer recommendations for addressing mold problems to prevent further health concerns.
- State Attorney General’s Office/Consumer Protection Agency: State-level agencies can offer support and resources for resolving consumer issues, including mold-related problems. These agencies can assist in navigating legal procedures and obtaining fair resolutions.
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency): The EPA provides comprehensive information on mold and its remediation. Their resources offer guidance on identifying, preventing, and removing mold.
- Property Law Attorneys: Consultations with property law attorneys specializing in mold remediation can help property owners understand their legal rights and responsibilities. Attorneys can provide crucial advice in navigating complex legal issues and achieving favorable outcomes.
DIY vs. Professional Remediation
Taking on mold remediation yourself might seem tempting, especially if costs are a concern. However, the risks and potential complications often outweigh the savings, particularly when dealing with the unseen dangers associated with mold. DIY efforts can lead to incomplete removal, spreading the problem, and ultimately, a far more expensive and difficult situation in the long run.Mold remediation is a complex process that requires specialized knowledge, equipment, and techniques.
Approaching it without the necessary expertise can lead to serious health risks and, worse, further damage to your property. Understanding the differences between DIY and professional remediation is crucial for making an informed decision.
Potential Risks of DIY Remediation
DIY mold remediation can lead to several negative consequences. A crucial concern is the potential spread of mold spores. Improper procedures can easily disseminate these microscopic organisms, contaminating other areas of the house or even spreading them to neighbors’ properties. This uncontrolled dispersion can create more extensive mold problems, requiring more extensive and expensive remediation efforts.Another major risk involves inadequate removal.
Mold often penetrates surfaces deeper than visible, requiring specialized tools and techniques to eliminate it completely. A DIY approach might only remove the visible mold, leaving behind hidden colonies that will continue to grow and spread, requiring multiple rounds of remediation.
Effectiveness of DIY Remediation
DIY mold remediation frequently falls short of achieving complete removal. The specialized knowledge and equipment used by professionals are essential for thorough remediation. Often, DIY efforts lack the meticulousness required to reach hidden mold growth and completely neutralize the problem. Furthermore, professional remediators utilize specialized filtration systems to prevent spore dispersion, a significant safety aspect often overlooked in DIY efforts.
Comparison of DIY vs. Professional Remediation
| Characteristic | DIY Remediation | Professional Remediation |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Increased risk of exposure to mold spores and associated health problems. Potential for spreading mold to other areas. | Minimized risk of exposure due to specialized equipment and techniques for containment. Trained personnel ensure proper disposal of contaminated materials. |
| Effectiveness | Lower chance of complete removal due to lack of expertise and specialized equipment. Risk of incomplete removal leading to recurring problems. | High likelihood of complete removal due to expertise, advanced equipment, and thorough inspection. |
| Cost | Potentially lower upfront cost, but can lead to higher overall costs if remediation needs to be repeated or if further damage is caused. | Higher initial cost, but often results in a more effective and permanent solution, preventing costly recurrences. |
| Time | May take longer due to lack of experience and proper tools. | Faster and more efficient due to expertise and advanced equipment. |
Importance of Professional Expertise
Professional mold remediation specialists possess the knowledge, skills, and equipment to effectively and safely remediate mold problems. They are trained to identify the source of the mold, assess the extent of the damage, and implement a tailored remediation plan. Their expertise is crucial to preventing health hazards, ensuring complete removal, and minimizing the risk of future contamination. Professional remediators understand the importance of containment procedures to prevent the spread of mold spores.Professional remediators are equipped with specialized tools like HEPA-filtered vacuums, air scrubbers, and specialized cleaning solutions.
These tools are vital for thorough and safe removal of mold and preventing re-contamination.
Examples of Professional Expertise
Professional mold remediation companies often have certified technicians who adhere to strict industry standards and guidelines. They utilize specialized testing equipment to determine the extent and type of mold contamination. For example, a trained professional can identify the specific type of mold, which is crucial for determining the appropriate remediation method. This can prevent the use of improper cleaning agents that may not effectively kill certain types of mold.
A professional’s expertise ensures a comprehensive and effective solution, mitigating the risks and ensuring a healthy environment.
Preventing Future Mold Growth
Mold remediation is a significant investment, but preventing future mold growth is often more cost-effective and less disruptive. Understanding the conditions that foster mold development allows homeowners and building owners to implement proactive strategies to maintain a healthy and mold-free environment. Proactive measures are essential for long-term building health and occupant well-being.Mold thrives in specific environmental conditions, primarily moisture and organic matter.
By controlling these factors, you can effectively prevent mold growth from recurring. A proactive approach to moisture control and building maintenance significantly reduces the risk of mold infestations.
Proper Ventilation
Adequate ventilation is crucial in preventing moisture buildup, a key factor in mold growth. Proper airflow helps remove excess moisture from the air, preventing condensation on surfaces. This includes strategically placing exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens to remove moisture generated by cooking and showering. Ensuring proper ventilation in attics and crawl spaces can also prevent moisture buildup and subsequent mold growth.
Moisture Control
Moisture control is paramount to preventing mold growth. Leaks, dripping pipes, and excessive humidity are common sources of moisture problems. Regularly inspecting for leaks, addressing water damage promptly, and installing moisture sensors are proactive measures to maintain a dry environment. Efficiently managing water drainage around the foundation and ensuring proper roof ventilation are crucial aspects of moisture control.
A well-maintained gutter system prevents water from pooling around the house.
Building Maintenance
Regular building maintenance is essential for preventing mold growth. This involves identifying and fixing any potential water damage issues, such as leaky roofs, pipes, or windows. Inspecting for and promptly addressing water damage is critical to preventing mold. Regular cleaning and maintenance of HVAC systems can also prevent moisture buildup and the spread of mold spores. Routine checks for potential moisture issues, such as damp basements or crawl spaces, are also vital.
Humidity Control
Maintaining appropriate humidity levels within a building is a critical aspect of mold prevention. High humidity provides the ideal environment for mold spores to grow and proliferate. Using a dehumidifier in areas prone to moisture buildup, like basements or bathrooms, can help regulate humidity levels and prevent mold growth. Regular monitoring of humidity levels with a hygrometer can assist in maintaining optimal humidity levels.
Mold-Free Environment Checklist
Regular maintenance and vigilance are key to maintaining a mold-free environment. This checklist will help you create a proactive plan to prevent mold growth.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular visual inspections of potential moisture sources (e.g., roofs, walls, pipes) for any signs of leaks, dampness, or water damage. Early detection is key to preventing significant mold problems.
- Moisture Control: Address any leaks or moisture issues immediately. Repair or replace damaged pipes, roofs, or gutters promptly. This preventative measure minimizes the risk of mold growth.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in bathrooms, kitchens, and other areas prone to moisture buildup. Proper ventilation helps remove moisture from the air.
- Humidity Control: Use dehumidifiers in areas with high humidity. Regularly monitor humidity levels with a hygrometer to maintain ideal levels.
- HVAC Maintenance: Clean and maintain HVAC systems regularly to prevent moisture buildup and the spread of mold spores. Schedule professional HVAC maintenance at least once a year.
- Building Maintenance: Regular inspections and maintenance of the building structure (roofing, gutters, plumbing) will identify and prevent potential sources of water damage.
- Cleaning and Hygiene: Regularly clean and dry affected areas. Implement good hygiene practices to minimize the spread of mold spores.
Closing Summary
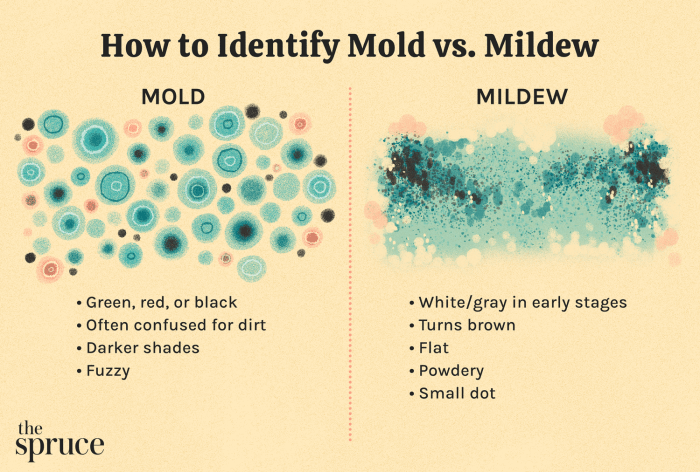
In conclusion, deciding whether mold remediation is worth it requires careful consideration of various factors. Assessing the extent of contamination, understanding potential health risks, and weighing the costs of professional services versus DIY options are crucial steps. Remember, safety should always be paramount. By thoroughly researching your options and consulting with experts when needed, you can make an informed decision that protects your health and property.
Ultimately, the choice is yours, but this guide has provided the tools and knowledge to make an informed decision.